| Kh-38 | |
|---|---|
 Kh-38ME | |
| Type | Tactical air-to-surface missile |
| Place of origin | Russia |
| Service history | |
| In service | 2012 (Kh-38ME) - 2019 (Kh-36) |
| Used by | Russia |
| Wars | Syrian Civil War[1][2] |
| Production history | |
| Designer | Tactical Missiles Corporation JSC |
| Designed | 2007 (Kh-38ME) - 2015 (Kh-36) |
| Manufacturer | Tactical Missiles Corporation JSC |
| Produced | 2015 (Kh-38M) - 2019 (Kh-36) |
| Specifications | |
| Mass | 520 kg (1,150 lb) |
| Length | 4.2 m (13 ft 9 in)[3] |
| Diameter | 0.31 m (12.2 in)[3] |
| Wingspan | 1.14 m (44.9 in) |
| Warhead | HE fragmentation, cluster warhead, armor-piercing |
| Warhead weight | up to 250 kg (551 lb)[3] |
Detonation mechanism | Contact fuse |
| Engine | Two-stage solid rocket motor[3] |
Operational range | up to 40 km (21.6 nmi)[3] |
| Flight altitude | 200-12000 m |
| Maximum speed | Mach 2.2[3] |
Guidance system | Laser, active radar, IR, satellite, depending on variant |
Launch platform | Kh-38: Su-34, Su-57, Ka-52K Kh-36: Su-57, MiG-35 |
The Kh-38/Kh-38M (Russian: Х-38) is a family of air-to-surface missiles meant to succeed the Kh-25 and Kh-29 missile families.
Design and development
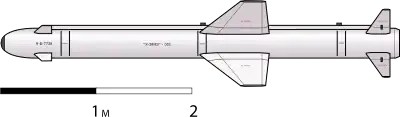
The basic configuration of the Kh-38M was revealed at the 2007 Moscow Air Show (MAKS). The first prototypes of the missile had initially folding wings and tail fins for internal carriage, and would have a variety of seeker heads for different variants.[4] Different warheads (fragmentation, cluster munitions, penetrating) can also be fitted. The Kh-38M is meant to succeed the Kh-25 and Kh-29 missile families. It can be used by combat aircraft such as the Sukhoi Su-34 and Sukhoi Su-57, and it is planned to be integrated on the Kamov Ka-52K helicopter. The first test firing took place in 2010 from a Su-34, and production was ordered to start in 2015.[3]
In a successive version, unveiled at MAKS 2017, both control surfaces were replaced by longer and narrower fixed ones, a solution similar to the one used in the Selenia Aspide missile.[5]
Operational history
The Kh-38M was first used in combat during the Russian military intervention in the Syrian civil war.[3] It was also used during the 2022 invasion of Ukraine.
Variants
- Kh-38MA - inertial, active radar homing[3]
- Kh-38MK - inertial, satellite guidance[3]
- Kh-38ML - inertial, semi-active laser guidance[3]
- Kh-38MT - inertial, imaging infrared guidance[3]
- Kh-36 Grom-E1 - AS-23 tactical cruise missile derivative/AGM with 120 km range[6]
- Kh-36 Grom-E2 - AS-23B/KAB-type guided glide bomb with 50 km range.[7]
Both versions of the Grom are of 600 kg weight, with various guidance mechanisms, and both are created on the basis of the Kh-38M short-range tactical missile and also have modular structures, warheads and seekers. This weapon was first seen at MAKS 2015, and intended to equip all types of fighters, including the MiG-35 and Su-57.[8]
See also
References
- ↑ "Russia to test new missiles in Syria later this year". 14 September 2016.
- ↑ "Russian MiG-29Ks will employ Kh-38 in Syria – Alert 5".
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 "[Actu] La bombe guidée 9A-7759 Grom". Red Samovar. 26 June 2018.
- ↑ Barrie, Douglas and Komarov, Alexey. "War on Two Fronts for Russia's Missile Builders ". Aviation Week, 10 September 2007. Retrieved: 25 May 2014.
- ↑ "MAKS: Tactical Missiles Corporation shows Kh-38 changes - Russian aviation news". 20 July 2017.
- ↑ "Airborne guided missile "GROM-E1"". Archived from the original on 26 July 2022.
- ↑ "Airborne guided gliding bomb "GROM-E2"". 20 July 2021. Archived from the original on 20 July 2021.
- ↑ "Производитель раскрыл характеристики новейших авиационных средств поражения "Гром"".