| 1973 Samita Border Skirmish | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of Iraq–Kuwait relations | |||||||
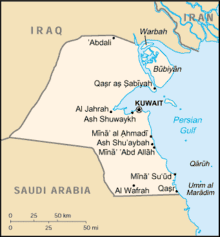 Map of Kuwait showing Warbah Island and Bubiyan Island | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| Unknown | Unknown | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| 4 killed | 2 killed | ||||||
Following the deterring effect of Operation Vantage (1961),[1] Kuwait gained its recognition by Iraq in 1963.[2] Both countries had ongoing border disputes throughout most of the 1960s, although often resolved and restrained within the history of Arab solidarity.
Since 1967 and during 1973, despite the unstable history between the Kuwaiti and the leadership of Iraq back then, the Kuwaiti military acted in alliance with the Iraqi military during the Six-Day War and participated with a token force during the 1973 October War of the same year.
1973 border skirmish
Known and designated as "Samita" (Arabic meaning: "quiet") skirmish; however, the proper border post in reference was "Sanita" as it referred to a northern border area post on the Kuwaiti border with Iraq and accordingly the skirmish was designated as such.
On December 26, 1972, Kuwait sent a delegation of members of the National Assembly of Kuwait to Iraq. The Kuwaiti delegation met with Saddam Hussein, then deputy President of Iraq, and discussed the border demarcation between Kuwait and Iraq and the need to resolve this conflict. The Kuwaiti delegation also met with Iraqi President Ahmed Hassan al-Bakr, who assured members of the delegation that the border situation would be resolved. Accordingly, on February 26, 1973, another Kuwaiti delegation headed by Sheikh Sabah Al-Ahmad Al-Jaber Al-Sabah, then Kuwait's Minister of Foreign Affairs, visited Iraq and remained until March 2, 1973.
Kuwaiti and Iraqi authorities conducted several meetings in which Iraqi authorities claimed that Warbah Island and Bubiyan Island were part of Iraq due to their importance as major water channels for the trade of Iraq and significant geopolitical strategic points. In response, the visiting delegation stated that Kuwait would not cede any of its territories and if the territories were needed for joint economic development purposes, then Kuwait would spare no effort in realizing such an endeavor advancing exclusively humanitarianism through a concession from the Emir of Kuwait within the formalization of a just mission approach and that following the finalization of border demarcations. As the Kuwaiti delegation was set to leave Iraq on March 3, 1973, the Iraqi government proposed an agreement between Kuwait and Iraq which would enhance the capabilities of Iraq in expanding trade through Kuwait. The Kuwaiti delegation was willing to cooperate as long as its territories were not compromised unjustifiably. In response, the government of Iraq and the leadership at the time withdrew their proposal and started applying pressure.
In the meantime and due to the history of restrained and calm disputes, Kuwait border posts were rotated between soldiers of the Kuwait Armed Forces and the Kuwait Police. On March 20, 1973, at 0300, a crisis occurred between Kuwait and Iraq based on land demarcations that Iraq was claiming. Units of the Iraqi military advanced to a Kuwaiti border police station, secured by members of the Kuwait border guards, and asked the border guards to vacate the premises. When the officer in charge refused, Iraqi forces attacked the lightly guarded border post. The border guards troops held their ground and battled the heavily armed Iraqi force throughout the night and morning. The skirmish wounded several and claimed the lives of the first lieutenant in charge and his corporal. As a result, Kuwait declared a state of emergency, and the borders were sealed.
Immediately after, Mubarak Abdullah Al-Jaber Al-Sabah and his deputy Brigadier General Sheikh Saleh Mohammed Al-Sabah mobilized the Kuwait Armed Forces and led the deployment towards the border with Iraq in preparation for the worst. The Kuwaiti combat quick reaction force contingent was led by a Kuwaiti colonel assisted by a lieutenant-colonel, consisting of elements of the Kuwait Army and the Kuwait Air Force. The combat reaction force included a Commando force led by a Kuwaiti lieutenant colonel being combat supported by an armored tank brigade and two supersonic English Electric Lightning fighter aircraft who were tasked with engaging the area of conflict as required and remain acting as armed air vanguards patrollers and monitor for the area from Umm Qasr in the east to Safwan in the west.
In response to the assembling of the Kuwait Armed Forces by Mubarak and Saleh, the Iraqi authorities issued a statement at 1300 on March 20, 1973, claiming that the Kuwaiti forces were the aggressors, which were intruding in Iraqi territory while Iraqi military units were conducting military drills and as a result, the Iraqi military responded with force. In response, Kuwait authorities issued a similar statement claiming that the assault on the "Sanita" post was an assault of Kuwaiti territory and subsequently an assault on Kuwait. In addition, the Kuwaiti statement added that the assault occurred during the time when Kuwait was expecting an Iraqi delegation from Iraq to come to Kuwait and settle the demarcation of borders between the two countries, based on the agreement that Baghdad signed on October 4, 1963. The Iraqi government proposed that the Iraqi Military and the Military of Kuwait should pull back 10 km from the assaulted post. Accordingly, Kuwaiti authorities refused this proposition and requested the Arab League to demand from Iraq to pull back their forces to the demarcation line set by the Arab League Forces during Operation Vantage. Also, Kuwaiti authorities insisted on the withdrawal of all Iraqi military units from the "Sanita" border post and also demanded to settle the demarcation of borders between Kuwait and Iraq. Consequently, the border dispute was shaping to be governed by a political resolution.
See also
References
- ↑ White, Christopher J; Robinson, Peter (2008–2010). "Operation Vantage". Historical RFA. Archived from the original on 2010-04-18. Retrieved 16 Jan 2010.
- ↑ White, Christopher J; Robinson, Peter (2008–2010). "Operation Vantage". Historical RFA. Retrieved 16 Jan 2010.