Kutai Kartanegara Regency
Kabupaten Kutai Kartanegara | |
|---|---|
_-_panoramio.jpg.webp) | |
 Coat of arms | |
| Motto(s): Bena Benua Etam (Kutai) (Care About Our Region) | |
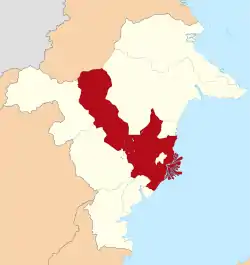 Location within East Kalimantan | |
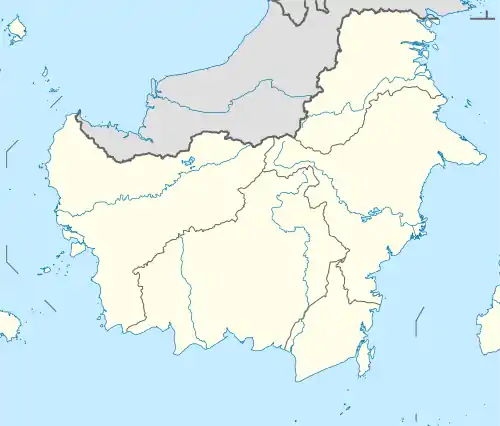 Kutai Kartanegara Regency Location in Kalimantan and Indonesia 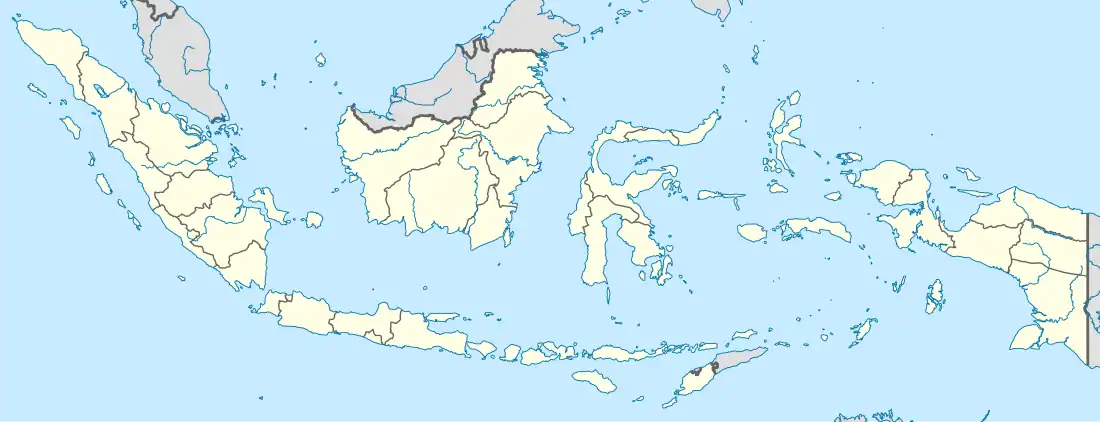 Kutai Kartanegara Regency Kutai Kartanegara Regency (Indonesia) | |
| Coordinates: 0°26′25″S 116°58′53″E / 0.44019°S 116.98139°E | |
| Country | Indonesia |
| Province | East Kalimantan |
| Capital | Tenggarong |
| Government | |
| • Regent | Edi Damansyah |
| • Vice Regent | vacant |
| Area | |
| • Total | 27,263.10 km2 (10,526.34 sq mi) |
| Population (mid 2022 estimate) | |
| • Total | 738,189 |
| • Density | 27/km2 (70/sq mi) |
| [1] | |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (ICST) |
| Area code | (+62) 541 |
| Website | kukarkab |
Kutai Kartanegara Regency (abbreviated as Kukar) is a regency of East Kalimantan province, Indonesia. It has a land area of 27,263.10 km2 and a water area of 4,097 km2, geographically located between 1°18′40″S and 116°31′36″E. The population of the regency was 626,286 at the 2010 Census[2] and 729,382 at the 2020 Census;[3] the official estimate as at mid 2022 was 738,189 (comprising 384,005 males and 354,184 females).[1] The town of Tenggarong is the capital of the regency.
In 2019, President Joko Widodo proclaimed that the new national capital of Indonesia will be built in an area partly in the Kutai Kartanegara Regency and partly in the adjacent Penajam North Paser Regency, and that the construction process will set off around 2024.[4][5]
History
Kutai Kartanegara Regency lies in the historical region of Kutai, home to the first and oldest Hindu kingdom of Indonesia, the Kutai Martadipura Kingdom founded in the 4th century CE by king Kudungga.[6]
Administrative districts
Kutai Kartanegara Regency is divided into twenty districts (kecamatan), tabulated below with their areas and their populations at the 2010 Census [2] and 2020 Census,[3] together with the official estimates as at mid 2022.[1] The newly formed Kota Bangun Darat and West Samboja districts were split from Kota Bangun and Samboja on 5 March 2021, but no separate figures are yet available for their areas and populations, which are still included in the figures for the districts from which they were removed.[7][8]
The table also includes the locations of the district administrative centres, the number of villages in each district (totaling 44 urban kelurahan and 193 rural desa) and its post code(s).
| Kode Wilayah | Name of District (kecamatan) | Area in km2 | Pop'n Census 2010 | Pop'n Census 2020 | Pop'n Estimate mid 2022 | Admin centre | No. of villages | Post codes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 64.02.13 | Samboja | 1,045.90 | 54,515 | 66,617 | 68,025 | Kampung Lama | 13 (a) | 75271, 76276, 75277, 75279 |
| 64.02.20 | West Samboja | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | Tani Bakti | 10 (a) | 75271 - 75274 |
| 64.02.14 | Muara Jawa (b) | 754.50 | 33,923 | 41,561 | 42,461 | Muara Jawa Ulu | 8 (c) | 75261 - 75267 |
| 64.02.15 | Sanga-Sanga | 233.40 | 17,588 | 19,728 | 19,814 | Sanga-Sanga Dalam | 5 (c) | 75251 - 75256 |
| 64.02.03 | Loa Janan | 644.20 | 56,071 | 67,471 | 68,692 | Loa Janan Ulu | 8 | 75391 |
| 64.02.02 | Loa Kulu (d) | 1,405.70 | 39,938 | 51,639 | 53,310 | Loh Sumber | 15 | 75571 |
| 64.02.01 | Muara Muntai (e) | 928.60 | 17,315 | 19,396 | 19,475 | Muara Muntai Ilir | 13 | 75562 |
| 64.02.18 | Muara Wis | 1,108.16 | 8,557 | 9,398 | 9,400 | Muara Wis | 7 | 75559 |
| 64.02.08 | Kota Bangun | 1,143.74 | 31,292 | 36,655 | 37,125 | Kota Bangun Ulu | 11 | 75561 |
| 64.02.19 | Kota Bangun Darat | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | Kedang Ipil | 10 | 75561 |
| 64.02.06 | Tenggarong (f) | 398.10 | 96,209 | 106,480 | 106,669 | Melayu | 14 (g) | 75511 - 75517 |
| 64.02.07 | Sebulu | 859.50 | 36,420 | 40,925 | 41,117 | Sebulu Ilir | 14 | 75552 |
| 64.02.16 | Tenggarong Seberang (h) | 437.00 | 61,441 | 67,877 | 67,972 | Manunggal Jaya | 18 | 75572 |
| 64.02.04 | Anggana (i) | 1,798.80 | 32,688 | 33,416 | 32,964 | Sungai Meriam | 8 | 75381 (j) |
| 64.02.05 | Muara Badak (k) | 939.09 | 39,834 | 46,656 | 47,253 | Muara Badak Ulu | 13 | 75382 |
| 64.02.17 | Marang Kayu | 1,165.71 | 23,394 | 26,823 | 27,054 | Sebuntal | 11 | 75385 |
| 64.02.11 | Muara Kaman | 3,410.10 | 33,909 | 45,885 | 47,789 | Muara Kaman Ulu | 20 | 75553 |
| 64.02.09 | Kenohan | 1,302.20 | 9,861 | 11,588 | 11,744 | Kahala | 9 | 75564 |
| 64.02.10 | Kembang Janggut | 1,923.90 | 23,817 | 25,810 | 25,750 | Kembang Janggut | 11 | 75557 |
| 64.02.12 | Tabang | 7,764.50 | 9,908 | 11,457 | 11,575 | Sidomulyo | 19 | 75558 |
| Totals | 27,263.10 | 626,286 | 729,382 | 738,189 | Tenggarong | 237 |
Notes: (a) Samboja District comprising 10 urban kelurahan (Handil Baru, Handil Baru Darat, Kampung Lama, Muara Sembilang, Samboja Kuala, Sanipah, Sungai Seluang, Tanjung Harapan, Teluk Pemedas and Wonotirto) and 3 rural desa; the new Samboja Barat District comprises 9 urban kelurahan (Amborawang Darat, Amborawang Laut, Argosari, Bukit Merdeka, Karya Merdeka, Margomulyo, Salok Api Darat, Salok Api Laut and Sungai Merdaka) and 1 rural desa.
(b) including 14 offshore islands. (c) all 8 are kelurahan (Dondang, Muara Jawa Pesisir, Muara Jawa Ilir, Muara Jawa Tengah, Muara Jawa Ulu, Muara Kembang, Tama Pole and Teluk Dalam).
(d) all 5 are kelurahan (Jawa, Pendingin, Sanga-Sanga Dalam, Sanga-Sanga Muara and Sarijaya). (e) including one offshore island.
(f) including offshore island of Pulau Kumala. (g) comprising 12 urban kelurahan (Baru, Bukit Biru, Jahab, Loa Ipuh, Loa Ipuh Darat, Loa Tebu, Maluhu, Mangkurawang, Melayu, Panji, Sukarame and Timbau) and 2 rural desa. (h) including offshore island of Pulau Yupa.
(i) including 32 offshore islands. (j) except desa of Sidomulyo, which has a post code of 76131. (k) including 6 offshore islands.
Bukit Bangkirai rainforest
Bukit Bangkirai (Bangkirai Hill) is a 1,500-hectare natural tropical located about 58 kilometres (around 45 minutes by car) from the city of Balikpapan.[9] Plants of the family Dipterocarpaceae dominate in the area, especially Bangkirai trees (Shorea laevis of the genus Shorea) growing to 40–50 metres in height. There are over 120 bird species as well as gibbons (Müller's Bornean gibbon), macaque monkeys (Southern pig-tailed macaques, Crab-eating macaques), Maroon leaf monkeys, Banded pigs, and Banggai crows. Black Orchids (Coelogyne pandurata), among 45 kinds of orchids, are endemic to Bukit Bangkirai.
To visit the forest, visitors can walk along a 64-metre canopy bridge which connects five big Bangkirai trees 30 metres above the ground.[10]
Mangrove information, research center
East Kalimantan province has developed an 18-hectare plot of land for mangrove information and research center in Sepatin village, in Anggana District, as Bali has done. It will functioning as a research, exhibition, information, breeding as well as education center on mangroves, especially in the Mahakam Delta.[11]
Smart City
In early 2015 it was announced that part of Kutai Kartanegara Regency had been selected to be a trial 'smart city', the first in Indonesia, based on the Fujisawa Sustainable Smart Town (SST) concept. The aim of the SST concept was to reduce CO2 emissions by 70 percent and reduce consumption of water by 30 percent. The Kutai Kartanegara area was chosen as a trial area because of good investment growth in the region, the extensive area, relatively moderate levels of population density, effective planning in the area, and rich energy resources.[12]
See also
- Kutai, (historical region in eastern Borneo)
- Kutainese language
- Legend of the Centipede Lake
References
- 1 2 3 Badan Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2023, Kabupaten Kutai Kartanegara Dalam Angka 2023 (Katalog-BPS 1102001.6402)
- 1 2 Biro Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2011.
- 1 2 Badan Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2021.
- ↑ Kusuma, Hendra (26 August 2019). "Resmi! Jokowi Putuskan Ibu Kota RI Pindah ke Kaltim". detikfinance (in Indonesian). Retrieved 6 January 2020.
- ↑ Picheta, Rob (26 August 2019). "Indonesia will build its new capital city in Borneo as Jakarta sinks into the Java Sea". CNN. Retrieved 6 January 2020.
- ↑ Vogel, J. Ph. (1918). "The Yupa Inscription of King Mulawarman, from Koetei (East Borneo)". BKI. 74.
- ↑ "Kode Wilayah Kota Bangun Darat dan Samboja Barat Sudah Ditetapkan, Dokumen Kependudukan Segera Diperbarui". korankaltim.com. Retrieved 9 February 2023.
- ↑ "Ada Samboja Barat dan Kota Bangun Darat, Kukar Kini Miliki 20 Kecamatan". pusaranmedia.com. Retrieved 10 February 2023.
- ↑ 'Bukit Bangkirai a rainforest wonderland', The Jakarta Post, 16 June 2007.
- ↑ "Visiting Kutai Bukit Bangkirai". Retrieved 28 March 2012.
- ↑ "E Kalimantan to build mangrove information, research center". 16 September 2011.
- ↑ "Kutai Jadi Contoh Pertama "Smart City" di Indonesia". 23 February 2015.