| Two Ocean Pass | |
|---|---|
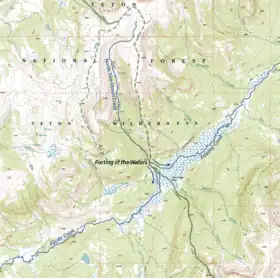 Modified portion of the USGS Two Ocean Pass Quadrangle[1] | |
| Elevation | 8,130 ft (2,478 m)[2] |
| Traversed by | North Two Ocean Creek |
| Location | Teton County, Wyoming |
| Range | Absaroka Range |
| Coordinates | 44°02′33″N 110°10′30″W / 44.04250°N 110.17500°W |
| Topo map | USGS Two Ocean Pass |
| Designated | October 1965 |
Two Ocean Pass is a mountain pass on North America's Continental Divide, in the Teton Wilderness, which is part of Wyoming's Bridger-Teton National Forest. The pass is notable for Parting of the Waters, where one stream, North Two Ocean Creek, splits into two distributaries, Pacific Creek and Atlantic Creek, at Parting of the Waters National Natural Landmark. These two creeks ultimately flow into their respective oceans.[3] Atlantic Creek water eventually flows into the Yellowstone River and empties into the Gulf of Mexico via the Missouri River and Mississippi River. Pacific Creek water eventually flows into the Snake River and empties into the Pacific via the Columbia River.
Recreation
The Continental Divide Trail reaches this location in northern Wyoming. It is accessible by foot or horseback from the south via Brooks Lake Trail head off of Highway 287 or from the north via an extensive hike from Fox Park near Yellowstone National Park's southern border.[4]
Fish dispersal
The pass is thought to have provided access for the Yellowstone cutthroat trout to have colonized Yellowstone Lake and the rest of the Yellowstone River watershed above Lower Falls.[5] Similarly, it has been considered as an alternative explanation for the arrival of non-native lake trout in Yellowstone Lake, which has traditionally been attributed to illegal or accidental stocking.[6]
Climate
Two Ocean Plateau has a subarctic climate (Köppen Dfc).
| Climate data for Two Ocean Plateau, Wyoming, 1991–2020 normals: 9240ft (2816m) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °F (°C) | 24.8 (−4.0) |
28.7 (−1.8) |
36.4 (2.4) |
42.7 (5.9) |
51.1 (10.6) |
58.1 (14.5) |
66.9 (19.4) |
65.8 (18.8) |
56.4 (13.6) |
43.1 (6.2) |
30.1 (−1.1) |
22.3 (−5.4) |
43.9 (6.6) |
| Daily mean °F (°C) | 16.1 (−8.8) |
17.8 (−7.9) |
24.2 (−4.3) |
30.0 (−1.1) |
39.0 (3.9) |
45.9 (7.7) |
53.8 (12.1) |
52.9 (11.6) |
44.8 (7.1) |
33.1 (0.6) |
21.3 (−5.9) |
14.3 (−9.8) |
32.8 (0.4) |
| Mean daily minimum °F (°C) | 7.3 (−13.7) |
6.8 (−14.0) |
11.9 (−11.2) |
17.4 (−8.1) |
26.8 (−2.9) |
33.6 (0.9) |
40.7 (4.8) |
39.9 (4.4) |
33.0 (0.6) |
23.0 (−5.0) |
12.5 (−10.8) |
6.3 (−14.3) |
21.6 (−5.8) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 4.65 (118) |
4.28 (109) |
4.71 (120) |
4.33 (110) |
3.77 (96) |
3.23 (82) |
1.41 (36) |
1.57 (40) |
2.21 (56) |
3.33 (85) |
4.51 (115) |
5.02 (128) |
43.02 (1,095) |
| Source 1: XMACIS2[7] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: NOAA (Precipitation)[8] | |||||||||||||
Gallery
 A drawing made in 1894 of Two Ocean Pass with a view to the northeast.[9] Atlantic Creek exits the pass between the hills in the upper center part of the image. Pacific Creek exits to the southwest in the bottom center of the image. North Two Oceans Creek enters from the left top center of the image and divides into its two distributaries and South Two Ocean Creek enters from the right center of the image and is also shown dividing into two streams. Evermann Creek also enters the area from the west (left center, just above the tents).
A drawing made in 1894 of Two Ocean Pass with a view to the northeast.[9] Atlantic Creek exits the pass between the hills in the upper center part of the image. Pacific Creek exits to the southwest in the bottom center of the image. North Two Oceans Creek enters from the left top center of the image and divides into its two distributaries and South Two Ocean Creek enters from the right center of the image and is also shown dividing into two streams. Evermann Creek also enters the area from the west (left center, just above the tents). Here Two Ocean Creek splits in two directions on the Continental Divide. Water on the left in this 2011 photo goes to the Atlantic and water on the right to the Pacific Ocean.
Here Two Ocean Creek splits in two directions on the Continental Divide. Water on the left in this 2011 photo goes to the Atlantic and water on the right to the Pacific Ocean.
References
- ↑ Two Ocean Pass Quadrangle, Wyoming-Teton Co. USGS Topographic Quadrangle, 1996: Note the 1996 quad does not show a split in the continental divide; however both the 1959 Two Ocean Pass, Wyoming 15 minute quadrangle and the 1982 Yellowstone National Park South, Wyo. 30x60 minute quad do show a split in the continental divide which includes the drainage basins of both North Two Ocean Creek and South Two Ocean Creek. The divide split is 8.7 kilometres (5.4 mi) in length.
- ↑ "Two Ocean Pass". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior. Retrieved February 19, 2011.
- ↑ Two Ocean Pass, National Natural Landmarks
- ↑ Davis, Lora (2000). Wyoming's Continental Divide Trail. Westcliffe Publishers, Inc. pp. 242–249. ISBN 1-56579-332-3.
- ↑ Carlson, Annie. "Two Ocean Pass—A place where fish can swim over the Continental Divide!". usgs.gov. Retrieved March 22, 2022.
- ↑ Koel, Todd M.; Detjens, Colleen R.; Zale, Alexander V. (2020). "Two Ocean Pass: An alternative hypothesis for the invasion of Yellowstone Lake by lake trout, and implications for future invasions". Water. 12 (6): 1629. doi:10.3390/w12061629.
- ↑ "xmACIS2". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved October 14, 2023.
- ↑ "Two Ocean Plateau, Wyoming 1991-2020 Monthly Normals". Retrieved October 14, 2023.
- ↑ Barton Warren Evermann: Two-Ocean Pass. In: Popular Science Monthly. V. 47, 1895, pp. 175–186
External links
- Two Ocean Pass National Natural Landmark, National Park Service website.
- U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: Two Ocean Pass