| Northern rufous mouse lemur | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Primates |
| Suborder: | Strepsirrhini |
| Family: | Cheirogaleidae |
| Genus: | Microcebus |
| Species: | M. tavaratra |
| Binomial name | |
| Microcebus tavaratra (Rasoloarison et al., 2000)[3] | |
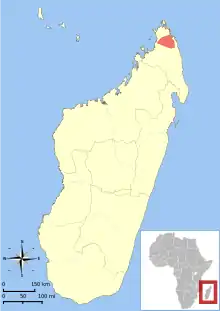 | |
| Distribution of M. tavaratra[1] | |
The northern rufous mouse lemur (Microcebus tavaratra), northern brown mouse lemur,[4] or Tavaratra mouse lemur[1] is found in northern Madagascar from the Ankarana Special Reserve in the west to the Manambato River in the northeast, and up to the Irodo River in the north of the Analamerana Special Reserve.[5] The complete distribution range of M. tavaratra is still to be defined as some areas surrounding the described distribution have not been visited yet. For example, M. tavaratra has been reported to possibly occur from the Irodo up to the Montagne des Français.[6] Its known distribution cover four protected areas – the Ankarana Special Reserve, and the Analamerana Special Reserve both managed by Madagascar National Parks,[7] the Loky-Manambato protected area (Daraina), and the Andavakoeira-Andrafiamena protected area, both Managed by the NGO Fanamby
Microcebus tavaratra has long, dense pelage that is bicolored to tricolored, raw umber, clay color, and yellow ochre, dorsally and a whitish-beige color ventrally. The middorsal stripe varies in color from raw umber to verona brown. The crown and ears of this species are a reddish shade and the area between the eyes is grayish-white. The orbital area is raw umber and cinnamon and around the anterior portion of the eyes there are black markings. The proximal part of the tail is bicolored raw umber and cinnamon, and the distal portion of the tail is cinnamon brown and raw umber. The pelage of the hands and feet of the northern rufous mouse lemur is whitish-gray in color. This species has vibrissae that are dark in color.
References
- 1 2 3 Sgarlata, G.M.; Le Pors, B.; Blanco, M.; Salmona, J.; Chikhi, L.; Louis, E.E.; Cotton, S.; Hending, D.; Dolch, R.; Ganzhorn, J.; Greene, L.K.; Lewis, R.; Rafalinirina, H.A.; Raharivololona, B.; Rakotoarisoa, G.; Ralison, J.; Randriahaingo, H.N.T.; Rasoloarison, R.M.; Razafindrasolo, M.; Wright, P.; Zaonarivelo, J. (2020). "Microcebus tavaratra". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2020: e.T41571A115579176. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-2.RLTS.T41571A115579176.en. Retrieved 19 November 2021.
- ↑ "Checklist of CITES Species". CITES. UNEP-WCMC. Retrieved 18 March 2015.
- ↑ Groves, C. P. (2005). Wilson, D. E.; Reeder, D. M. (eds.). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 113. ISBN 0-801-88221-4. OCLC 62265494.
- ↑ Mittermeier, R.; Ganzhorn, J.; Konstant, W.; Glander, K.; Tattersall, I.; Groves, C.; Rylands, A.; Hapke, A.; Ratsimbazafy, J.; Mayor, M.; Louis, E.; Rumpler, Y.; Schwitzer, C. & Rasoloarison, R. (December 2008). "Lemur Diversity in Madagascar". International Journal of Primatology. 29 (6): 1607–1656. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.888.2333. doi:10.1007/s10764-008-9317-y. hdl:10161/6237. S2CID 17614597.
- ↑ Weisrock DW, Rasoloarison RM, Fiorentino I, Ralison JM, Goodman SM, Kappeler PM, Yoder AD (2010) Delimiting species without nuclear monophyly in Madagascar’s mouse lemurs. PLoS One 5:e9883
- ↑ Schwitzer C, Mittermeier RA, Davies N, Johnson S, Ratsimbazafy J, Razafindramanana J, Louis Jr EE, Rajaobelina S (2013) Lemurs of Madagascar A Strategy for their Conservation 2013–2016. IUCN SSC Primate Specialist Group, Bristol Conservation and Science Foundation, and Conservation International, Bristol, UK
- ↑ "Madagascar National Parks". www.parcs-madagascar.com.
