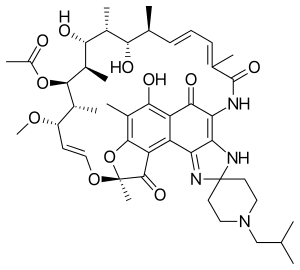
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Mycobutin[1] |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a693009 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth (capsules) |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 85% |
| Protein binding | 85% |
| Metabolism | liver |
| Elimination half-life | 28 to 62 hours (mean) |
| Excretion | kidney and fecal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.133.627 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C46H62N4O11 |
| Molar mass | 847.019 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Rifabutin (Rfb) is an antibiotic used to treat tuberculosis and prevent and treat Mycobacterium avium complex.[1] It is typically only used in those who cannot tolerate rifampin such as people with HIV/AIDS on antiretrovirals.[1] For active tuberculosis it is used with other antimycobacterial medications.[1] For latent tuberculosis it may be used by itself when the exposure was with drug-resistant TB.[1]
Common side effects include abdominal pain, nausea, rash, headache, and low blood neutrophil levels.[1] Other side effects include muscles pains and uveitis.,[1] especially when hitting Bartonella and Babesia colonies in the capillaries of the ciliary body in the eye anterior chamber. While no harms have been found during pregnancy it has not been well studied in this population.[1] Rifabutin is in the rifamycin family of medications.[1] It works by blocking RNA production in bacteria.[2]
Rifabutin was approved for medical use in the United States in 1992.[1] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[3]
Medical uses
Rifabutin is now recommended as first-line treatment for tuberculosis (TB),[4] but rifampicin was used more widely because of its cheaper cost. However, due to the expiration of patents, prices are now similar.
Rifabutin is also used in the treatment of Mycobacterium avium complex disease, a bacterial infection most commonly encountered in people with late-stage AIDS. Its has fewer drug interactions than rifampicin, therefore people with HIV/AIDS on HAART are typically prescribed rifabutin instead of rifampicin for the treatment of TB.
Rifabutin is well-tolerated in people with HIV-related TB, but new findings suggest that those with low CD4+ cell counts have a higher risk of treatment failure or relapse due to acquired rifamycin resistance. Since patients co-infected with TB and HIV are likely to be treated for TB first, when the CD4+ cell population is depressed at the time TB treatment begins, doctors and patients should be aware of the possibility for rifamycin resistance to develop.
Crohn's disease
Rifabutin is being tested in clinical trials for treating Crohn's disease as part of the anti-MAP therapy. In a Phase III study administering sub-therapeutic doses of rifabutin in combination therapy to patients not identified with Mycobacterium avium paratuberculosis (MAP) infections, it was associated with significant short term benefits.[5][6]
Others
Rifabutin is also being investigated for the treatment of infections caused by the Gram-negative bacillus Acinetobacter baumannii, which has shown promise in animal studies.[7]
Rifamycins, including rifabutin, are useful in the treatment of Chlamydophila pneumoniae (Cpn) infection.
History
Scientists at the Italian drug company Achifar discovered rifabutin in 1975. (Eventually Archifar became part of Farmitalia Carlo Erba, a unit of the conglomerate Montedison which was subsequently bought by Pharmacia) This company's Adria Laboratories subsidiary filed for Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval of rifabutin under the brand name Mycobutin in the early 1990s and the drug gained FDA approval in December 1992.
Rifabutin is primarily bactericidal antibiotic drug used to treat tuberculosis. Its effect on bacteria is based on the DNA-dependent RNA polymerase blocking drug rifamycin S, a semi-synthetic derivative. It is effective, for example, in highly resistant mycobacteria, Gram-positive bacteria (and some are effective against Gram-negative bacteria), but also against Mycobacterium tuberculosis, M. leprae, and M. avium intracellulare.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 "Rifabutin". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 20 December 2016. Retrieved 8 December 2016.
- ↑ Rockwood N, Cerrone M, Barber M, Hill AM, Pozniak AL (July 2019). "Global access of rifabutin for the treatment of tuberculosis - why should we prioritize this?". Journal of the International AIDS Society. 22 (7): e25333. doi:10.1002/jia2.25333. PMC 6637439. PMID 31318176.
Rifabutin is a rifamycin, which like rifampicin, works via inhibition of DNA‐dependent RNA synthesis in prokaryotes.
- ↑ World Health Organization (2019). World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 21st list 2019. Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/325771. WHO/MVP/EMP/IAU/2019.06. License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
- ↑ Guidelines for the programmatic management of drug-resistant tuberculosis: emergency update 2008 (WHO/HTM/TB/2008.402). Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization. 2008. p. ix. ISBN 978-92-4-154758-1. Archived from the original on 2008-10-18.
- ↑ Selby W, Pavli P, Crotty B, Florin T, Radford-Smith G, Gibson P, et al. (Antibiotics in Crohn's Disease Study Group) (June 2007). "Two-year combination antibiotic therapy with clarithromycin, rifabutin, and clofazimine for Crohn's disease". Gastroenterology. 132 (7): 2313–2319. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2007.03.031. PMID 17570206.
- ↑ Kuenstner JT (November 2007). "The Australian antibiotic trial in Crohn's disease: alternative conclusions from the same study". Gastroenterology. 133 (5): 1742–1743. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2007.09.012. PMID 17983824.
- ↑ Luna B, Trebosc V, Lee B, Bakowski M, Ulhaq A, Yan J, et al. (September 2020). "A nutrient-limited screen unmasks rifabutin hyperactivity for extensively drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii". Nature Microbiology. 5 (9): 1134–1143. doi:10.1038/s41564-020-0737-6. PMC 7483275. PMID 32514072. S2CID 219543106.
External links
- "Rifabutin". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.