Luftflotte 3[1] (Air Fleet 3) was one of the primary divisions of the German Luftwaffe in World War II. It was formed on 1 February 1939 from Luftwaffengruppenkommando 3 in Munich and redesignated Luftwaffenkommando West (Air Command West) on 26 September 1944. This Luftwaffe detachment was based in German-occupied areas of Northern France, the Netherlands, Belgium, and Vichy France, to support the Axis power's forces in area. Its command offices were in Paris, France (on 26 June 1944).
Strategic Reconnaissance
- Stab/FAGr.123 (Toussus le Noble – Buc)
- 4.(F)/123 (Saint-André-de-l'Eure)
- 5.(F)/123 (Monchy-Breton)
- 1.(F)/121 (Toussus le Noble – Buc)
II.Fliegerkorps (II.Air Corps) Chartres
- Fliegerführer West (Flight Director in West Area/Land Air Attack)
Tactical Reconnaissance
Land Air Attack
- III./SG 4 (Clermont-Ferrand)
- III./SG 4 (Detach) (Avord)
IX. Fliegerkorps (IX.Air Corps) Beauvais-Lille
Strategic Reconnaissance
- 3.(F)/122 (Soesterberg)
- 6.(F)/123 (Cormeilles)
Bombers(Medium)
- Stab/KG 2 (Gilze en Rijen)
- I./KG 2 (Gilze en Rijen)
- II./KG 2 (Gilze en Rijen)
- III./KG 2 (Hesepe)
- Stab/KG 6 (Melun-Villaroche)
- I./KG 6 (Melun-Villaroche)
- II./KG 6 (Melun-Villaroche)
- III./KG 6 (Melun-Villaroche)
- 16./KG 6(JABO/Rapid) (Soesterberg)
- Stab/KG 30 (Zwischenhan)
- I./KG 30 (Leck)
- 4./KG 51 (JABO/Rapid) (Soesterberg)
- 5./KG 51(JABO/Rapid) (Gilze en Rijen)
- 6./KG 51(JABO/Rapid) (Soesterberg)
- Stab/KG 54 (Eindhoven)
- I./KG 54 (Eindhoven)
- III./KG 54 (Eindhoven)
- III./KG 66 (Montdidier)
- (Eins)St. IV./KG 101 (Saint-Dizier)
- Stab(KG)/LG 1 (Melsbroek)
- I.(KG)/LG 1 (Le Culot)
- II.(KG)/LG 1(Melsbroek)
JABO (Fighter-Bombers/Incursion strike groups)
X.Fliegerkorps (X.Air Corps) Angers
Special duties/long-distance operations
- 1./KG 200 (Mont-de-Marsan)
- 1./KG 200(Detach) (Bordeaux–Mérignac)
- II/KG 200 (Biscarrosse)
Strategic/Maritime Reconnaissance (Ultra Long Range)
- Stab/FAGr.5 (Mont-de-Marsan)
- 1.(F)/5 (Mont-de-Marsan)
- 2.(F)/5 (Mont-de-Marsan)
- 4.(F)/5 (Nantes)
- 3.(F)/123 (Corme-Écluse)
- 1.(F)/SAGr.129 (Biscarrosse)
- 1.(F)/JG.52 "BF 109"
Bombers (Heavy) Submarine Support/Merchant Strike (Long Range)
2.Fliegerdivision (2.Air Division) Montfrin
Strategic/Tactical/Maritime Reconnaissance (Medium-Short Range)
Bombers (Medium)
- Stab/KG 26 (Montpellier)
- II./KG 26 (LT) (Valence)
- III./KG 26 (LT) (Montpellier)
- III./KG 26 (LT)(Detach) (Valence)
- Stab/KG 77 (Salon-de-Provence)
- I./KG 77 (LT) (Orange-Caritat)
- III./KG 77 (LT) (Orange-Caritat)
- 6./KG 77 (Istres)
- 4./KG 76 (Istres)
- 6./KG 76 (Istres)
- Stab/KG 100 (Toulouse–Francazal)
- III./KG 100 (Toulouse–Francazal)
II.Jagdkorps (II.Fighter Corps) Chantilly
4.Jagddivision (4°Fighter Division) Metz
Jagdabschnittführer 4 (Fighter Direction 4°) St Pol-Brias
Fighters
- Stab/JG 1 (St.Quentin–Clastres)
- I./JG 3 (St.Quentin–Clastres)
- I./JG 5 (St.Quentin–Clastres)
- II./JG 11 (Mons en Chaussée)
- I./JG 301 (Épinoy)
- Stab/JG 27 (Champfleury)
- I./JG 27 (Vertus)
- III./JG 27 (Connantre)
- IV./JG 27 (Champfleury)
Night Fighters
- Stab/NJG 4 (Chenay)
- I./NJG 4 (Florennes)
- III./NJG 4 (Junvincourt)
- Stab/NJG 5 (Haguenau)
- I./NJG 5 (Saint-Dizier)
- III./NJG 5 (Athies-sous-Laon)
5.Jagddivision (5° Fighter Division) Jouy-en-Josas
Jagdabschnittführer 5 (Fighter Director 5) Bernay
Fighters
Night Fighters
- Stab/NJG 2 (Coulommiers)
- I./NJG 2 (Châteaudun)
- II./NJG 2 (Coulommiers)
- II./NJG 4 (Coulommiers)
Jagdabschnittführer Bretagne (Fighter Direction in Brittany) Brest
Fighters
Jagdabschnittführer Südfrankreich (Southern France Fighter Direction) Aix
Fighters
- 1./JGr 200 (Orange-Caritat)
- 2./JGr 200 (Avignon)
- 3./JGr 200 (Orange-Caritat)
Jagdlehrer-Gr Bordeaux (Instruction Wing in Bordeaux sector)
- Jagdabschnittführer Bordeaux (Fighter Direction in Bordeaux) Bordeaux-Mérignac
- Zerstörer (Heavy Fighters)
- Stab/ZG 1 (Bordeaux–Mérignac)
- 1./ZG 1 (Corme-Écluse)
- 3./ZG 1 (Corme-Écluse)
- 2./ZG 1 (Châteauroux)
- III./ZG 1 (Cazaux)
Luftwaffe Special Strike Units
- Jet Bombers/Jet Fighter-Bombers
- (R)"Blitz" KG 76 (Istres)
- II.St.(JABO)/KG 51 (Soesterberg)
- Mistel Special Section
- 2. (Mistel I) /KG 101 (Saint-Dizier)
- II. (Mistel I) -(Detach)/KG 200 (Saint-Dizier)
- Bombers with V-1 Launchers
- Stab/KG 3 (Venlo)
- II./KG 3 (also known as I./KG.5) (Venlo)
- I./KG 53 "Legion Condor" (Gilze en Rijen)
- III./KG 53 "Legion Condor" (Gilze en Rijen)
- Luftwaffe V-1 fixed/mobile ramps units; operated near Calais (France), and in Belgium and the Netherlands.
- Untergruppenbezeichnung FZG (Flakzielgerät) 76 (also known as 5th Flak Division (W), later as Armeekorps zur Vergeltung)
- I./155 Artillerie Abt (W)
- II./155 Artillerie-Abt (W)
- III./155 Artillerie-Abt (W)
- Luftwaffe special transport units(1944–45); based in Muhldorf, Bavaria, and composed of Helicopters:
- Focke-Achgelis Fa 223 Drachen
- Flettner Fl 265
- Flettner 282B Kolibri
- Heer/Luftwaffe V-2 mobile ramps sections
- Division zur Vergeltung(Div.z.V.); led by Heer and SS Commanders, working along with Luftwaffe personnel and facilities. They operated in France, Belgium and the Netherlands.
- "Div.z.V." Nordgruppe
- 444° Artillerie-Abt
- 485° Artillerie- Abt (also known as Artillerie Regiment z. V. 902)
- 2°./485° Artillerie-Abt
- "Div.z.V." Südgruppe
- 500° Waffen SS Artillerie-Abt (also known as 500° SS Werfer Abt.)
- 836° Artillerie-Abt (also known as Artillerie Regiment zur Vergeltung 901)
- Heer V-4 "Rheinbote" Mobile ramps units
- I./709 Artillerie Abt
- Heer V-3 Artillery group
- 705° Artillerie Abt.
Abbreviations
- FAGr = Fernaufklärungsgruppe = Long-range/strategic Reconnaissance aircraft.
- JG = Jagdgeschwader = Fighters.
- Geschwader = equivalent to a USAAF Wing.
- JGr = Jagdgruppe = Fighters.
- KG = Kampfgeschwader = Bombers.
- LG = Lehrgeschwader = Operational Training.
- NAGr = Nahaufklärungsgruppe = Short-range/tactical Observation aircraft.
- NJG = Nachtjagdgeschwader = Night Fighters
- SAGr = Seeaufklärungsgruppe = Maritime Patrol aircraft
- SKG = Schnellkampfgeschwader = Fast Bombers.
- St = Staffel = equivalent to a RAF Squadron.
- ZG = Zerstörergeschwader = Twin engined diurnal heavy fighters.
Commanding officers

Flag for the Chief of a Luftflotte
- Generalfeldmarschall Hugo Sperrle, 1 February 1939 – 23 August 1944
- Generaloberst Otto Deßloch, 23 August 1944 – 22 September 1944
- Generalleutnant Alexander Holle, 22 September 1944 – 26 September 1944
- redesignated to Luftwaffenkommando West
- Generalleutnant Alexander Holle, 28 September 1944 – 15 November 1944
- Generalleutnant Joseph Schmid, 16 November 1944 – 27 April 1945
- Generalleutnant Martin Harlinghausen, 28 April 1945 – 8 May 1945
Chief of staff
- Generalmajor Maximilian Ritter von Pohl, 1 February 1939 – 10 June 1940
- Oberst Günther Korten, 11 June 1940 – 31 December 1940
- Generalmajor Karl Koller, 1 January 1941 – 23 August 1943
- Generalleutnant Hermann Plocher, 1 October 1943 – 26 September 1944
- redesignated to Luftwaffenkommando West
- Oberst Hans Wolters, September 1944 – March 1945
- Oberst Heinrich Wittmer, March 1945 – May 1945
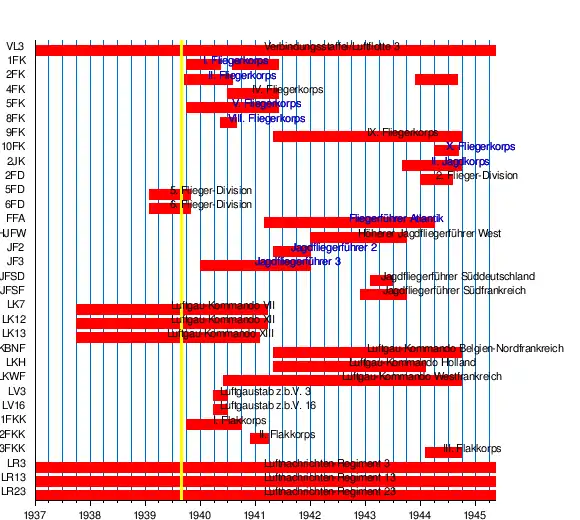
Subordinated units
References
Notes
- ↑ For an explanation of the meaning of Luftwaffe unit designation see Luftwaffe Organisation
References
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.