Kehl | |
|---|---|
 Kehl, August 2020 | |
 Coat of arms | |
Location of Kehl within Ortenaukreis district 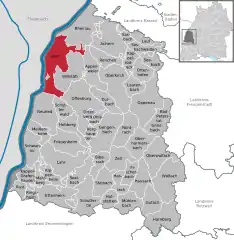 | |
 Kehl  Kehl | |
| Coordinates: 48°34′N 7°49′E / 48.567°N 7.817°E | |
| Country | Germany |
| State | Baden-Württemberg |
| Admin. region | Freiburg |
| District | Ortenaukreis |
| Government | |
| • Mayor (2022–30) | Wolfram Britz[1] (Ind.) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 75.07 km2 (28.98 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 139 m (456 ft) |
| Population (2021-12-31)[2] | |
| • Total | 37,378 |
| • Density | 500/km2 (1,300/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| Postal codes | 77671-77694 |
| Dialling codes | 07851 |
| Vehicle registration | OG, BH, KEL, LR, WOL |
| Website | www.kehl.de |
Kehl (German pronunciation: [keːl] ⓘ; Low Alemannic: Kaal) is a town in southwestern Germany in the Ortenaukreis, Baden-Württemberg. It is on the river Rhine, directly opposite the French city of Strasbourg. The two share some municipal services – for example the Strasbourg tramway, which now reaches Kehl.
History
The village of Kehl was first mentioned in 1038. In 1338, the first permanent bridge between Kehl and Strasbourg was completed. In 1678, the city was taken over by France, as it was considered to be part of the defence system of Strasbourg. Hence the village was transformed into a fortress in 1683 by the French architect Vauban.[3]
In 1681, the Imperial City of Strasbourg, a territory of the Holy Roman Empire that included Kehl, was annexed by Louis XIV, King of France. This annexation was recognised by the Treaty of Ryswick in 1697, but all right-bank territories were restored to the Empire,[3] leading to Kehl's cession to the Margraviate of Baden the following year.
On May 7, 1770, Marie Antoinette was officially handed over by Austria to France on an island on the Rhine near Kehl. This island, which was settled until the First World War, became known as Kommissionsinsel after the commission that took over Marie Antoinette.
In 1774, Kehl received town rights by the Charles Frederick, Margrave of Baden. The village was badly damaged during the French Revolutionary Wars, especially during the Rhine Campaign of 1796, during the first and second battles of Kehl, and it was besieged by the Austrians in late 1796 until its surrender on 9 January 1797. During the First French Empire, Kehl was reunited with Strasbourg under the French First Republic, before being restored to Baden (now raised to an Electorate) in 1803. After briefly being subject to Austria, the city was finally returned to Baden (now a Grand Duchy) in 1815 and the fortress was dismantled.
Between 1842 and 1847, the first port facility was created by the Baden State Railway Administration. In 1861, the first railway bridge was built and the first direct connection from Paris to Vienna was established, with locomotives being changed over in Kehl.
After the First World War, under article 65 of the Treaty of Versailles the harbour of Kehl was placed under French administration for seven years to prevent possible German attacks on the opposite newly French town of Strasbourg.[4]
During World War II Kehl was located in the so-called "Red Zone" on the western wall, which was cleared when the war broke out: in the night from 3 to 4 September 1939, the population was evacuated to the Black Forest by special trains and was only allowed to return after German troops occupied France. Kehl then became a suburb of Strasbourg. This status was retained even after the war. Kehl was released in accordance with the Washington Agreement on the Clearance of the City of Kehl by France from April 8, 1949, in 42 partial releases from July 29, 1949, to April 8, 1953. At that time (1945 to 1953) Sundheim was an independent municipality, which was then reunited with the city of Kehl. The city and the entire district of Kehl then belonged to the administrative district of South Baden within Baden-Württemberg.
Religion
Until 1519, Kehl was part of the diocese of Strasbourg. Then, the village had to change religion at the order of the margraves and the first Lutheran minister took office. During the French occupation of the 1690s, Kehl became Roman Catholic again, only to revert to Lutheranism after being ceded back to the margrave of Baden.
From the early 19th century up to 1914, Lutherans and Catholics shared one church building; then, as the first building on the Kommissionsinsel the Catholic Church of St. Johann Nepomuk was erected.
Several free churches are situated in Kehl, including Mennonites and the New Apostolic Church.
Demographics
Population development:[5]
|
Gateway to Strasbourg

The city of Strasbourg lies opposite Kehl over the river Rhine and the two share some municipal services. Kehl station is located near the Europabrücke (Europe Bridge), which can be crossed on foot to enter Strasbourg. Bus line 21 used to connect Kehl with the nearest tram stations across the Rhine in Strasbourg, but Strasbourg tramway line D has since been extended to Kehl. It opened on April 28, 2017 to Kehl station, and to Kehl town centre in November 2018.[6][7]
Twin towns – sister cities
 Montmorency, France
Montmorency, France
Notable people
- Hermann Flick (1905–1944), footballer
- Georg Nückles (born 1948), athlete
- Jean-Jacques Favier (born 1949), astronaut
- Dieter Eckstein (born 1964), footballer
- Rainer Schütterle (born 1966), footballer
References
- ↑ Aktuelle Wahlergebnisse, Staatsanzeiger, accessed 9 July 2022.
- ↑ "Bevölkerung nach Nationalität und Geschlecht am 31. Dezember 2021" [Population by nationality and sex as of December 31, 2021] (CSV) (in German). Statistisches Landesamt Baden-Württemberg. June 2022.
- 1 2 Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 15 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 714.
- ↑ . Treaty of Versailles. 28 June 1919 – via Wikisource.
- ↑ "Kehl - Wegweiser Kommune". www.wegweiser-kommune.de. Retrieved 2023-06-18.
- ↑ "Un tram pour l'Europe entre Strasbourg et Kehl". FIGARO. 28 April 2017.
- ↑ Krebs, Eric (4 August 2022). "Europe's New Trams Are Reviving a Golden Age of Transit". Reasons to be Cheerful.
- ↑ "Städtepartnerschaften". kehl.de (in German). Kehl. Archived from the original on 2020-04-24. Retrieved 2021-02-15.
External links
- (in German) Official website
