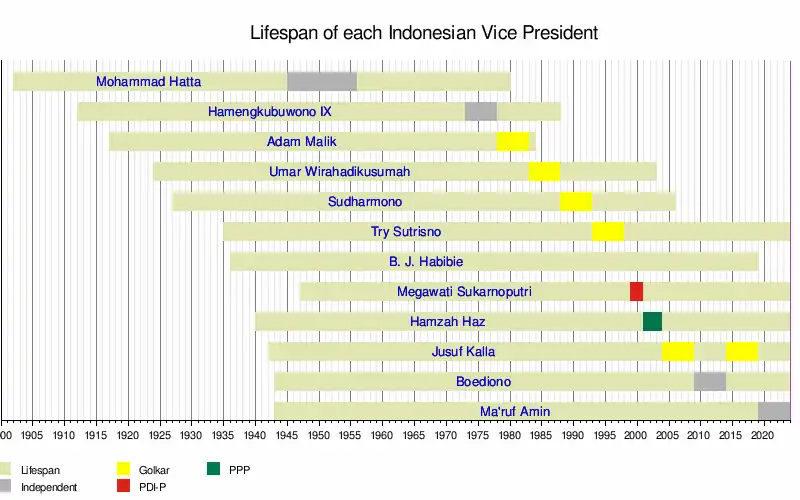
- Top left: Mohammad Hatta was the first and longest-serving vice president of Indonesia.
- Top right: Megawati Sukarnoputri is the first female vice president as well as the first and remains the only to be born after 1945.
- Bottom left: Jusuf Kalla is the first and remains the only to serve two terms as vice president.
- Bottom right: Ma'ruf Amin is the incumbent vice president of Indonesia since 2019.
| This article is part of a series on the |
| Politics of Indonesia |
|---|
 |
The vice president of the Republic of Indonesia (Indonesian: Wakil Presiden Republik Indonesia) is the second-highest officer in the executive branch of the Indonesian government, after the president, and ranks first in the presidential line of succession. Since 2004, the president and vice president are directly elected to a five-year term.
The vice presidency was established during the formulation of the 1945 Constitution by the Investigating Committee for Preparatory Work for Independence (BPUPK), a research body for the preparation of Indonesian independence. On 18 August 1945, the Preparatory Committee for Indonesian Independence (PPKI), which was created on 7 August to replace the BPUPK, selected Sukarno as the country's first president and Mohammad Hatta as vice president.[1]
Vice presidents
| No. | Portrait | Name (Birth–Death) |
Term of office | Political party | President(s) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Took office | Left office | Time in office | ||||||
| 1 |  |
Mohammad Hatta (1902–1980) |
18 August 1945[2] | 1 December 1956[A] | 11 years, 105 days | Independent | Sukarno | |
| Vacant[B] (1 December 1956 – 23 March 1973) | ||||||||
| 2 | .jpg.webp) |
Hamengkubuwono IX (1912–1988) |
23 March 1973[3] | 23 March 1978[C] | 5 years | Independent | Suharto | |
| 3 | .jpg.webp) |
Adam Malik (1917–1984) |
23 March 1978 | 11 March 1983[4] | 4 years, 353 days | Golkar | ||
| 4 |  |
Umar Wirahadikusumah (1924–2003) |
11 March 1983 | 11 March 1988[4] | 5 years | Golkar | ||
| 5 |  |
Sudharmono (1927–2006) |
11 March 1988 | 11 March 1993[5] | 5 years | Golkar | ||
| 6 |  |
Try Sutrisno (born 1935) |
11 March 1993 | 11 March 1998 | 5 years | Golkar | ||
| 7 |  |
B. J. Habibie (1936–2019) |
11 March 1998 | 21 May 1998[D] | 71 days | Golkar | ||
| Vacant (21 May 1998 – 21 October 1999) | ||||||||
| 8 |  |
Megawati Sukarnoputri (born 1947) |
21 October 1999 | 23 July 2001[E] | 1 year, 275 days | Indonesian Democratic Party of Struggle | Abdurrahman Wahid | |
| Vacant[E] (23–26 July 2001) | ||||||||
| 9 |  |
Hamzah Haz (born 1941) |
26 July 2001 | 20 October 2004 | 3 years, 86 days | United Development Party | Megawati Sukarnoputri | |
| 10 |  |
Jusuf Kalla (born 1941) |
20 October 2004 | 20 October 2009 | 5 years | Golkar | Susilo Bambang Yudhoyono | |
| 11 |  |
Boediono (born 1943) |
20 October 2009 | 20 October 2014 | 5 years | Independent | ||
| 12 (10) |
 |
Jusuf Kalla (born 1941) |
20 October 2014 | 20 October 2019 | 5 years | Golkar | Joko Widodo | |
| 13 |  |
Ma'ruf Amin (born 1943) |
20 October 2019 | Incumbent | 4 years, 85 days | Independent | ||
By age
| # | Vice president | Born | Age at start of vice presidency |
Age at end of vice presidency |
Post-VP timespan | Lifespan | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Died | Age | ||||||
| 1 | Mohammad Hatta | 12 August 1902 | 43 years, 6 days 18 August 1945 |
54 years, 111 days 1 December 1956[lower-alpha 1] |
23 years, 165 days | 14 May 1980 | 77 years, 276 days |
| 2 | Hamengkubuwono IX | 12 April 1912 | 60 years, 345 days 23 March 1973 |
65 years, 345 days 23 March 1978 |
10 years, 193 days | 2 October 1988 | 76 years, 173 days |
| 3 | Adam Malik | 22 July 1917 | 60 years, 244 days 23 March 1978 |
65 years, 232 days 11 March 1983 |
1 year, 178 days | 5 September 1984 | 67 years, 45 days |
| 4 | Umar Wirahadikusumah | 10 October 1924 | 58 years, 152 days 11 March 1983 |
63 years, 153 days 11 March 1988 |
15 years, 10 days | 21 March 2003 | 78 years, 162 days |
| 5 | Sudharmono | 12 March 1927 | 60 years, 365 days 11 March 1988 |
65 years, 364 days 11 March 1993 |
12 years, 320 days | 25 January 2006 | 78 years, 319 days |
| 6 | Try Sutrisno | 15 November 1935 | 57 years, 116 days 11 March 1993 |
62 years, 116 days 11 March 1998 |
25 years, 308 days | (living) | 88 years, 59 days |
| 7 | B. J. Habibie | 25 June 1936 | 61 years, 259 days 11 March 1998 |
61 years, 330 days 21 May 1998[lower-alpha 2] |
21 years, 113 days | 11 September 2019 | 83 years, 78 days |
| 8 | Megawati Sukarnoputri | 23 January 1947 | 52 years, 271 days 21 October 1999 |
54 years, 181 days 23 July 2001[lower-alpha 2] |
22 years, 174 days | (living) | 76 years, 355 days |
| 9 | Hamzah Haz | 15 February 1941 | 60 years, 161 days 26 July 2001[lower-alpha 3] |
63 years, 248 days 20 October 2004 |
19 years, 85 days | (living) | 82 years, 332 days |
| 10 | Jusuf Kalla | 15 May 1941 | 63 years, 158 days 20 October 2004 |
68 years, 158 days 20 October 2009 |
5 years, 0 days[lower-alpha 4] | (living) | 82 years, 243 days |
| 11 | Boediono | 25 February 1943 | 66 years, 237 days 20 October 2009 |
71 years, 237 days 20 October 2014 |
9 years, 85 days | (living) | 80 years, 322 days |
| 12 | Jusuf Kalla | 15 May 1941 | 73 years, 158 days 20 October 2014 |
78 years, 158 days 20 October 2019 |
4 years, 85 days[lower-alpha 5] | (living) | 82 years, 243 days |
| 13 | Ma'ruf Amin | 11 March 1943 | 76 years, 223 days 20 October 2019 |
(incumbent) | (incumbent) | (living) | 80 years, 308 days |
| # | Vice president | Born | Age at start of vice presidency |
Age at end of vice presidency |
Post-VP timespan | Lifespan | |
| Died | Age | ||||||
Notes
- ↑ Resigned from office.
- 1 2 Succeeded to the presidency.
- ↑ Elected by the MPR to fill an intra-term vacancy in the vice presidency.
- ↑ Kalla was vice president for two non-consecutive terms; this was his first post vice-presidential retirement between his terms (2009–2014).
- ↑ Kalla was vice president for two non-consecutive terms; this was his post vice-presidency retirement counting only from after his second term (from 20 October 2019).
By time in office
| Rank | Vice president | Length in days | Order of vice presidency | Number of terms |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Mohammad Hatta | 4,123[lower-alpha 1] | 1st • 18 August 1945 – 1 December 1956[lower-alpha 2] | N/A: Appointed by the Preparatory Committee for Indonesian Independence, never faced reelection. |
| 2 | Jusuf Kalla | 3,652[lower-alpha 3] | 10th • 20 October 2004 – 20 October 2009 | Two full terms (non-consecutive) |
| 12th • 20 October 2014 – 20 October 2019 | ||||
| 3 | Umar Wirahadikusumah | 1,827[lower-alpha 4] | 4th • 11 March 1983 – 11 March 1988 | One full term |
| 4 tie | Hamengkubuwono IX | 1,826 | 2nd • 23 March 1973 – 23 March 1978 | One full term |
| Sudharmono | 1,826 | 5th • 11 March 1988 – 11 March 1993 | One full term | |
| Try Sutrisno | 1,826 | 6th • 11 March 1993 – 11 March 1998 | One full term | |
| Boediono | 1,826 | 11th • 20 October 2009 – 20 October 2014 | One full term | |
| 8 | Adam Malik | 1,814[lower-alpha 5] | 3rd • 23 March 1978 – 11 March 1983 | One full term |
| 9 | Ma'ruf Amin | 1,546[lower-alpha 6] | 13th • 20 October 2019 – Incumbent | Serving first term |
| 10 | Hamzah Haz | 1,182[lower-alpha 7] | 9th • 26 July 2001 – 20 October 2004 | One partial term (3 years, 2 months, and 24 days) |
| 11 | Megawati Sukarnoputri | 641 | 8th • 21 October 1999 – 23 July 2001[lower-alpha 8] | One partial term (1 year, 9 months, and 2 days) |
| 12 | B. J. Habibie | 71 | 7th • 11 March 1998 – 21 May 1998[lower-alpha 8] | One partial term (2 months and 10 days) |
Notes
- ↑ Hatta was detained by Dutch troops on 19 December 1948 during Operation Kraai. During this time, the Emergency Government of the Republic of Indonesia, led by Sjafruddin Prawiranegara, acted as the country's government-in-exile until 13 July 1949 (206 days). Hatta became Prime Minister of the United States of Indonesia instead of the Vice President between 27 December 1949 and 15 August 1950 (231 days).
- ↑ Resigned from office
- ↑ Each of Jusuf Kalla's two non-consecutive terms in office was 1,826 days long.
- ↑ Umar Wirahadikusumah's term had two leap days instead of one.
- ↑ The 1983 inauguration day was moved from 23 March to 11 March, 12 days shorter than a normal term.
- ↑ As of 13 January 2024
- ↑ Elected by the MPR to fill an intra-term vacancy in the vice presidency.
- 1 2 Succeeded to presidency.
Footnotes
- A Hatta announced his resignation from office on 26 July 1956, effective on 1 December 1956 and legitimized retroactively on 5 February 1957.[6]
- B President Sukarno did not name Hatta's successor as vice president. In December 1965, there were calls for a vice president to be named to assist Sukarno with the fallout of the 30 September Movement and General Suharto's attempts to take over the government.[7] It was not until the New Order regime of President Suharto that the vice president post became filled again.
- C Vice President Hamengkubuwono IX rejected his nomination for Vice President by the People's Consultative Assembly (MPR) in March 1978, due to poor health.[8]
- D Following the 1997 Asian financial crisis, there were calls for Suharto's resignation as president. On 21 May 1998, Suharto resigned from office. Habibie became his successor as the President of Indonesia.[9]
- E After Abdurrahman Wahid was impeached by the MPR, Vice President Megawati replaced him as President of Indonesia.[10]
See also
References
- Specific
- ↑ Cribb & Kahin 2004, p. 312
- ↑ Cribb & Kahin 2004, p. 171
- ↑ Abdulgani-Knapp 2007, p. 91
- 1 2 Cribb & Kahin 2004, p. 479
- ↑ Abdulgani-Knapp 2007, p. 162
- ↑ Cribb & Kahin 2004, p. lii
- ↑ Hughes 2002, p. 215
- ↑ McIntyre 2005, p. 118
- ↑ Vickers 2005, pp. 203–207
- ↑ Cribb & Kahin 2004, p. lx
- General
- Abdulgani-Knapp, Retnowati (2007), Soeharto: The Life and Legacy of Indonesia's Second President, Singapore: Marshall Cavendish, ISBN 981-261-340-4, OCLC 155758606.
- Cribb, Robert; Kahin, Audrey (2004), Historical Dictionary of Indonesia (2nd ed.), Lanham, Maryland: Scarecrow Press, ISBN 0-8108-4935-6, OCLC 53793487.
- Hughes, John (2002), The End of Sukarno: A Coup That Misfired: A Purge That Ran Wild (3rd ed.), Singapore: Archipelago Press, ISBN 981-4068-65-9, OCLC 52567484.
- McIntyre, Angus (2005), The Indonesian Presidency: The Shift from Personal Toward Constitutional Rule (3rd ed.), Lanham, Maryland: Rowman & Littlefield, ISBN 0-7425-3827-3, OCLC 59137499.
- Suryadinata, Leo (2005), "Indonesia: The Year of a Democratic Election", Southeast Asian Affairs, Singapore: Institute of Southeast Asian Studies, 2005: 133–149, doi:10.1355/SEAA-05H, ISSN 0377-5437.
- Vickers, Adrian (2005), A History of Modern Indonesia: An Enduring Rivalry, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, ISBN 0-521-83493-7, OCLC 60794234.
