
The Natural Color System (NCS) is a proprietary perceptual color model. It is based on the color opponency hypothesis of color vision, first proposed by German physiologist Ewald Hering.[1] The current version of the NCS was developed by the Swedish Colour Centre Foundation, from 1964 onwards. The research team consisted of Anders Hård, Lars Sivik and Gunnar Tonnquist, who in 1997 received the AIC Judd award for their work.[2][3] The system is based entirely on the phenomenology of human perception and not on color mixing. It is illustrated by a color atlas, marketed by NCS Colour AB in Stockholm.
Definition
The NCS states that there are six elementary color percepts of human vision—which might coincide with the psychological primaries—as proposed by the hypothesis of color opponency: white, black, red, yellow, green, and blue. The last four are also called unique hues. In the NCS all six are defined as elementary colors, irreducible qualia, each of which would be impossible to define in terms of the other elementary colors. All other experienced colors are considered composite perceptions, i.e. experiences that can be defined in terms of similarity to the six elementary colors. E.g. a saturated pink would be fully defined by its visual similarity to red, blue, black and white.[2]
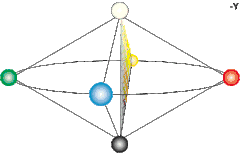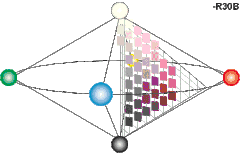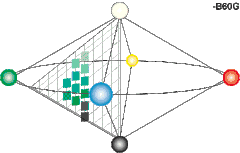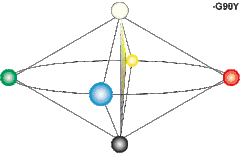
Colors in the NCS are defined by three values, expressed in percentages, specifying the degree of blackness (s , = relative visual similarity to the black elementary color), chromaticness (c, = relative visual similarity to the "strongest", most saturated, color in that hue triangle), and hue (Φ, = relative similarity to one or two of the chromatic elementary colors red, yellow, green and blue, expressed in at most two percentages). This means that a color can be expressed as either Y (yellow), YR (yellow with a red component), R (Red), RB (red with a blue component), B (blue), etc. No hue is considered to have visual similarity to both hues of an opponent pair; i.e. there is no "redgreen" or "yellowblue". The blackness and the chromaticness together add up to less than or equal to 100%. The remainder from 100%, if any, gives the amount of whiteness (w).[2] Achromatic colors, i.e. colors that lack chromatic contents (ranging from black, to grey and finally white), have their hue component replaced with a capital "N", for example "NCS S 9000-N" (a more or less complete black). NCS color notations are sometimes prepended by a capital "S", which denotes that the current version of the NCS color standard was used to specify the color.
In summary, the NCS color notation for S 2030-Y90R (light, pinkish red) is described as follows.
with
Saturation and lightness
In addition to the above values s (blackness), w (whiteness), c (chromaticness) and Φ (hue), the NCS system can also describe the two perceptual quantities saturation and lightness. NCS saturation (m) refers to a color's relation between its chromaticness and whiteness (regardless of hue), defined as the ratio between the chromaticness and the sum of its whiteness and chromaticness . The NCS saturation ranges between 0 and 1.
NCS lightness (v) is a color's perceptual characteristic to contain more of the achromatic elementary colors black or white than another color. NCS lightness values varies from 0 for the elementary color black (S) to 1 for the elementary color white (W). For achromatic colors, that is any black, gray or white with no chromatic component (c = 0), lightness is defined as
For chromatic colors, the NCS lightness is determined by comparing the chromatic color to a reference scale of achromatic colors (c = 0), and is determined to have the same lightness value v as the sample on the reference scale to which it has the least noticeable edge-to-edge difference.
Examples
Two examples of NCS color notation—the yellow and blue shades of the Swedish flag:[4]
- Yellow – NCS 0580-Y10R (nuance = 5% blackness, 80% chromaticness, hue = 90% yellow + 10% red. Strong, very slightly blackish yellow with a slight orangish tinge)
- Blue – NCS 4055-R95B (nuance = 40% blackness, 55% chromaticness, hue = 5% red + 95% blue. Somewhat dark, medium strong blue with a very slight purplish tinge)
The NCS is represented in nineteen countries and is the reference norm for color designation in Sweden (since 1979), Norway (since 1984), Spain (since 1994) and South Africa (since 2004). It is also one of the standards used by the International Colour Authority, a leading publisher of color trend forecasts for the interior design and textile markets.
NCS 1950 Standard Colors
In order to be able to manufacture physical representations of the NCS color space (such as color atlases), a reduced set of colors had to be selected that would illustrate the system well. Originally developed in 1979 as part of becoming the Swedish national color standard by the SIS (Swedish Standards Institute), the Natural Color System was described in an atlas containing 1412 colors. In 1984, an additional 118 colors were added for a total of 1530 colors. Eleven years later, in 1995, a second edition of the NCS Color Samples was released containing 1750 standard colors. In 2004, 200 more colors (184 light colors and 16 in the blue-green space) were added, resulting in the NCS 1950 standard colors. Colors that have a representation in the NCS 1950 samples are denoted with a leading capital "S", for example NCS S 1070-Y10R (a chromatic, slightly reddish yellow).
Comparisons to other color systems
The most important difference between NCS and most other color systems resides in their starting points. The aim of NCS is to define colors from their visual appearance, as they are experienced by human consciousness. Other color models, such as CMYK and RGB, are based on an understanding of physical processes, how colors can be achieved or "made" in different media.[5]
The underlying physiological mechanisms involved in color opponency include the bipolar and ganglion cells in the retina, which process the signal originated by the retinal cones before it is sent to the brain. Models like RGB are based on what happens at the lower, retinal cone level, and thus are fitted for presenting self-illuminated, dynamic images as done by TV sets and computer displays; see additive color. The NCS model, for its part, describes the organization of the color sensations as perceived at the upper, brain level, and thus is much better fitted than RGB to deal with how humans experience and describe their color sensations (hence the "natural" part of its name). More problematic is the relation with the CMYK-model which is generally seen as a correct prediction of the behavior of mixing pigments, as a system of subtractive color. The NCS coincides with the CMYK as regards the green-yellow-red segment of the color circle, but differs from it in seeing the saturated subtractive primary colors magenta and cyan as complex sensations of a "redblue" and a "greenblue" respectively and in seeing green, not as a secondary color mix of yellow and cyan, but as a unique hue. The NCS explains this by assuming that the behavior of paint is partly counterintuitive to human phenomenology. Observing that the mix of yellow and cyan paint results in a green color, would thus be at odds with the intuition of pure human perception which would be unable to account for such a "yellowblue".
Hering argued that yellow is not a "redgreen" but a unique hue. Colorimetrist Jan Koenderink, in a critique of Hering's system, considered it inconsistent not to apply the same argument to the other two subtractive primaries, cyan and magenta, and see them as unique hues as well, not a "greenblue" or a "redblue". He also pointed out the difficulty within a four color theory that the primaries would not be equally spaced in the color circle; and the problem that Hering does not account for the fact that cyan and magenta are brighter than green, blue and red, whereas this is, in his view, elegantly explained within the CMYK-model. He concluded that Hering's scheme fitted common language better than color experience.[6]
Overview of the six base colors in Natural Color System with their equivalent in hex triplet, RGB and HSV coordinates systems. However, note that these codes are only approximate, as the definition of NCS elementaries is based on perception and not production of color.
See also
- Color chart, other color systems and charts
References
- ↑ Hering, Ewald (1964) [1878, Zur Lehre vom Lichtsinne, Wien]. Hurvich, L.M.; Jameson, D. (eds.). Outlines of a Theory of the light sense. Cambridge Mass.: Harvard University Press.
- 1 2 3 Hård, A.; Sivik, L.; Tonnquist, G. (1996). "NCS Natural Color System - from Concepts to Research and Applications. Part I and II". Color Research and Application. 21: 180–220. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1520-6378(199606)21:3<180::AID-COL2>3.0.CO;2-O.
- ↑ "International Colour Association".
- ↑ "Swedish legal regulation on flag colour". 2016-03-29.
- ↑ Green-Armytage, Paul (2006). "The Value of Knowledge for Color Design". Color Research and Application. 31 (31:4): 253–269. doi:10.1002/col.20222.
- ↑ Jan J. Koenderink, 2010, Color for the Sciences, The MIT Press, pp. 579–582
External links
NCS Colour – Universal Language for Colour Communication – official site
