| Nuclear physics |
|---|
 |
|
Nuclear fission products are the atomic fragments left after a large atomic nucleus undergoes nuclear fission. Typically, a large nucleus like that of uranium fissions by splitting into two smaller nuclei, along with a few neutrons, the release of heat energy (kinetic energy of the nuclei), and gamma rays. The two smaller nuclei are the fission products. (See also Fission products (by element)).
About 0.2% to 0.4% of fissions are ternary fissions, producing a third light nucleus such as helium-4 (90%) or tritium (7%).
The fission products themselves are usually unstable and therefore radioactive. Due to being relatively neutron-rich for their atomic number, many of them quickly undergo beta decay. This releases additional energy in the form of beta particles, antineutrinos, and gamma rays. Thus, fission events normally result in beta and additional gamma radiation that begins immediately after, even though this radiation is not produced directly by the fission event itself.
The produced radionuclides have varying half-lives, and therefore vary in radioactivity. For instance, strontium-89 and strontium-90 are produced in similar quantities in fission, and each nucleus decays by beta emission. But 90Sr has a 30-year half-life, and 89Sr a 50.5-day half-life. Thus in the 50.5 days it takes half the 89Sr atoms to decay, emitting the same number of beta particles as there were decays, less than 0.4% of the 90Sr atoms have decayed, emitting only 0.4% of the betas. The radioactive emission rate is highest for the shortest lived radionuclides, although they also decay the fastest. Additionally, less stable fission products are less likely to decay to stable nuclides, instead decaying to other radionuclides, which undergo further decay and radiation emission, adding to the radiation output. It is these short lived fission products that are the immediate hazard of spent fuel, and the energy output of the radiation also generates significant heat which must be considered when storing spent fuel. As there are hundreds of different radionuclides created, the initial radioactivity level fades quickly as short lived radionuclides decay, but never ceases completely as longer lived radionuclides make up more and more of the remaining unstable atoms.[1] In fact the short lived products are so predominant that 87 percent decay to stable isotopes within the first month after removal from the reactor core.[2]
Formation and decay
The sum of the atomic mass of the two atoms produced by the fission of one fissile atom is always less than the atomic mass of the original atom. This is because some of the mass is lost as free neutrons, and once kinetic energy of the fission products has been removed (i.e., the products have been cooled to extract the heat provided by the reaction), then the mass associated with this energy is lost to the system also, and thus appears to be "missing" from the cooled fission products.
Since the nuclei that can readily undergo fission are particularly neutron-rich (e.g. 61% of the nucleons in uranium-235 are neutrons), the initial fission products are often more neutron-rich than stable nuclei of the same mass as the fission product (e.g. stable zirconium-90 is 56% neutrons compared to unstable strontium-90 at 58%). The initial fission products therefore may be unstable and typically undergo beta decay to move towards a stable configuration, converting a neutron to a proton with each beta emission. (Fission products do not decay via alpha decay.)
A few neutron-rich and short-lived initial fission products decay by ordinary beta decay (this is the source of perceptible half life, typically a few tenths of a second to a few seconds), followed by immediate emission of a neutron by the excited daughter-product. This process is the source of so-called delayed neutrons, which play an important role in control of a nuclear reactor.
The first beta decays are rapid and may release high energy beta particles or gamma radiation. However, as the fission products approach stable nuclear conditions, the last one or two decays may have a long half-life and release less energy.
Radioactivity over time
Fission products have half-lives of 90 years (samarium-151) or less, except for seven long-lived fission products that have half lives of 211,100 years (technetium-99) or more. Therefore, the total radioactivity of a mixture of pure fission products decreases rapidly for the first several hundred years (controlled by the short-lived products) before stabilizing at a low level that changes little for hundreds of thousands of years (controlled by the seven long-lived products).
This behavior of pure fission products with actinides removed, contrasts with the decay of fuel that still contains actinides. This fuel is produced in the so-called "open" (i.e., no nuclear reprocessing) nuclear fuel cycle. A number of these actinides have half lives in the missing range of about 100 to 200,000 years, causing some difficulty with storage plans in this time-range for open cycle non-reprocessed fuels.
Proponents of nuclear fuel cycles which aim to consume all their actinides by fission, such as the Integral Fast Reactor and molten salt reactor, use this fact to claim that within 200 years, their fuel wastes are no more radioactive than the original uranium ore.[3]
Fission products emit beta radiation, while actinides primarily emit alpha radiation. Many of each also emit gamma radiation.
Yield

Each fission of a parent atom produces a different set of fission product atoms. However, while an individual fission is not predictable, the fission products are statistically predictable. The amount of any particular isotope produced per fission is called its yield, typically expressed as percent per parent fission; therefore, yields total to 200%, not 100%. (The true total is in fact slightly greater than 200%, owing to rare cases of ternary fission.)
While fission products include every element from zinc through the lanthanides, the majority of the fission products occur in two peaks. One peak occurs at about (expressed by atomic numbers 85 through 105) strontium to ruthenium while the other peak is at about tellurium to neodymium (expressed by atomic numbers 130 through 145). The yield is somewhat dependent on the parent atom and also on the energy of the initiating neutron.
In general the higher the energy of the state that undergoes nuclear fission, the more likely that the two fission products have similar mass. Hence, as the neutron energy increases and/or the energy of the fissile atom increases, the valley between the two peaks becomes more shallow.[4] For instance, the curve of yield against mass for 239Pu has a more shallow valley than that observed for 235U when the neutrons are thermal neutrons. The curves for the fission of the later actinides tend to make even more shallow valleys. In extreme cases such as 259Fm, only one peak is seen; this is a consequence of symmetric fission becoming dominant due to shell effects.[5]
The adjacent figure shows a typical fission product distribution from the fission of uranium. Note that in the calculations used to make this graph, the activation of fission products was ignored and the fission was assumed to occur in a single moment rather than a length of time. In this bar chart results are shown for different cooling times (time after fission). Because of the stability of nuclei with even numbers of protons and/or neutrons, the curve of yield against element is not a smooth curve but tends to alternate. Note that the curve against mass number is smooth.[6]
Production
Small amounts of fission products are naturally formed as the result of either spontaneous fission of natural uranium, which occurs at a low rate, or as a result of neutrons from radioactive decay or reactions with cosmic ray particles. The microscopic tracks left by these fission products in some natural minerals (mainly apatite and zircon) are used in fission track dating to provide the cooling (crystallization) ages of natural rocks. The technique has an effective dating range of 0.1 Ma to >1.0 Ga depending on the mineral used and the concentration of uranium in that mineral.
About 1.5 billion years ago in a uranium ore body in Africa, a natural nuclear fission reactor operated for a few hundred thousand years and produced approximately 5 tonnes of fission products. These fission products were important in providing proof that the natural reactor had occurred. Fission products are produced in nuclear weapon explosions, with the amount depending on the type of weapon. The largest source of fission products is from nuclear reactors. In current nuclear power reactors, about 3% of the uranium in the fuel is converted into fission products as a by-product of energy generation. Most of these fission products remain in the fuel unless there is fuel element failure or a nuclear accident, or the fuel is reprocessed.
Power reactors
Commercial nuclear fission reactors are operated in the otherwise self-extinguishing prompt subcritical state. Certain fission products decay over seconds to minutes, producing additional delayed neutrons crucial to sustaining criticality.[7] [8] An example is bromine-87 with a half-life of about a minute.[9] Operating in this delayed critical state, power changes slowly enough to permit human and automatic control. Analogous to fire dampers varying the movement of wood embers towards new fuel, control rods are moved as the nuclear fuel burns up over time.[10] [11] [12][13]
In a nuclear power reactor, the main sources of radioactivity are fission products along with actinides and activation products. Fission products are most of the radioactivity for the first several hundred years, while actinides dominate roughly 103 to 105 years after fuel use.
Most fission products are retained near their points of production. They are important to reactor operation not only because some contribute delayed neutrons useful for reactor control, but some are neutron poisons that inhibit the nuclear reaction. Buildup of neutron poisons is a key to how long a given fuel element can be kept in the reactor. Fission product decay also generates heat that continues even after the reactor has been shut down and fission stopped. This decay heat requires removal after shutdown; loss of this cooling damaged the reactors at Three Mile Island and Fukushima.
If the fuel cladding around the fuel develops holes, fission products can leak into the primary coolant. Depending on the chemistry, they may settle within the reactor core or travel through the coolant system and chemistry control systems are provided to remove them. In a well-designed power reactor running under normal conditions, coolant radioactivity is very low.
The isotope responsible for most of the gamma exposure in fuel reprocessing plants (and the Chernobyl site in 2005) is caesium-137. Iodine-129 is a major radioactive isotope released from reprocessing plants. In nuclear reactors both caesium-137 and strontium-90 are found in locations away from the fuel because they're formed by the beta decay of noble gases (xenon-137, with a 3.8-minute half-life, and krypton-90, with a 32-second half-life) which enable them to be deposited away from the fuel, e.g. on control rods.
Nuclear reactor poisons
Some fission products decay with the release of delayed neutrons, important to nuclear reactor control.
Other fission products, such as xenon-135 and samarium-149, have a high neutron absorption cross section. Since a nuclear reactor must balance neutron production and absorption rates, fission products that absorb neutrons tend to "poison" or shut the reactor down; this is controlled with burnable poisons and control rods. Build-up of xenon-135 during shutdown or low-power operation may poison the reactor enough to impede restart or interfere with normal control of the reaction during restart or restoration of full power. This played a major role in the Chernobyl disaster.
Nuclear weapons
Nuclear weapons use fission as either the partial or the main energy source. Depending on the weapon design and where it is exploded, the relative importance of the fission product radioactivity will vary compared to the activation product radioactivity in the total fallout radioactivity.
The immediate fission products from nuclear weapon fission are essentially the same as those from any other fission source, depending slightly on the particular nuclide that is fissioning. However, the very short time scale for the reaction makes a difference in the particular mix of isotopes produced from an atomic bomb.
For example, the 134Cs/137Cs ratio provides an easy method of distinguishing between fallout from a bomb and the fission products from a power reactor. Almost no caesium-134 is formed by nuclear fission (because xenon-134 is stable). The 134Cs is formed by the neutron activation of the stable 133Cs which is formed by the decay of isotopes in the isobar (A = 133). So in a momentary criticality, by the time that the neutron flux becomes zero too little time will have passed for any 133Cs to be present. While in a power reactor plenty of time exists for the decay of the isotopes in the isobar to form 133Cs, the 133Cs thus formed can then be activated to form 134Cs only if the time between the start and the end of the criticality is long.
According to Jiri Hala's textbook,[14] the radioactivity in the fission product mixture in an atom bomb is mostly caused by short-lived isotopes such as iodine-131 and barium-140. After about four months, cerium-141, zirconium-95/niobium-95, and strontium-89 represent the largest share of radioactive material. After two to three years, cerium-144/praseodymium-144, ruthenium-106/rhodium-106, and promethium-147 are responsible for the bulk of the radioactivity. After a few years, the radiation is dominated by strontium-90 and caesium-137, whereas in the period between 10,000 and a million years it is technetium-99 that dominates.
Application
Some fission products (such as 137Cs) are used in medical and industrial radioactive sources. 99TcO4− (pertechnetate) ion can react with steel surfaces to form a corrosion resistant layer. In this way these metaloxo anions act as anodic corrosion inhibitors - it renders the steel surface passive. The formation of 99TcO2 on steel surfaces is one effect which will retard the release of 99Tc from nuclear waste drums and nuclear equipment which has become lost prior to decontamination (e.g. nuclear submarine reactors which have been lost at sea).
In a similar way the release of radio-iodine in a serious power reactor accident could be retarded by adsorption on metal surfaces within the nuclear plant.[15] Much of the other work on the iodine chemistry which would occur during a bad accident has been done.[16]
Decay

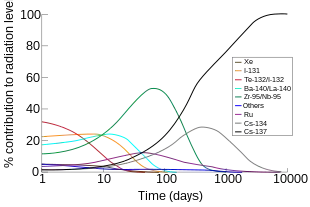
For fission of uranium-235, the predominant radioactive fission products include isotopes of iodine, caesium, strontium, xenon and barium. The threat becomes smaller with the passage of time. Locations where radiation fields once posed immediate mortal threats, such as much of the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant on day one of the accident and the ground zero sites of U.S. atomic bombings in Japan (6 hours after detonation) are now relatively safe because the radioactivity has decreased to a low level. Many of the fission products decay through very short-lived isotopes to form stable isotopes, but a considerable number of the radioisotopes have half-lives longer than a day.
The radioactivity in the fission product mixture is initially mostly caused by short lived isotopes such as 131I and 140Ba; after about four months 141Ce, 95Zr/95Nb and 89Sr take the largest share, while after about two or three years the largest share is taken by 144Ce/144Pr, 106Ru/106Rh and 147Pm. Later 90Sr and 137Cs are the main radioisotopes, being succeeded by 99Tc. In the case of a release of radioactivity from a power reactor or used fuel, only some elements are released; as a result, the isotopic signature of the radioactivity is very different from an open air nuclear detonation, where all the fission products are dispersed.
Fallout countermeasures
| Part of a series on |
| Pollution |
|---|
 |
The purpose of radiological emergency preparedness is to protect people from the effects of radiation exposure after a nuclear accident or bomb. Evacuation is the most effective protective measure. However, if evacuation is impossible or even uncertain, then local fallout shelters and other measures provide the best protection.[18]
Iodine
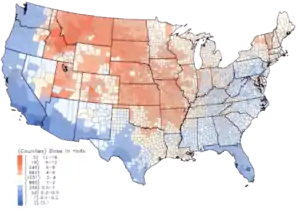
At least three isotopes of iodine are important. 129I, 131I (radioiodine) and 132I. Open air nuclear testing and the Chernobyl disaster both released iodine-131.
The short-lived isotopes of iodine are particularly harmful because the thyroid collects and concentrates iodide – radioactive as well as stable. Absorption of radioiodine can lead to acute, chronic, and delayed effects. Acute effects from high doses include thyroiditis, while chronic and delayed effects include hypothyroidism, thyroid nodules, and thyroid cancer. It has been shown that the active iodine released from Chernobyl and Mayak[19] has resulted in an increase in the incidence of thyroid cancer in the former Soviet Union.
One measure which protects against the risk from radio-iodine is taking a dose of potassium iodide (KI) before exposure to radioiodine. The non-radioactive iodide "saturates" the thyroid, causing less of the radioiodine to be stored in the body. Administering potassium iodide reduces the effects of radio-iodine by 99% and is a prudent, inexpensive supplement to fallout shelters. A low-cost alternative to commercially available iodine pills is a saturated solution of potassium iodide. Long-term storage of KI is normally in the form of reagent-grade crystals.[20]
The administration of known goitrogen substances can also be used as a prophylaxis in reducing the bio-uptake of iodine, (whether it be the nutritional non-radioactive iodine-127 or radioactive iodine, radioiodine - most commonly iodine-131, as the body cannot discern between different iodine isotopes). Perchlorate ions, a common water contaminant in the USA due to the aerospace industry, has been shown to reduce iodine uptake and thus is classified as a goitrogen. Perchlorate ions are a competitive inhibitor of the process by which iodide is actively deposited into thyroid follicular cells. Studies involving healthy adult volunteers determined that at levels above 0.007 milligrams per kilogram per day (mg/(kg·d)), perchlorate begins to temporarily inhibit the thyroid gland's ability to absorb iodine from the bloodstream ("iodide uptake inhibition", thus perchlorate is a known goitrogen).[21] The reduction of the iodide pool by perchlorate has dual effects – reduction of excess hormone synthesis and hyperthyroidism, on the one hand, and reduction of thyroid inhibitor synthesis and hypothyroidism on the other. Perchlorate remains very useful as a single dose application in tests measuring the discharge of radioiodide accumulated in the thyroid as a result of many different disruptions in the further metabolism of iodide in the thyroid gland.[22]
Treatment of thyrotoxicosis (including Graves' disease) with 600-2,000 mg potassium perchlorate (430-1,400 mg perchlorate) daily for periods of several months or longer was once common practice, particularly in Europe,[21][23] and perchlorate use at lower doses to treat thyroid problems continues to this day.[24] Although 400 mg of potassium perchlorate divided into four or five daily doses was used initially and found effective, higher doses were introduced when 400 mg/day was discovered not to control thyrotoxicosis in all subjects.[21][22]
Current regimens for treatment of thyrotoxicosis (including Graves' disease), when a patient is exposed to additional sources of iodine, commonly include 500 mg potassium perchlorate twice per day for 18–40 days.[21][25]
Prophylaxis with perchlorate-containing water at concentrations of 17 ppm, which corresponds to 0.5 mg/kg-day personal intake, if one is 70 kg and consumes 2 litres of water per day, was found to reduce baseline radioiodine uptake by 67%[21] This is equivalent to ingesting a total of just 35 mg of perchlorate ions per day. In another related study where subjects drank just 1 litre of perchlorate-containing water per day at a concentration of 10 ppm, i.e. daily 10 mg of perchlorate ions were ingested, an average 38% reduction in the uptake of iodine was observed.[26]
However, when the average perchlorate absorption in perchlorate plant workers subjected to the highest exposure has been estimated as approximately 0.5 mg/kg-day, as in the above paragraph, a 67% reduction of iodine uptake would be expected. Studies of chronically exposed workers though have thus far failed to detect any abnormalities of thyroid function, including the uptake of iodine.[27] this may well be attributable to sufficient daily exposure or intake of healthy iodine-127 among the workers and the short 8 hr biological half life of perchlorate in the body.[21]
To completely block the uptake of iodine-131 by the purposeful addition of perchlorate ions to a populace's water supply, aiming at dosages of 0.5 mg/kg-day, or a water concentration of 17 ppm, would therefore be grossly inadequate at truly reducing radioiodine uptake. Perchlorate ion concentrations in a region's water supply would need to be much higher, at least 7.15 mg/kg of body weight per day, or a water concentration of 250 ppm, assuming people drink 2 liters of water per day, to be truly beneficial to the population at preventing bioaccumulation when exposed to a radioiodine environment,[21][25] independent of the availability of iodate or iodide drugs.
The continual distribution of perchlorate tablets or the addition of perchlorate to the water supply would need to continue for no less than 80–90 days, beginning immediately after the initial release of radioiodine was detected. After 80–90 days passed, released radioactive iodine-131 would have decayed to less than 0.1% of its initial quantity, at which time the danger from biouptake of iodine-131 is essentially over.[28]
In the event of a radioiodine release, the ingestion of prophylaxis potassium iodide, if available, or even iodate, would rightly take precedence over perchlorate administration, and would be the first line of defense in protecting the population from a radioiodine release. However, in the event of a radioiodine release too massive and widespread to be controlled by the limited stock of iodide and iodate prophylaxis drugs, then the addition of perchlorate ions to the water supply, or distribution of perchlorate tablets would serve as a cheap, efficacious, second line of defense against carcinogenic radioiodine bioaccumulation.
The ingestion of goitrogen drugs is, much like potassium iodide also not without its dangers, such as hypothyroidism. In all these cases however, despite the risks, the prophylaxis benefits of intervention with iodide, iodate, or perchlorate outweigh the serious cancer risk from radioiodine bioaccumulation in regions where radioiodine has sufficiently contaminated the environment.
Caesium
The Chernobyl accident released a large amount of caesium isotopes which were dispersed over a wide area. 137Cs is an isotope which is of long-term concern as it remains in the top layers of soil. Plants with shallow root systems tend to absorb it for many years. Hence grass and mushrooms can carry a considerable amount of 137Cs, which can be transferred to humans through the food chain.
One of the best countermeasures in dairy farming against 137Cs is to mix up the soil by deeply ploughing the soil. This has the effect of putting the 137Cs out of reach of the shallow roots of the grass, hence the level of radioactivity in the grass will be lowered. Also the removal of top few centimeters of soil and its burial in a shallow trench will reduce the dose to humans and animals as the gamma rays from 137Cs will be attenuated by their passage through the soil. The deeper and more remote the trench is, the better the degree of protection. Fertilizers containing potassium can be used to dilute cesium and limit its uptake by plants.
In livestock farming, another countermeasure against 137Cs is to feed to animals prussian blue. This compound acts as an ion-exchanger. The cyanide is so tightly bonded to the iron that it is safe for a human to consume several grams of prussian blue per day. The prussian blue reduces the biological half-life (different from the nuclear half-life) of the caesium. The physical or nuclear half-life of 137Cs is about 30 years. Caesium in humans normally has a biological half-life of between one and four months. An added advantage of the prussian blue is that the caesium which is stripped from the animal in the droppings is in a form which is not available to plants. Hence it prevents the caesium from being recycled. The form of prussian blue required for the treatment of animals, including humans is a special grade. Attempts to use the pigment grade used in paints have not been successful.[29]
Strontium
The addition of lime to soils which are poor in calcium can reduce the uptake of strontium by plants. Likewise in areas where the soil is low in potassium, the addition of a potassium fertilizer can discourage the uptake of cesium into plants. However such treatments with either lime or potash should not be undertaken lightly as they can alter the soil chemistry greatly, so resulting in a change in the plant ecology of the land.[30]
Health concerns
For introduction of radionuclides into organism, ingestion is the most important route. Insoluble compounds are not absorbed from the gut and cause only local irradiation before they are excreted. Soluble forms however show wide range of absorption percentages.[31]
| Isotope | Radiation | Half-life | GI absorption |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strontium-90/yttrium-90 | β | 28 years | 30% |
| Caesium-137 | β, γ | 30 years | 100% |
| Promethium-147 | β | 2.6 years | 0.01% |
| Cerium-144 | β, γ | 285 days | 0.01% |
| Ruthenium-106/rhodium-106 | β, γ | 1.0 years | 0.03% |
| Zirconium-95 | β, γ | 65 days | 0.01% |
| Strontium-89 | β | 51 days | 30% |
| Ruthenium-103 | β, γ | 39.7 days | 0.03% |
| Niobium-95 | β, γ | 35 days | 0.01% |
| Cerium-141 | β, γ | 33 days | 0.01% |
| Barium-140/lanthanum-140 | β, γ | 12.8 days | 5% |
| Iodine-131 | β, γ | 8.05 days | 100% |
| Tritium | β | 12.3 years | 100%[lower-alpha 1] |
See also
Notes
- ↑ Tritiated water can also be absorbed through skin. Note that the effective half life (the combination of the biological half life and decay half life) is relatively short: approx. 10 days (10 days and 13 years).[32]
References
- ↑ F. William Walker, Dr. George J. Kirouac, Francis M. Rourke. 1977. Chart of the Nuclides, twelfth edition. Knolls Atomic Power Laboratory, General Electric Company.
- ↑ https://nei.org/news/2019/what-happens-nuclear-waste-us
- ↑ "Introduction to ANL's IFR Program". 9 October 2007. Archived from the original on 9 October 2007.
- ↑ Newton, Amos S. (1 January 1949). "The Fission of Thorium with Alpha-Particles". Physical Review. 75 (1): 17–29. Bibcode:1949PhRv...75...17N. doi:10.1103/PhysRev.75.17. S2CID 93655149.
- ↑ Paşca, H.; Andreev, A.V.; Adamian, G.G.; Antonenko, N.V. (2018). "Charge distributions of fission fragments of low- and high-energy fission of Fm, No, and Rf isotopes". Physical Review C. 97 (3): 034621–1–034621–12. Bibcode:2018PhRvC..97c4621P. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.97.034621.
- ↑ "Nuclear Fission Yield". Archived from the original on 28 May 2007. Retrieved 13 May 2009.
- ↑ "Elementary Physics of Reactor Control" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 12 July 2019. Retrieved 15 April 2018.
- ↑ "Nuclear Fission - Fission Reaction". Nuclear Power.
- ↑ "PROMPT AND DELAYED NEUTRONS". nuclearpowertraining.tpub.com.
- ↑ Prompt and Delayed Neutrons The fact the neutron is produced via this type of decay and this happens orders of magnitude later compared to the emission of the prompt neutrons, plays an extremely important role in the control of the reactor.
- ↑ ""In view of the very low concentration of Uranium used, it is not possible for a commercial nuclear reactor to explode like an atomic bomb from the perspective of physics. A good analogy would be to compare alcoholic spirits to beer. Alcoholic spirits, such as Vodka, typically have a 40% alcohol content, and are highly flammable. Beer, which generally has an alcohol content of less than 5%, does not burn."". Archived from the original on 1 August 2018. Retrieved 15 April 2018.
- ↑ "Nuclear Explained By Analogy Metaphor Examples". www.metamia.com.
- ↑ nuclear education for K-12 students Myths About Nuclear Energy It is impossible for a reactor to explode like a nuclear weapon; these weapons contain very special materials in very particular configurations, neither of which are present in a nuclear reactor.
- ↑ Hala, Jiri; James D. Navratil (2003). Radioactivity, Ionizing Radiation, and Nuclear Energy. Brno: Konvoj. ISBN 80-7302-053-X.
- ↑ H. Glänneskog. Interactions of I2 and CH3I with reactive metals under BWR severe-accident conditions, Nucl. Engineering and Design, 2004, 227, 323-329
- ↑ Workshop on iodine aspects of severe accident management. Summary and conclusions. Nuclear Energy Agency. Committee on the safety of nuclear installations. OCDE. March 7, 2000.
- ↑ "Nuclear Data Evaluation Lab". Retrieved 13 May 2009.
- ↑ C. Kearney, Nuclear War Survival Skills, Oregon Institute of Science and Medicine, http://www.oism.org/
- ↑ G. Mushkacheva, E. Rabinovich, V. Privalov, S. Povolotskaya, V. Shorokhova, S. Sokolova, V. Turdakova, E. Ryzhova, P. Hall, A. B. Schneider, D. L. Preston, and E. Ron, "Thyroid Abnormalities Associated with Protracted Childhood Exposure to 131I from Atmospheric Emissions from the Mayak Weapons Facility in Russia", Radiation Research, 2006, 166(5), 715-722
- ↑ C. Kearney, Nuclear War Survival Skills (Ch. 13), Oregon Institute of Science and Medicine, http://www.oism.org/
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Greer, Monte A.; Goodman, Gay; Pleus, Richard C.; Greer, Susan E. (2002). "Health Effects Assessment for Environmental Perchlorate Contamination: The Dose Response for Inhibition of Thyroidal Radioiodine Uptake in Humans". Environmental Health Perspectives. 110 (9): 927–37. doi:10.1289/ehp.02110927. PMC 1240994. PMID 12204829.
- 1 2 Wolff, J (1998). "Perchlorate and the thyroid gland". Pharmacological Reviews. 50 (1): 89–105. PMID 9549759.
- ↑ Barzilai, D; Sheinfeld, M (1966). "Fatal complications following use of potassium perchlorate in thyrotoxicosis. Report of two cases and a review of the literature". Israel Journal of Medical Sciences. 2 (4): 453–6. PMID 4290684.
- ↑ Woenckhaus, U.; Girlich, C. (2005). "Therapie und Prävention der Hyperthyreose" [Therapy and prevention of hyperthyroidism]. Der Internist (in German). 46 (12): 1318–23. doi:10.1007/s00108-005-1508-4. PMID 16231171. S2CID 13214666.
- 1 2 Bartalena, L.; Brogioni, S; Grasso, L; Bogazzi, F; Burelli, A; Martino, E (1996). "Treatment of amiodarone-induced thyrotoxicosis, a difficult challenge: Results of a prospective study". Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. 81 (8): 2930–3. doi:10.1210/jcem.81.8.8768854. PMID 8768854.
- ↑ Lawrence, J. E.; Lamm, S. H.; Pino, S.; Richman, K.; Braverman, L. E. (2000). "The Effect of Short-Term Low-Dose Perchlorate on Various Aspects of Thyroid Function". Thyroid. 10 (8): 659–63. doi:10.1089/10507250050137734. PMID 11014310.
- ↑ Lamm, Steven H.; Braverman, Lewis E.; Li, Feng Xiao; Richman, Kent; Pino, Sam; Howearth, Gregory (1999). "Thyroid Health Status of Ammonium Perchlorate Workers: A Cross-Sectional Occupational Health Study". Journal of Occupational & Environmental Medicine. 41 (4): 248–60. doi:10.1097/00043764-199904000-00006. PMID 10224590.
- ↑ "Nuclear Chemistry: Half-Lives and Radioactive Dating".
- ↑ For further details of the use of prussian blue please see the IAEA report on the Goiânia accident.
- ↑ Development, Office of Research &. "Full-Scale and Bench-Scale Studies on the Removal of Strontium from Water (abstract)". cfpub.epa.gov. Retrieved 14 June 2019.
- ↑ Baratta, Edmond J.; Nations, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United (10 February 1994). Manual of Food Quality Control: Radionuclides in food. Food & Agriculture Org. ISBN 9789251035788 – via Google Books.
- ↑ "Half-life, effective". www.euronuclear.org. Archived from the original on 9 July 2014. Retrieved 25 December 2012.
Bibliography
Paul Reuss, Neutron Physics, chp 2.10.2, p 75
External links
- Iodine fallout studies in the United States
 The Live Chart of Nuclides - IAEA Color-map of product yields, and detailed data by click on a nuclide.
The Live Chart of Nuclides - IAEA Color-map of product yields, and detailed data by click on a nuclide.