| Այրարատ | |
|---|---|
| Province of the ancient kingdom of Armenia | |
| 189 BC–650 AD | |
 | |
| Capital | Artashat |
| History | |
• Artaxias I declaring himself independent | 189 BC |
| 650 AD 650 AD | |
Ayrarat (Armenian: Այրարատ) was the central province of the ancient kingdom of Armenia, located in the plain of the upper Aras River. Most of the historical capitals of Armenia were located in this province, including Armavir, Yervandashat, Artashat, Vagharshapat, Dvin, Bagaran, Shirakavan, Kars and Ani (the current capital of Armenia, Yerevan, is also located on the territory of historical Ayrarat).
Name
The name Ayrarat is clearly connected with Uruatri/Urartu and the biblical Ararat, and perhaps also with the Alarodians mentioned by Herodotus.[1][2] It is not used by any of the classical Greek and Roman authors who write about Armenia, which suggests that it was a purely local name used to refer to the central lands of Armenia.[1][2] Robert H. Hewsen does not rule out the possibility that Armenians applied the name to the great plain surrounding Mount Masis after converting to Christianity in the early fourth century and identifying the biblical Ararat with Masis.[3] If this is the case, then Ayrarat may be identical with the Araxēnon Pedion ("Araxes plain") mentioned by Strabo.[4]
The ultimate etymology of the names Urartu, Ayrarat, and Ararat is not known for certain. In the Armenian tradition, Ayrarat and the Ararat plain are associated with the legendary Armenian king Ara the Handsome.[5]
The province is also referred to in Armenian sources as the Mijnashkharh Hayotsʻ ("central province of Armenia") or as the Glukh erkrin Hayotsʻ ("head province of Armenia").[6] During the Arsacid period, Ayrarat referred to, in its narrowest sense, the royal domain consisting of the Ararat plain and its adjacent districts.[7] The author of the seventh-century geography Ashkharhatsʻoytsʻ used the term Ayrarat to refer to a much larger territory.[2] The name Ayrarat gradually fell out of use after the fall of the Bagratid Kingdom of Armenia and the conquest of Armenia by the Seljuks in the eleventh century.[4]
Districts
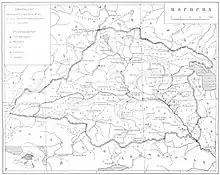
The seventh-century Ashkharhatsʻoytsʻ attributed to Anania Shirakatsi depicts Ayrarat as a very large province with 22 districts, but this is probably based on the new administrative divisions created after the Byzantine-Persian partition of Armenia in 591.[2]
See also
References
- 1 2 Hewsen 1992, p. 210.
- 1 2 3 4 Hewsen 1987.
- ↑ Hewsen 1992, pp. 210–211.
- 1 2 Hewsen 1992, p. 211.
- ↑ Petrosyan 2007, p. 26.
- ↑ Hakobyan, Melikʻ-Bakhshyan & Barseghyan 1986, p. 239.
- ↑ Eremyan 1963, p. 35.
Bibliography
- Eremyan, S. (1975). "Ayrarat". In Hambardzumyan, Viktor (ed.). Soviet Armenian Encyclopedia (in Armenian). Vol. 1. Erevan. pp. 352–353.
{{cite encyclopedia}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Eremyan, S. T. (1963). Hayastaně ěst Ashxarhatsʻoytsʻ-i [Armenia according to the Ashkharhatsʻoytsʻ] (in Armenian). Erevan: Armenian SSR Academy of Sciences Publishing.
- Hakobyan, Tʻ. Kh.; Melikʻ-Bakhshyan, St. T.; Barseghyan, H. Kh. (1986). "Ayrarat". Hayastani ev harakitsʻ shrjanneri teghanunneri baṛaran [Dictionary of toponymy of Armenia and adjacent territories] (in Armenian). Vol. 1. Yerevan State University. pp. 239–240.
- Hewsen, R. H. (1987). "AYRARAT". In Yarshater, Ehsan (ed.). Encyclopædia Iranica, Volume III/2: Awāʾel al-maqālāt–Azerbaijan IV. London and New York: Routledge & Kegan Paul. pp. 150–151. ISBN 978-0-71009-114-7.
- Hewsen, Robert H. (1992). The Geography of Ananias of Širak (Ašxarhacʻoycʻ): The Long and the Short Recensions. Wiesbaden: Dr. Ludwig Reichert Verlag. pp. 210–220. ISBN 3-88226-485-3.
- Petrosyan, Armen (2007). "The Problem of Identification of the Proto-Armenians: A Critical Review". Journal of the Society for Armenian Studies. 16: 25–66.
.svg.png.webp)