A craton is an ancient part of the Earth's continental crust which has been more or less stable since Precambrian times. Cratons whose ancient rocks are widely exposed at the surface, often with relatively subdued relief, are known as shields. If the ancient rocks are largely overlain by a cover of younger rocks then the 'hidden' craton may be referred to as a platform.
List of shields
- Western Ethiopian Shield
- Amazonian Shield of central South America
- Guiana Shield
- Guaporé or Central Brazilian Shield
- The Angaran Shield of West Siberia
- Arabian-Nubian Shield
- (Western) Australian Shield
- Baltic Shield of Scandinavia and Eastern Europe
- Canadian Shield a.k.a. Laurentian Shield
- The China-Korean Shield containing the North China Craton
- The East Antarctic Shield containing the East Antarctic Craton
- Indian Shield
- Man Shield
List of named cratons
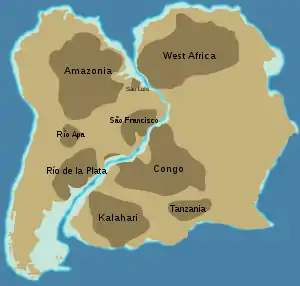
Approximate location of Mesoproterozoic (older than 1.3 Ga) cratons in South America and Africa. The São Luís and Luís Alves cratonic fragments are shown.

Gondwana and the Kuungan orogen
Listed by modern continent and Gondwana, include:
West Gondwana
South America
- Amazonian Craton
- Guiana Shield
- Amazonian Shield
- Sao Francisco Craton (Congo Craton)
- Rio Apa Craton
- Río de la Plata Craton
- Arequipa–Antofalla Craton
- São Luís cratonic fragment
- Luís Alves cratonic fragment
Africa
- West African Craton
- East Saharan Meta-craton
- Congo Craton, central southern Africa
- Tanzanian Craton
- Kalahari Craton
- Kaapvaal Craton, South Africa (3.6–2.5 Ga)
- Zimbabwe Craton (3.5 Ga)
- Sebakwe Craton
Antarctic-East African Orogen
- Arabian plate
- Part of the Arabian–Nubian Shield
- Western Ethiopian Shield
- Eastern Ethiopian Shield (part of the Somali Plate)
- Part of Madagascar
East Gondwana
Indian Subcontinent
Antarctica
Australia
- Altjawarra Craton
- Central Craton
- Curnamona Craton, South Australia
- Gawler Craton, central South Australia
- Pilbara Craton, Western Australia
- Yilgarn Craton, Western Australia (4.4 Ga)
North America
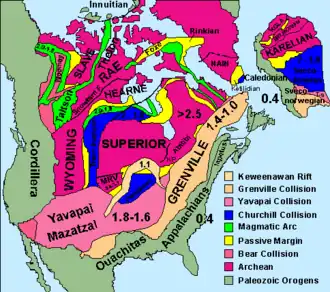
North American cratons and basement rocks

- Canadian Shield (or Laurentian Shield)
- Churchill Craton
- Hearne Craton
- Nain Craton (part of North Atlantic Craton)
- North American Craton (Laurentia)
- Rae Craton
- Sask Craton
- Sclavia Craton
- Slave Craton, Northwest Territories, Canada (4.03–3.5 Ga)
- Superior Craton, Canada and northern United States (3.7–2.7 Ga)
- Wyoming Craton
Eurasia
Eastern Eurasia
- East China Craton
- North China Craton (sometimes called Sino-Korean Craton), (2.5 Ga)
- South China Craton (also known as Yangtze Craton)
- Siberian Craton, sometimes called Angara Craton.
- Tarim Craton, China
Northern and Eastern Europe
- East European Craton, the core of Baltica
- Volgo-Uralian Craton, Russia (3.0–2.7 Ga)
- Baltic Shield, part of the East European Craton; Fennoscandian Shield, the exposed Northwestern part of the Baltic Shield in Norway, Sweden and Finland (3.1 Ga)
- Karelian Craton, part of the Fennoscandian Shield in Southeast Finland and Karelia Russia, (3.4 Ga)
- Kola Craton, part of the Fennoscandian Shield, Kola Peninsula, Northwest Russia
- Belomorian Craton, part of the Fennoscandian Shield, between the Karelian and Kola cratons
- Sarmatian Craton (3.7–2.8 Ga)
- Midlands Microcraton of England and Wales
- North Atlantic Craton
See also
References
- Dov Avigad and Zohar Gvirtzman (2009). "Late Neoproterozoic rise and fall of the northern Arabian–Nubian shield: The role of lithospheric mantle delamination and subsequent thermal subsidence" (PDF). Tectonophysics. 477 (3–4): 217–228. Bibcode:2009Tectp.477..217A. doi:10.1016/j.tecto.2009.04.018. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-04-09.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.