Morgan Cyprian McMahon O'Brien (1886–1968) was born in New Zealand to Irish parents, and was an engineer and inventor with numerous patents particularly in the area of high-street and bank security, alarm systems, and ciphers. He moved to England in 1925, and patented an advanced cipher typewriter in 1928 which has been referred to as "Britain's Enigma",[1] and just before WW2 he patented the coding device known as the SYKO cipher device used throughout the war by the allied air forces, and to some extent by the allied navies too.
Early life
Morgan O'Brien was born in Auckland on September 25, 1886 to Charles O'Brien (proprietor of the Alpha Hotel, Kihikihi) and Elizabeth.[2] Charles was born 1855 in Youghal, County Cork, Ireland and died in 1922 in New Zealand. Although O'Brien finished high in the New Zealand civil service examinations in 1904 aged 17, by 1911 he had become a miner at the infamous Waihi mine in the Hauraki District. In 1914 O'Brien enlisted as a field artillery gunner in the main body of the New Zealand Expeditionary Force headed for Egypt and Gallipoli. He survived the war and was discharged in 1919 with rank of sergeant, however his brother Daniel died in hospital of wounds on 15 Nov 1918,[3] just days after the armistice.[4] Morgan's mother died in 1920,[5] and his father died in 1922,[6] all three are buried together in Hairini Catholic Cemetery near Te Awamutu. It was around this time Morgan married Vera Burmester, who was born in New Zealand in 1893, father John Alfred, mother Ada. In the early 1920s Morgan was designing security systems and applied for several British patents relating to shop and bank security. However, in 1925, he left with his wife for Sydney, and then via Vancouver and through Montreal to England (his father-in-law had been born in Canada).
Inventions
While living in Mount Eden, Auckland, New Zealand, Morgan issued several GB patents relating to security. GB231851, GB257509, GB257510 and GB259109 cover using pressure activated locking systems on safes and strong room doors, and the use of pressurised cavities to trigger alarms, and pressure system to protect cashiers from attack. GB293068 in 1927 is on a related theme, by which time Morgan was living in England, and had created a security company O'Brien Security Ltd, which is also named on the patent.
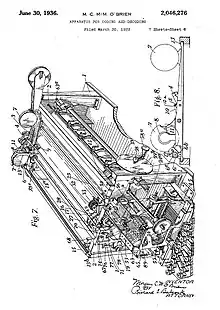
In April 1928, Morgan O'Brien applied for a patent "Improvement in or relating to Means or Apparatus for Encoding and De-Coding Messages" (GB320315,[7] US 2046276[8]). This was a remarkably complex typewriter style cipher device, and unlike anything that Morgan had patented before. It attracted the attention of official sources who funded the building of 3 machines for test – one for each of the armed services. There was also interest from America where the U.S. Navy's cipher expert, Lieutenant J.N. Wenger, said it created a "tremendously long and complex cipher". He had recently reviewed Enigma and could see that the O'Brien system offered vastly more "starting points" than Enigma.[1] W. Watson & Sons Ltd, a leading instrument maker, built the prototypes. The prototypes weren't complete until Autumn 1931, and there were teething troubles that revealed the machines to depend on "absolute accuracy of the timing, registering or meshing of certain parts". This let to problems with the prototypes, and in-spite of continued development and a further patent in 1935 (GB453660[9]), it appears to be this that ultimately led to the failure to secure orders, although there were some commercial difficulties also.
However, Morgan O'Brien was successful with a far simpler cipher device he had been working on. This he patented in 1939,[10][11] and it was rapidly adopted by the allied air forces, who named it the SYKO Cipher Device and used it extensively. It was also operated by the Navy using their own code cards. Although during the war the code was broken by the Germans, the code changed every day and took time and sufficient messages to break. For this reason it remained useful for information like aircraft to ground communication, where the information would no longer be useful by the time the code was broken. In 1942, they altered the code cards which used to be reciprocal codes, so that if A encoded as X, then X encoded as A. Instead they had separate sides of the code card for coding and decoding, which they called non-reciprocal codes. This significantly increased the security of the SYKO device, and it was still in use at the end of the war.
There were no further patents from Morgan O'Brien after the war. He lived to the age of 81, and died in 1968 in Biggleswade, Bedfordshire.
References
- 1 2 Intelligence and Strategy: Selected Essays, John Robert Ferris, Routledge, 2005, ISBN 0415361958, 9780415361958
- ↑ New Zealand, Civil Records Indexes, 1800-1966, Reg No 1886/14244
- ↑ Find a Grave, Hairini Catholic Cemetery Memorials, https://www.findagrave.com/memorial/197348338/dan-o'brien
- ↑ DigitalNZ, Archives New Zealand Te Rua Mahara o te Kawanatanga
- ↑ Find a Grave, Hairini Catholic Cemetery Memorials, https://www.findagrave.com/memorial/197347561/elizabeth-o'brien
- ↑ Find a Grave, Hairini Catholic Cemetery Memorials, https://www.findagrave.com/memorial/197347517/charles-o'brien
- ↑ Improvements in and relating to Means or Apparatus for Coding and De-coding Messages. GP Patent 320315, Application Date 4 April 1928
- ↑ Apparatus for coding and decoding, US Patent 2046276, Applied for March 30th 1929
- ↑ Improvements in or relating to Machines for Enciphering and Deciphering Messages, GB Patent 453660, Applied for 3 April 1935
- ↑ Cipher Apparatus, US Patent 2270137, Applied for 11 May 1939
- ↑ Improvements in or related to Enciphering and Deciphering Machines, GB534625, Applied for 3 July 1939