| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Presidential election | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Results by state | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
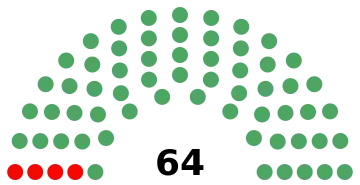
All 64 seats in the Senate of the Republic 33 seats needed for a majority | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This lists parties that won seats. See the complete results below. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 500 seats in the Chamber of Deputies 251 seats needed for a majority | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This lists parties that won seats. See the complete results below. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
|---|
|
|
General elections were held in Mexico on 6 July 1988.[1] They were the first competitive presidential elections in Mexico since the Institutional Revolutionary Party (PRI) took power in 1929. The elections were widely considered to have been fraudulent, with Salinas de Gortari and the PRI resorting to electoral tampering to remain in power.
Carlos Salinas de Gortari was declared the winner of the presidential election, with the Ministry of Interior saying he had received 50.7% of the vote. It was the lowest for a winning candidate since direct elections were introduced for the presidency in 1917; in all previous presidential elections, the PRI had faced no serious opposition and had won with percentages of votes well over 70%.[2] In the Chamber of Deputies election, the Institutional Revolutionary Party won 260 of the 500 seats,[3] as well as winning 60 of the 64 seats in the Senate election.[4]
Although early results of the parallel vote tabulation had indicated Cuauhtemoc Cárdenas was winning, when the official results were announced, Salinas was said to have won by a wide margin. All of the opposition candidates denounced that the elections had been rigged, and there were many protests throughout the country against the electoral fraud, including demonstrations by opposition lawmakers in the Congress. Salinas de Gortari, however, was able to take office on 1 December as President, after the PRI-dominated Congress declared that his election had been valid.[5]
Background



This was the first time that a parallel vote tabulation was implemented in Mexico, and the results were informed by telephone from the electoral districts to the secretariat of the Interior. The institution in charge of counting the votes was the Comisión Federal Electoral (CFE), presided by the Secretary of the Interior, Manuel Bartlett.
On 2 July, four days before the elections, Francisco Xavier Ovando, a top adviser of Cárdenas, was assassinated along with his assistant Román Gil in Mexico City. According to Cárdenas, Ovando had designed a network to obtain information from the 300 electoral districts on election day, to prevent an electoral fraud from the PRI. Two days later, FDN representatives protested the assassination in front of the Secretariat of the Interior. Manuel Bartlett promised that the government would immediately look into the crime, but many years passed before four agents of the Michoacán Police were charged with the assassination, with José Franco Villa (then attorney general of Michoacán) among the intellectual authors. The Governor of Michoacán at the time of the assassinations, Luis Martínez Villicaña, had been one of Cárdenas fiercest rivals, and had heavily repressed FDN officials and sympathizers in the State.[6][7]
Results
The first results arrived very slowly and inconsistently, but they showed that Cárdenas was in the lead.[8] The first official preliminary results were expected to arrive at 7 pm on election day, but once that time arrived, the CFE informed that the counting system had "broken down", and that the CFE president had scheduled a meeting with the Technical Secretariat to "correct the issue". In the meantime, the opposition candidates began to denounce that they had not been granted full access to the counting centers, and marched together to the headquarters of the Secretariat of the Interior to denounce irregularities in the elections. [9]
Later that day, the aforementioned Bartlett said that the telephone network was saturated due to, among other things, adverse weather conditions, characterizing it as a "breakdown of the system."[10] Then-president Miguel de la Madrid later admitted that this "breakdown" was a fabrication.[11] One observer said, "For the ordinary citizen, it was not the network but the Mexican political system that had crashed."[12]
Although the CFE itself stated that it was not able to proclaim a winner yet due to the aforementioned "Network breakdown" (and in fact, would not release results until a week later), on 7 July at 3:10 am the then-Secretary General of the PRI, Jorge de la Vega Domínguez, proclaimed that Salinas de Gortari had won by a great margin, stating that "Mexico has won and has given Carlos Salinas de Gortari a strong, legal and unobjectionable victory". Later that day, Salinas de Gortari himself also proclaimed that he had won.[9] This sparked immediate protests from the opposition, who denounced that a massive electoral fraud was taking place.
President
| Candidate | Party | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carlos Salinas de Gortari | Institutional Revolutionary Party | 9,687,926 | 50.71 | |
| Cuauhtémoc Cárdenas | National Democratic Front | 5,929,585 | 31.03 | |
| Manuel Clouthier | National Action Party | 3,208,584 | 16.79 | |
| Gumersindo Magaña Negrete | Mexican Democratic Party | 190,891 | 1.00 | |
| Rosario Ibarra | Workers' Revolutionary Party | 74,857 | 0.39 | |
| Non-registered candidates | 14,333 | 0.08 | ||
| Total | 19,106,176 | 100.00 | ||
| Valid votes | 19,106,176 | 96.49 | ||
| Invalid/blank votes | 695,042 | 3.51 | ||
| Total votes | 19,801,218 | 100.00 | ||
| Registered voters/turnout | 38,074,926 | 52.01 | ||
| Source: Becerra Chávez | ||||
Senate
 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party or alliance | Votes | % | Seats | +/– | |||
| Institutional Revolutionary Party | 9,263,810 | 50.83 | 60 | –3 | |||
| National Action Party | 3,293,460 | 18.07 | 0 | 0 | |||
| National Democratic Front | Party of the Cardenist Front of National Reconstruction | 1,727,376 | 9.48 | 0 | New | ||
| Popular Socialist Party | 1,702,203 | 9.34 | 0 | –1 | |||
| Authentic Party of the Mexican Revolution | 1,154,811 | 6.34 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Socialist Mexican Party | 770,659 | 4.23 | 4 | +4 | |||
| Mexican Democratic Party | 223,631 | 1.23 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Workers' Revolutionary Party | 76,135 | 0.42 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Non-registered and common candidates | 14,095 | 0.08 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Total | 18,226,180 | 100.00 | 64 | 0 | |||
| Valid votes | 18,226,180 | 96.35 | |||||
| Invalid/blank votes | 689,542 | 3.65 | |||||
| Total votes | 18,915,722 | 100.00 | |||||
| Registered voters/turnout | 38,074,926 | 49.68 | |||||
| Source: Becerra Chávez, Nohlen, Villalpando Rojas | |||||||
Chamber of Deputies
_1988.svg.png.webp) 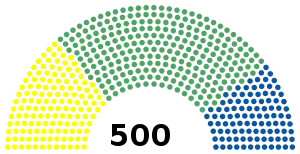 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party or alliance | Votes | % | Seats | +/– | |||
| Institutional Revolutionary Party | 9,276,934 | 50.97 | 260 | –32 | |||
| National Action Party | 3,276,824 | 18.00 | 101 | +63 | |||
| National Democratic Front | Party of the Cardenist Front of National Reconstruction | 1,704,532 | 9.37 | 36 | New | ||
| Popular Socialist Party | 1,673,863 | 9.20 | 49 | +38 | |||
| Authentic Party of the Mexican Revolution | 1,124,575 | 6.18 | 30 | +19 | |||
| Socialist Mexican Party | 810,372 | 4.45 | 24 | +6 | |||
| Mexican Democratic Party | 244,458 | 1.34 | 0 | –12 | |||
| Workers' Revolutionary Party | 88,637 | 0.49 | 0 | –6 | |||
| Total | 18,200,195 | 100.00 | 500 | +100 | |||
| Valid votes | 18,200,195 | 96.70 | |||||
| Invalid/blank votes | 620,220 | 3.30 | |||||
| Total votes | 18,820,415 | 100.00 | |||||
| Registered voters/turnout | 38,074,926 | 49.43 | |||||
| Source: Nohlen, Villalpando Rojas | |||||||
Analysis
Years later, the aforementioned Miguel de la Madrid admitted in an autobiography that the infamous "network breakdown" never happened, and that there was not yet any official vote count when the PRI declared Salinas as the winner. In 1991, the ruling PRI and the opposition PAN approved a motion to burn all the ballots, therefore removing all evidence of the fraud.[11] In 2011, PRI politician and contender for the PRI presidential candidacy in 1988 Ramón Aguirre Velázquez, stated that while he believed that Salinas de Gortari had indeed won, the real percentage of votes for him had been around 49%, which greatly alarmed the PRI since they had never obtained less than half of the votes in previous presidential elections they participated in since their foundation, and that the "network breakdown" was precisely an excuse Bartlett came up with to rig the election and to give Salinas enough votes to reach at least 50%.[13]
A 2019 study in the American Political Science Review found "evidence of blatant alterations" in approximately one third of the tallies in the election.[14]
Aftermath
Numerous protests were held throughout the country in the following days. Some of the many irregularities denounced by the opposition included duplicated Voter ID's, anticipated delivery of ballots with votes already marked for the PRI, and even votes from dead people.[9]
On 13 July, exactly one week after the election, the CFE finally released its official results, according to which Carlos Salinas de Gortari had won the election with 50.36% of the votes. Bartlett asked all the political parties to "accept the popular will". However, the nationwide protests continued.
On 1 September, in an unprecedented act, while president De la Madrid was giving his final Address to the Congress, he was interrupted by opposition legislators from the FDN, who protested against the fraud; meanwhile, the PAN legislators stood silent, holding ballots as proof of the fraud. Other legislators threw punches. This was a stark contrast with all previous Addresses to the Congress under the PRI regime, which until then had been little more than ceremonies dedicated to celebrate the President, who would receive unanimous praise from the chamber. Journalist Fidel Samaniego noted that on 1 September 1988 the old ritual of the Address to the Congress had died.[15] The opposition legislators noted that the Constitution established the right of interpellation in Congress.
On 9 September the Chamber of Deputies met to validate the elections. It was already expected that the Deputies would validate the election since the PRI held 263 out of its 500 seats, and thus the PRI legislators could validate the election by themselves even if the opposition unanimously voted against. After a 20-hour session in which the opposition legislators presented evidence of the fraud while the PRI members emphatically denied the accusations, the election results were validated: all 263 PRI legislators voted in favor, 85 opposition members voted against, and the rest abstained. The FDN legislators walked out during the voting. Thus, Salinas de Gortari was now officially President-elect.[16]
Of the five federal entities (the states of Baja California, Michoacán, Morelos, the State of Mexico and the Federal District) in which, according to the official results, Cárdenas had won, three of their State Governors (the Governor of Baja California Xicoténcatl Leyva Mortera, the Governor of Michoacán Luis Martínez Villicaña and the Governor of the State of Mexico Mario Ramón Beteta) were forced to resign in the following months by the PRI, which held them responsible for the party's defeat in those states.
See also
References
- ↑ Dieter Nohlen (2005) Elections in the Americas: A data handbook, Volume I, p453 ISBN 978-0-19-928357-6
- ↑ Nohlen, pp471-474
- ↑ Nohlen, p469
- ↑ Nohlen, p470
- ↑ Cantú, Francisco (2019). "The Fingerprints of Fraud: Evidence from Mexico's 1988 Presidential Election". American Political Science Review. 113 (3): 710–726. doi:10.1017/S0003055419000285. ISSN 0003-0554.
- ↑ Castro, Doralicia. "Son asesinados Xavier Ovando y su ayudante Román Gil, del equipo de campaña del candidato presidencial Cuauhtémoc Cárdenas". Memoria Política de México. Retrieved 5 July 2021.
- ↑ Caño, Antonio (4 July 1988). "Asesinado un colaborador de Cárdenas". El País. Retrieved 5 July 2021.
- ↑ Carmona, Doralicia. "Se "cae" el sistema que recibía los resultados de la votación de 54,641 casillas desde los distritos electorales". Memoria Política de México. Retrieved 19 April 2021.
- 1 2 3 Castro Sánchez, Aida. "El día en que "se cayó el sistema" y ganó Salinas". El Universal. Retrieved 19 April 2021.
- ↑ quoted in Enrique Krauze, Mexico: Biography of Power. New York: HarperCollins 1997, p. 770.
- 1 2 Ex-President in Mexico Casts New Light on Rigged 1988 Election New York Times, 9 March 2004
- ↑ Krauze, Mexico: Biography of Power, p. 770.
- ↑ Chavolla Alcalá, María Gisela. "Salinas me pidió declinar, yo obedecí: Ramón Aguirre". Zona Franca. Retrieved 19 April 2021.
- ↑ Cantú, Francisco (2019). "The Fingerprints of Fraud: Evidence from Mexico's 1988 Presidential Election". American Political Science Review. 113 (3): 710–726. doi:10.1017/S0003055419000285. ISSN 0003-0554.
- ↑ Samaniego, Fidel. "La interpelación de 1988 enterró el ritual envejecido". Retrieved 19 April 2021.
- ↑ "Salinas de Gortari, declarado presidente electo de México con los votos del PRI". El País. El País. Retrieved 19 April 2021.


