Methoxytoluenes (methylanisoles or cresyl methyl ethers) are a group of three isomeric organic compounds with the formula CH3OC6H4CH3. They consist of a disubstituted benzene ring with methoxy group and one methyl group. All three are colorless flammable liquids which are soluble in organic solvents but poorly soluble in water. They are not of major commercial interest although they are precursors to the corresponding methoxybenzoic acids and methoxybenzaldehydes.[1]
Chemical properties
| Methoxytoluene Isomers | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Common names | 2-Methoxytoluene 2-Methylanisole Ortho cresyl methyl ether |
3-Methoxytoluene 3-Methylanisole Meta cresyl methyl ether |
4-Methoxytoluene 4-Methylanisole Para cresyl methyl ether |
| Structure | 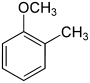 |
 |
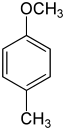 |
| PubChem number | [33637] | [7530] | [7731] |
| CAS number | [578-58-5] | [100-84-5] | [104-93-8] |
| Melting point | -34.1 °C (−31 °F; 238 K) | -47 °C (−52.6 °F; 226 K) | -23 °C (44.6 °F; 280 K) |
| Boiling point | 171 °C (318.2 °F; 432 K) | 175.5 °C (323.6 °F; 435 K) | 175.5 °C (323.6 °F; 435 K) |
| Density | 0.9798 g/cm3 | 0.9716 g/cm3 | 0.969 g/cm3 |
See also
- Phenetole, a structural isomer
References
- ↑ Yasutaka Ishii; Takahiro Iwahama; Satoshi Sakaguchi; Kouichi Nakayama; Yutaka Nishiyama (1996). "Alkane Oxidation with Molecular Oxygen Using a New Efficient Catalytic System: N-Hydroxyphthalimide (NHPI) Combined with Co(acac)n (n = 2 or 3)". J. Org. Chem. 61 (14): 4520–4526. doi:10.1021/jo951970l. PMID 11667375.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.