Nuclear Explosions for the National Economy (Russian: Ядерные взрывы для народного хозяйства, romanized: Yadernyye vzryvy dlya narodnogo khozyaystva; sometimes referred to as Program #7[1]) was a Soviet program to investigate peaceful nuclear explosions (PNEs). It was analogous to the United States program Operation Plowshare.
One of the better-known tests was Chagan of January 15, 1965. Radioactivity from the Chagan test was detected over Japan by both the U.S. and Japan in apparent violation of the 1963 Partial Test Ban Treaty (PTBT). The United States complained to the Soviets, but the matter was dropped.[2]
History
In November 1949, shortly after the test of their first nuclear device on September 23, 1949, Andrey Vyshinsky, the Soviet representative to the United Nations, delivered a statement justifying their efforts to develop their own nuclear weapons capability. He said:
The representative of the USSR stated that although the Soviet Union would have as many atom bombs as it would need in the unhappy event of war, it was using its atomic energy for purposes of its own domestic economy; blowing up mountains, changing the course of rivers, irrigating deserts, charting new paths of life in regions untrodden by human foot ... The Ukrainian SSR representative pointed out that, despite the fact that the USSR had come into possession of the secrets of atomic energy production, it had not swerved from its insistence upon the prohibition of atomic weapons.
However the USSR did not immediately follow the U.S. lead in 1958 in establishing a program. Presumably, their position in support of a comprehensive nuclear testing ban stalled any efforts to establish such a program until the mid-1960s.
When Nuclear Explosions for the National Economy was finally formally established, Alexander D. Zakharenkov, a chief weapons designer, was appointed head of the program. Initially, the Soviet program was focused on two applications, nuclear excavation and petroleum stimulation, similar to the U.S. program. However, interest in other applications quickly developed, and within five years the Soviet program was actively exploring six or seven applications involving participation by some ten government departments.
Once underway the Soviets conducted a much more vigorous program than the Americans' Operation Plowshare, consisting of some 156 nuclear tests, some with multiple devices, between 1965 and 1989. These tests were similar in aims to the American effort, with the exception that six of the shots were considered of an applied nature, that is they were not tests as such, but were used to put out runaway gas well fires and a methane blow out.
There were in fact two programs:
- "Employment of Nuclear Explosive Technologies in the Interests of National Economy", also referred to as "Program 6", involved industrial underground PNEs and testing of new PNE technologies. As part of the program, 124 tests with 135 devices were conducted. Primary objectives of the program were water reservoir development, dam and canal construction, and creation of underground cavities for toxic waste storage.
- "Peaceful Nuclear Explosions for the National Economy", also referred to as "Program 7", involved testing of industrial nuclear charges for use in peaceful activities. Nuclear detonations were conducted with the stated purpose of searching for useful mineral resources with reflection seismology, breaking up ore bodies, stimulating the production of oil and gas, and forming underground cavities for storing the recovered oil and gas. The "Program" numbers come from the USSR's classification system of nuclear explosions, the first five programs designating various phases of nuclear weapon development.
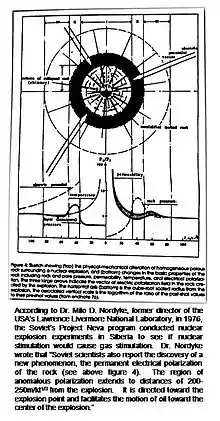
All together, the Program 7 conducted 115 nuclear explosions. Among them:
- 39 explosions for the purpose of geological exploration (trying to find new natural gas deposits by studying seismic waves produced by small nuclear explosions)
- 25 explosions for intensification of oil and gas debits
- 22 explosions for creating underground storage for natural gas
- 5 explosions for extinguishing large natural gas fountains that were burning[3]
- 4 explosions for creating channels and dams (including the Chagan test in Kazakhstan, and the Taiga test on the potential route of the Pechora–Kama Canal)
- 2 explosions for crushing ore in open-pit mines
- 2 explosions for creating underground storage for toxic wastes
- 1 explosion to facilitate coal mining in an underground mine
- 19 explosions were performed for research purposes (studying possible migration of the radioactivity from the place of the explosions).
These explosions were financed by various ministries: 51 explosions were financed by the Ministry for Geology, 26 explosions were financed by the Ministry for Natural Gas, 13 explosions were financed by the Ministry for Oil, 19 explosions were financed by the MinSredMash itself (the predecessor of the Federal Atomic Energy Agency). There were two large explosions of 140 kilotons and 105 kilotons; all others were relatively small with an average yield of 12.5 kilotons. For example, one 30-kiloton explosion was used to close the Uzbekistan Urtabulak gas well in 1966 that had been blowing since 1963, and a few months later a 47-kiloton explosive was used to seal a higher pressure blowout at the nearby Pamuk gas field. These successful experiments were later cited as possible precedents for stopping the Deepwater Horizon oil spill.[4][5]
The last nuclear explosion by the Program 7, codenamed Rubin-1, was performed in Arkhangelsk Oblast on September 6, 1988. The explosion was a part of a seismic program for geological exploration. The Soviets agreed to stop their PNE program at the end of 1988 as a result of then-president Mikhail Gorbachev's disarmament initiative.
There are proponents for continuing the PNE programs in modern Russia. They (e.g. A. Koldobsky) state that the program has already paid for itself and saved the USSR billions of rubles and can save even more if it would continue. They also allege that the PNE is the only feasible way to put out large fountains and fires on natural gas deposits, and it is the safest and most economically viable way to destroy chemical weapons.
Their opponents, including Alexey Yablokov, state that all PNE technologies have non-nuclear alternatives and that many PNEs actually caused nuclear disasters.[6]
Problems
Among the catastrophes was the Kraton-3 explosion in Vilyuy, Yakutia, in 1978, that was supposed to unearth diamond-rich ores. Instead, the amount of diamonds was insignificant but the plutonium pollution of water was much higher than predicted. According to the anti-nuclear activist Alexei Yablokov, the level of plutonium in the drinking water of Vilyuy region 20 years after the explosion is ten thousand times higher than the maximal sanitary norm.
Another catastrophe resulted from the Globus-1 explosion near the village of Galkino at 57°31′00″N 42°36′43″E / 57.51667°N 42.61194°E, 40 kilometers from Kineshma city on September 19, 1971.[7] It was a small underground explosion of 2.5 kilotons that was a part of the seismological program for oil and gas exploration. Unexpectedly a large amount of radioactive gases escaped through cracks in the ground, creating a significant radioactive hot spot two kilometers in diameter, in the relatively densely populated area of European Russia. A small tributary of the Volga, the Shacha, changed its location and threatened to flood the explosion site. This could have led to nuclear pollution of the entire Volga region. Some engineers suggested building a sarcophagus (similar to the Chernobyl's "Object Shelter") covering the site, and excavating a 12 km channel to shift the Shacha river away from the place of the explosion, but the plans appeared prohibitively expensive.
The experiments ended with the adoption of a unilateral moratorium on nuclear weapons testing at Soviet sites in 1989. Although this primarily was designed to support Mikhail Gorbachev's call for a worldwide ban on nuclear weapons tests, the Russians apparently applied the moratorium to peaceful nuclear explosions as well.
Implications
The Soviet PNE program was many times larger than the U.S. Plowshare program in terms of both the number of applications explored with field experiments and the extent to which they were introduced into industrial use. Several PNE applications, such as deep seismic sounding and oil stimulation, were explored in depth and appeared to have had a positive cost benefit at minimal public risk. Several others, such as storage, developed significant technical problems that cast a shadow on their general applicability. Some, such as closure of runaway gas wells, demonstrated a unique technology that may yet find application as a last resort. Still others were the subject of one or two tests but were not explored further for reasons that have never been explained. Overall, the program represented a significant technical effort to explore what was seen at the time to be a promising new technology, and it generated a large body of data, although only a small fraction of it has been made public.[8]
See also
- Peaceful nuclear explosions
- Soviet atomic bomb project
- 1971 Soviet nuclear tests
- Категория:Мирные ядерные взрывы на территории СССР (Articles on individual explosions in Russian Wikipedia) (in Russian)
Notes
- ↑ Seife, Charles (October 2008). Sun in a Bottle: The Strange History of Fusion and the Science of Wishful Thinking (Print). Viking Adult. ISBN 978-0-670-02033-1.
- ↑ The Nuclear Weapon Archive, Chagan: The First Soviet "Industrial" Test
- ↑ English, Trevor (10 April 2020). "Soviet Engineers Detonated a Nuke Miles Underground to Put Out a Gas Well Fire". Interesting Engineering. Retrieved 21 January 2022.
- ↑ Nordyke 1998, p. 35-36.
- ↑ Broad, William J. (2010-06-02). "Nuclear Option on Gulf Oil Spill? No Way, U.S. Says". New York Times. Retrieved 2010-06-18.
- ↑ (in Russian) A.V. Yablokov: Nuclear Mythology at the End of Twentieth Century BioMetrica Magazine.
- ↑ (in Russian) Gazeta35: Horishima, Volgograd-style
- ↑ Nordyke 1998, p. 74.
References
- Nordyke, Milo D. (1998). "The Soviet program for peaceful uses of nuclear explosions". Science & Global Security. 7 (1): 1–117. Bibcode:1998S&GS....7....1N. doi:10.1080/08929889808426448. Retrieved 15 March 2015.
External links
- USSR Nuclear Weapons Tests and Peaceful Nuclear Explosions. 1949 through 1990, an official publication of Federal Atomic Energy Agency.
- 1966 Urta-Bulak well #11 blowout
- Nordyke, M. D. (1975). "A review of Soviet data on the peaceful uses of nuclear explosions". Annals of Nuclear Energy. 2 (9–10): 657–660. doi:10.1016/0306-4549(75)90120-6. S2CID 121936501.