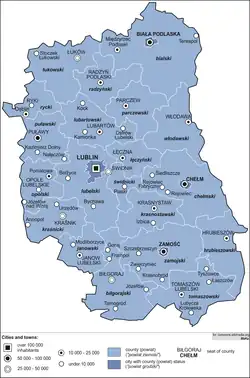
The Lublin Voivodeship (Polish: województwo lubelskie [vɔjɛˈvut͡stfɔ luˈbɛlskʲɛ] ⓘ), also known as the Lublin Province,[3] is a voivodeship (province) of Poland, located in southeastern part of the country. It was created on January 1, 1999, out of the former Lublin, Chełm, Zamość, Biała Podlaska and (partially) Tarnobrzeg and Siedlce Voivodeships, pursuant to Polish local government reforms adopted in 1998. The region is named after its largest city and regional capital, Lublin, and its territory is made of four historical lands: the western part of the voivodeship, with Lublin itself, belongs to Lesser Poland, the eastern part of Lublin Area belongs to Red Ruthenia, and the northeast belongs to Polesie and Podlasie.[4] Lublin Voivodeship borders Subcarpathian Voivodeship to the south, Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship to the south-west, Masovian Voivodeship to the west and north, Podlaskie Voivodeship along a short boundary to the north, Belarus (Brest Region) and Ukraine (Lviv Oblast and Volyn Oblasts) to the east. The region's population as of 2019 was 2,112,216. It covers an area of 25,155 square kilometres (9,712 sq mi).
History
The Polish historical region that encompasses Lublin, and approximates Lublin Voivodeship as it was before the Partitions of Poland, is known as Lubelszczyzna. Provinces centred on Lublin have existed throughout much of Poland's history; for details see the section below on Previous Lublin Voivodeships.
The region was, before World War II, one of the world's leading centres of Judaism. Before the middle of the 16th century, there were few Jews in the area, concentrated in Lublin, Kazimierz Dolny, and perhaps Chełm; but the founding of new private towns led to a large movement of Jews into the region to develop trade and services. Since these new towns competed with the existing towns for business, there followed a low-intensity, long-lasting feeling of resentment, with failed attempts to limit the Jewish immigration. The Jews tended to settle mostly in the cities and towns, with only individual families setting up businesses in the rural regions; this urban/rural division became another factor feeding resentment of the newly arrived economic competitors. By the middle of the 18th century, Jews were a significant part of the population in Kraśnik, Lubartów and Łęczna.
By the 20th century, Jews represented greater than 70% of the population in eleven towns and close to 100% of the population of Laszczów and Izbica. From this region came both religious figures such as Mordechai Josef Leiner of Izbica, Chaim Israel Morgenstern of Puławy, and Motele Rokeach of Biłgoraj, as well as famous secular authors Israel Joshua Singer. Israel's brother, the Nobel prize winner Isaac Bashevis Singer, was not born in Biłgoraj but lived part of his life in the city. The "Old Town" of the city of Lublin contained a famous yeshiva, Jewish hospital, synagogue, cemetery, and kahal, as well as the Grodzka Gate (known as the Jewish Gate).
Before the war, there were 300,000 Jews living in the region, which became the site of the Majdanek concentration camp and Bełżec extermination camp as well as several labour camps (Trawniki, Poniatowa, Budzyn, Puławy, Zamość, Biała Podlaska, and the Lublin work camps Lipowa 7 camp , Flugplatz, and Sportplatz) which produced military supplies for the Wehrmacht and Luftwaffe). This was once one of the biggest forced labour centres in occupied Europe, with approximately 45,000 Jewish prisoners. As well, the Sobibór extermination camp was located in the Lublin Voivodeship. After the war, the few surviving Jews largely left the area; today there is some restoration of areas of Jewish historical interest, and a surge of tourism by Jews seeking to view their families' historical roots.
Cities and towns

_(oficyna_p%C3%B3%C5%82nocno-wschodnia)_(biblioteka_ty%C5%82)_-_Bia%C5%82a_Podlaska_ul._Warszawska_woj._lubelskie_ArPiCh_A-134.JPG.webp)



The voivodeship contains 5 cities and 43 towns. These are listed below in descending order of population (according to official figures for 2019:[5]
- Lublin (339,770)
- Zamość (63,511)
- Chełm (62,331)
- Biała Podlaska (57,264)
- Puławy (47,634)
Towns:
- Świdnik (39,217)
- Kraśnik (34,355)
- Łuków (29,885)
- Biłgoraj (26,309)
- Lubartów (21,948)
- Tomaszów Lubelski (19,050)
- Łęczna (18,884)
- Krasnystaw (18,675)
- Hrubieszów (17,634)
- Międzyrzec Podlaski (16,736)
- Dęblin (16,026)
- Radzyń Podlaski (15,709)
- Włodawa (13,167)
- Janów Lubelski (11,901)
- Parczew (10,602)
- Ryki (9,625)
- Poniatowa (9,144)
- Opole Lubelskie (8,421)
- Bełżyce (6,504)
- Terespol (5,537)
- Szczebrzeszyn (4,991)
- Bychawa (4,893)
- Rejowiec Fabryczny (4,406)
- Nałęczów (3,749)
- Tarnogród (3,333)
- Kock (3,293)
- Zwierzyniec (3,175)
- Krasnobród (3,091)
- Kazimierz Dolny (2,563)
- Piaski (2,553)
- Stoczek Łukowski (2,520)
- Annopol (2,515)
- Józefów (2,486)
- Lubycza Królewska (2,447)
- Łaszczów (2,139)
- Tyszowce (2,112)
- Ostrów Lubelski (2,078)
- Rejowiec (2,066)
- Urzędów (1,699)
- Modliborzyce (1,462)
- Frampol (1,428)
- Siedliszcze (1,413)
- Józefów nad Wisłą (915)
Administrative division
Lublin Voivodeship is divided into 24 counties (powiats): 4 city counties and 20 land counties. These are further divided into 213 gminas.
The counties are listed in the following table (ordering within categories is by decreasing population).
| English and Polish names |
Area (km2) |
Population (2019) |
Seat | Other towns | Total gminas |
| City counties | |||||
| Lublin | 147 | 339,770 | 1 | ||
| Zamość | 30 | 63,511 | 1 | ||
| Chełm | 35 | 62,331 | 1 | ||
| Biała Podlaska | 49 | 57,264 | 1 | ||
| Land counties | |||||
| Lublin County powiat lubelski |
1,679 | 154,760 | Lublin * | Bełżyce, Bychawa | 16 |
| Puławy County powiat puławski |
933 | 113,441 | Puławy | Nałęczów, Kazimierz Dolny | 11 |
| Biała Podlaska County powiat bialski |
2,754 | 111,078 | Biała Podlaska * | Międzyrzec Podlaski, Terespol | 19 |
| Zamość County powiat zamojski |
1,872 | 106,526 | Zamość * | Szczebrzeszyn, Zwierzyniec, Krasnobród | 15 |
| Łuków County powiat łukowski |
1,394 | 107,144 | Łuków | Stoczek Łukowski | 11 |
| Biłgoraj County powiat biłgorajski |
1,678 | 101,152 | Biłgoraj | Tarnogród, Józefów, Frampol | 14 |
| Kraśnik County powiat kraśnicki |
1,005 | 95,618 | Kraśnik | Annopol, Urzędów | 10 |
| Lubartów County powiat lubartowski |
1,290 | 88,591 | Lubartów | Kock, Ostrów Lubelski | 13 |
| Tomaszów Lubelski County powiat tomaszowski (lubelski) |
1,487 | 83,148 | Tomaszów Lubelski | Tyszowce, Łaszczów, Lubycza Królewska | 13 |
| Chełm County powiat chełmski |
1,780 | 78,074 | Chełm * | Rejowiec Fabryczny, Rejowiec | 15 |
| Świdnik County powiat świdnicki (lubelski) |
469 | 71,897 | Świdnik | Piaski | 5 |
| Krasnystaw County powiat krasnostawski |
1,067 | 63,554 | Krasnystaw | 10 | |
| Hrubieszów County powiat hrubieszowski |
1,269 | 63,320 | Hrubieszów | 8 | |
| Opole Lubelskie County powiat opolski (lubelski) |
804 | 59,511 | Opole Lubelskie | Poniatowa, Józefów nad Wisłą | 7 |
| Radzyń Podlaski County powiat radzyński |
965 | 59,057 | Radzyń Podlaski | 8 | |
| Ryki County powiat rycki |
616 | 55,919 | Ryki | Dęblin | 6 |
| Łęczna County powiat łęczyński |
634 | 57,372 | Łęczna | 6 | |
| Janów Lubelski County powiat janowski |
875 | 45,845 | Janów Lubelski | Modliborzyce | 7 |
| Włodawa County powiat włodawski |
1,256 | 38,524 | Włodawa | Siedliszcze | 8 |
| Parczew County powiat parczewski |
953 | 34,809 | Parczew | 7 | |
| * seat not part of the county | |||||
Protected areas


Protected areas in Lublin Voivodeship include two National Parks and 17 Landscape Parks. These are listed below.
- Polesie National Park (this and surrounding areas form the West Polesie biosphere reserve designated by UNESCO in 2002)
- Roztocze National Park
- Chełm Landscape Park
- Janów Forests Landscape Park (partly in Subcarpathian Voivodeship)
- Kazimierz Landscape Park
- Kozłówka Landscape Park
- Krasnobród Landscape Park
- Krzczonów Landscape Park
- Łęczna Lake District Landscape Park
- Podlaskie Bug Gorge Landscape Park (partly in Masovian Voivodeship)
- Polesie Landscape Park
- Puszcza Solska Landscape Park (partly in Subcarpathian Voivodeship)
- Skierbieszów Landscape Park
- Sobibór Landscape Park
- South Roztocze Landscape Park (partly in Subcarpathian Voivodeship)
- Strzelce Landscape Park
- Szczebrzeszyn Landscape Park
- Wieprz Landscape Park
- Wrzelowiec Landscape Park
Economy
The Gross domestic product (GDP) of the province was 18.5 billion euros in 2018, accounting for 3.7% of Polish economic output. GDP per capita adjusted for purchasing power was 14,400 euros or 48% of the EU27 average in the same year. The GDP per employee was 54% of the EU average. Lublin Voivodship is the province with the lowest GDP per capita in Poland.[6]
Demographics
Population according to 2002 census:[7]
- Poles - 2,171,415
- Ukrainians - 694
Most common surnames in the region
Previous Lublin Voivodeships
Lublin Voivodeship 1474–1795
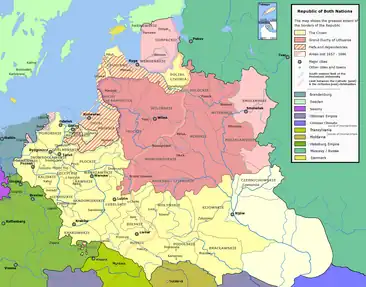
Lublin Voivodeship (Latin: Palatinatus Lublinensis; Polish: Województwo Lubelskie) was an administrative region of the Kingdom of Poland created in 1474 out of parts of Sandomierz Voivodeship and lasting until the Partitions of Poland in 1795. It was part of the prowincja of Lesser Poland.
Lublin Voivodeship 1816–1837
Lublin Voivodeship was one of the voivodeships of Congress Poland. It was formed in 1816 from Lublin Department, and in 1837 was transformed into Lublin Governorate.
Lublin Voivodeship 1919–1939
Lublin Voivodeship (Województwo Lubelskie) was one of the administrative regions of the interwar Second Polish Republic. In early 1939 its area was 26,555 square kilometres (10,253 sq mi) and its population was 2,116,200.[8] According to the 1931 census, 85.1% of its population was Polish, 10.5% Jewish, and 3% Ukrainian.
Lublin Voivodeship 1945–1975
Lublin Voivodeship (województwo lubelskie) was an administrative region of Poland between 1945 and 1975. In 1975 it was transformed into Chełm, Zamość, Biała Podlaska, Tarnobrzeg and Siedlce Voivodeships and a smaller Lublin Voivodeship.
Lublin Voivodeship 1975–1998
Lublin Voivodeship (województwo lubelskie) existed as one of Poland's 49 voivodeships from 1975 until 1998, when it was incorporated into the current (larger) Lublin Voivodeship.
References
- ↑ "EU regions by GDP, Eurostat". Retrieved 18 September 2023.
- ↑ "Sub-national HDI - Subnational HDI - Global Data Lab". globaldatalab.org. Radboud University Nijmegen. Retrieved 2021-12-13.
- ↑ Arkadiusz Belczyk,Tłumaczenie polskich nazw geograficznych na język angielski Archived 2016-03-03 at the Wayback Machine [Translation of Polish Geographical Names into English], 2002-2006.
- ↑ Arkadiusz Belczyk,Tłumaczenie polskich nazw geograficznych na język angielski Archived 2016-03-03 at the Wayback Machine [Translation of Polish Geographical Names into English], 2002-2006.
- ↑ GUS. "Population. Size and structure and vital statistics in Poland by territorial division in 2019. As of 30th June". stat.gov.pl. Retrieved 2020-09-11.
- ↑ "Regional GDP per capita ranged from 30% to 263% of the EU average in 2018". Eurostat.
- ↑ "Ethnic composition of Poland". pop-stat.mashke.org. Archived from the original on 2021-11-22. Retrieved 2016-05-04.
- ↑ Mały Rocznik Statystyczny (Concise Statistical Year-Book), Warsaw, 1939



.svg.png.webp)