Legislative Assembly of Macau Special Administrative Region 澳門特別行政區立法會 Assembleia Legislativa da Região Administrativa Especial de Macau | |
|---|---|
| 6th Legislative Assembly | |
 | |
| Type | |
| Type | |
| Leadership | |
Kou Hoi In since 17 July 2019 | |
Vice President | Chui Sai Cheong since 16 October 2017 |
First Secretary | Kou Hoi In since 16 October 2017 |
Second Secretary | Chan Hong since 16 October 2017 |
| Structure | |
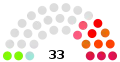
| Seats | 33 |
 | |
Political groups |
|
| Elections | |
Last election | 12 September 2021 |
| Meeting place | |
 | |
| Macau Legislative Assembly Building, 1 Praça da Assembleia Legislativa, Sé, Macau Special Administrative Region | |
| Website | |
| al | |
| Legislative Assembly | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 立法會 | ||||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 立法会 | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| Portuguese name | |||||||||||||
| Portuguese | Assembleia Legislativa | ||||||||||||
The Legislative Assembly of the Macau Special Administrative Region[2] (Chinese: 澳門特別行政區立法會; Portuguese: Assembleia Legislativa da Região Administrativa Especial de Macau) is the organ of the legislative branch of Macau. It is a 33-member body comprising 14 directly elected members, 12 indirectly elected members representing functional constituencies and 7 members appointed by the chief executive. It is located at Sé.
Charter
The assembly has the following charter:
- To enact, amend, suspend or repeal laws;
- To examine and approve budgets; and examine the report on audit;
- To decide on taxation and approve debts to be undertaken by the government
- To debate the policy addresses by the Chief Executive;
- To debate any issue concerning public interests;
- To receive and handle complaints from Macau residents
Election results
 |
| Politics and government of Macau |
| Related topics |
Legislative assembly buildings
The assembly sits at a special Legislative Assembly building, a modern three-storey structure located in the Nam Van area.
From 1784 to 1999, the Assembly met at the Leal Senado Building.
Selection methods
According to Annex II of the Basic Law of Macau, the first Legislative Assembly following the establishment of the special administrative region would be constituted in accordance with the Decision of the National People's Congress on the Methodology for the Formation of the First Government, the First Legislative Assembly and the Judicial Bodies of the Macau Special Administrative Region – i.e., 23 members: 8 directly elected, 8 indirectly elected and 7 appointed members.[3][4]
The second Legislative Assembly would be composed of 27 members: 10 directly elected, 10 indirectly elected and 7 appointed members.[5]
In accordance with Annex II, the number of directly elected legislators for the third Legislative Assembly increased from 10 to 12 in 2005, bringing the number of legislators to 29. After 2009, the selection of the Chief Executive may be changed by ⅔ endorsement of the Legislative Assembly and approval by the National People's Congress Standing Committee. Following 2012 reforms, the Legislative Assembly is now composed of 33 members: 14 directly elected, 12 indirectly elected and 7 appointed members.
Compositions
| Number of Members | Returned by | Voting Method | Number of Voters (2021) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Suffrage | 14 | Popular Vote | Proportional representation (highest averages method: D'Hondt method) | 305,615 |
| Indirect Suffrage | 12 | Electors nominated by legal persons of specified sectors | 6,275 | |
| Nominated Members | 7 | Nominated by the Chief Executive | — | |
| Term (Election) | Diagram | Composition (at commencement) |
Speaker | Pro-Beijing | Pro-democracy | Centrist | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st (1999) | 1:22
|
Susana Chou | 22 | 1 | – | ||
| 2nd (2001) | 2:25
|
Susana Chou | 25 | 2 | – | ||
| 3rd (2005) | 3:26
|
Susana Chou | 26 | 3 | – | ||
| 4th (2009) | 4:25
|
Lau Cheok-vá | 25 | 4 | – | ||
| 5th (2013) | 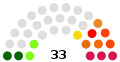 |
4:29
|
Ho Iat-seng | 29 | 4 | – | |
| 6th (2017) | 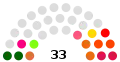 |
4:1:28
|
Ho Iat-seng (2017–19) Chui Sai-cheong (2019) Kou Hoi-in (2019–) |
28 | 4 | 1 | |
| 7th (2021) |  |
2:1:30
|
Kou Hoi-in | 30 | 2 | 1 | |
See also
References
- ↑ FNunes. "Translation of the Basic Law of Macao on Macao's government website". Bo.io.gov.mo. Archived from the original on 5 February 2012. Retrieved 29 January 2012.
- ↑ Sometimes translated in English as the Legislative Council, as in a translation provided by the Printing Bureau of the territory's Basic Law.[1]
- ↑ 全国人民代表大会关于澳门特别行政区第一届政府、立法会和司法机关产生办法的决定 [Decision of the National People's Congress on the Methods for the Formation of the First Government, Legislative Assembly and Judicial Organs of the Macau Special Administrative Region] (in Chinese). Retrieved 6 February 2021 – via www.npc.gov.cn.
- ↑ "Decisão da Assembleia Popular Nacional relativa à Metodologia para a Formação do Primeiro Governo, da Primeira Assembleia Legislativa e dos Órgãos Judiciais da Região Administrativa Especial de Macau" [Decision of the National People's Congress on the Methodology for the Formation of the First Government, the First Legislative Assembly and the Judicial Bodies of the Macau Special Administrative Region] (in Portuguese) – via Imprensa Oficial.
- ↑ Basic Law, Annex II
External links
- Official website
- Members of the Assembly of Macau (in Portuguese)
- The Basic Law of Macau: The Legislature (Government website) University of Macau
- Regulations of the Legislative Assembly (Approved by Legislative Assembly Resolution No. 1/1999, as amended): in Chinese, in Portuguese
- Legislative Session of the Legislative Assembly and the Member Statute (Law No. 3/2000, as amended) in Chinese, in Portuguese
- Organic Law of the Legislative Assembly (Law No. 11/2000, as amended): in Chinese, in Portuguese
- Electoral Law (Law No. 3/2001): in Chinese, in Portuguese