| Kileskus Temporal range: Bathonian, | |
|---|---|
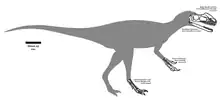 | |
| Diagram showing fossil remains described in initial description | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Dinosauria |
| Clade: | Saurischia |
| Clade: | Theropoda |
| Family: | †Proceratosauridae |
| Genus: | †Kileskus Averianov et al., 2010 |
| Species: | †K. aristotocus |
| Binomial name | |
| †Kileskus aristotocus Averianov et al., 2010 | |
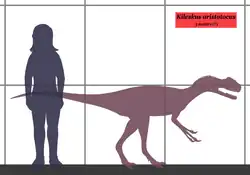
Kileskus (meaning lizard in the Khakas language) is a genus of tyrannosauroid dinosaur known from partial remains found in Middle Jurassic (Bathonian stage) Itat Formation of Sharypovsky District, Krasnoyarsk Krai (Russia). Fossils recovered include the holotype maxilla, a premaxilla, a surangular, and a few bones from the hand and foot.[1] Additional remains referred to the species include cervical and caudal vertebrae, as well as a fibula.[2] The skull bones are similar to those of Proceratosaurus. The type species is K. aristotocus. Kileskus was named in 2010 by Averianov and colleagues. Its size has been estimated at 5.2 meters (17 ft) in length and 700 kg (1,540 lbs) in weight.[3]
Classification
Kileskus has been included in two phylogenetic analyses and found to be a basal proceratosaurid both times.[1][4]
Although it is unknown whether Kileskus sported a nasal crest, it can be assigned to Proceratosauridae due to a number of other features. These include elongated external nares, a short ventral margin of the premaxilla, and the area of the antorbital fossa directly below the antorbital fenestra being deeper than the maxilla directly below it. Kileskus also shares with Proceratosaurus nares inclined posterodorsally at a 40 degree angle to the skull. Kileskus is distinguished from other proceratosaurids by the anterior rim of its maxilla being confluent with the ascending process of the maxilla and gently sloping posterodorsally.[1]
Below is a cladogram published in 2013 by Loewen et al..[4]
| Tyrannosauroidea |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cladogram published in 2018.[5]
| Tyrannosauroidea |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See also
References
- 1 2 3 Averianov, A. O.; Krasnolutskii, S. A.; Ivantsov, S. V. (2010). "A new basal coelurosaur (Dinosauria: Theropoda) from the Middle Jurassic of Siberia". Proceedings of the Zoological Institute. 314 (1): 42–57.
- ↑ O. Averianov, Alexander; Osochnikova, Anastasia; Skutschas, Pavel; Krasnolutskii, Sergei; Schellhorn, Rico; A. Schultz, Julia; Martin, Thomas (2019-09-16). "New data on the tyrannosauroid dinosaur Kileskus from the Middle Jurassic of Siberia, Russia". Historical Biology. 33 (7): 897–903. doi:10.1080/08912963.2019.1666839. ISSN 0891-2963. S2CID 203890300.
- ↑ Molina-Pérez & Larramendi (2016). Récords y curiosidades de los dinosaurios Terópodos y otros dinosauromorfos. Spain: Larousse. p. 264.
- 1 2 Loewen, M.A.; Irmis, R.B.; Sertich, J.J.W.; Currie, P. J.; Sampson, S. D. (2013). Evans, David C (ed.). "Tyrant Dinosaur Evolution Tracks the Rise and Fall of Late Cretaceous Oceans". PLoS ONE. 8 (11): e79420. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...879420L. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0079420. PMC 3819173. PMID 24223179.
- ↑ Delcourt, R.; Grillo, O. N. (2018). "Tyrannosauroids from the Southern Hemisphere: Implications for biogeography, evolution, and taxonomy". Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology. 511: 379–387


.jpg.webp)