| OLFM1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | OLFM1, AMY, NOE1, NOELIN1, OlfA, olfactomedin 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 605366 MGI: 1860437 HomoloGene: 8612 GeneCards: OLFM1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Olfactomedin 1, also known as noelin 1 or pancortin, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the OLFM1 gene.[5][6] The name noelin stands for "neuronal olfactomedin-related endoplasmic reticulum-localized 1".[7]
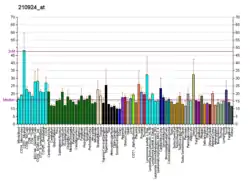
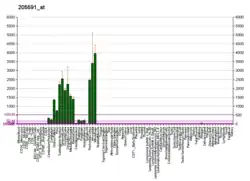
This gene product shares extensive sequence similarity with the rat neuronal olfactomedin-related ER localized protein. While the exact function of the encoded protein is not known, its abundant expression in brain suggests that it may have an essential role in nerve tissue. Several alternatively spliced transcripts encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene.[6]
Cancer
OLFM1 gene has been detected progressively overexpressed in Human papillomavirus-positive neoplastic keratinocytes derived from uterine cervical preneoplastic lesions at different levels of malignancy.[8] For this reason, this gene is likely to be associated with tumorigenesis and may be a potential prognostic marker for uterine cervical preneoplastic lesions progression.[8]
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000130558 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000026833 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Yokoyama M, Nishi Y, Yoshii J, Okubo K, Matsubara K (May 1997). "Identification and cloning of neuroblastoma-specific and nerve tissue-specific genes through compiled expression profiles". DNA Res. 3 (5): 311–20. doi:10.1093/dnares/3.5.311. PMID 9039501.
- 1 2 "Entrez Gene: OLFM1 olfactomedin 1".
- ↑ Anholt RR (2014). "Olfactomedin proteins: central players in development and disease". Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology. 2: 6. doi:10.3389/fcell.2014.00006. PMC 4206993. PMID 25364714.
- 1 2 Rotondo JC, Bosi S, Bassi C, Ferracin M, Lanza G, Gafà R, Magri E, Selvatici R, Torresani S, Marci R, Garutti P, Negrini M, Tognon M, Martini F (April 2015). "Gene expression changes in progression of cervical neoplasia revealed by microarray analysis of cervical neoplastic keratinocytes". J Cell Physiol. 230 (4): 802–812. doi:10.1002/jcp.24808. hdl:11392/2066612. PMID 25205602. S2CID 24986454.
Further reading
- Andersson B, Wentland MA, Ricafrente JY, et al. (1996). "A "double adaptor" method for improved shotgun library construction". Anal. Biochem. 236 (1): 107–13. doi:10.1006/abio.1996.0138. PMID 8619474.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: overridden setting (link) - Yu W, Andersson B, Worley KC, et al. (1997). "Large-Scale Concatenation cDNA Sequencing". Genome Res. 7 (4): 353–8. doi:10.1101/gr.7.4.353. PMC 139146. PMID 9110174.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: overridden setting (link) - Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. Bibcode:2002PNAS...9916899M. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: overridden setting (link) - Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: overridden setting (link) - Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The Status, Quality, and Expansion of the NIH Full-Length cDNA Project: The Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: overridden setting (link) - Liu T, Qian WJ, Gritsenko MA, et al. (2006). "Human Plasma N-Glycoproteome Analysis by Immunoaffinity Subtraction, Hydrazide Chemistry, and Mass Spectrometry". J. Proteome Res. 4 (6): 2070–80. doi:10.1021/pr0502065. PMC 1850943. PMID 16335952.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: overridden setting (link) - Kimura K, Wakamatsu A, Suzuki Y, et al. (2006). "Diversification of transcriptional modulation: Large-scale identification and characterization of putative alternative promoters of human genes". Genome Res. 16 (1): 55–65. doi:10.1101/gr.4039406. PMC 1356129. PMID 16344560.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: overridden setting (link) - Camargo LM, Collura V, Rain JC, et al. (2007). "Disrupted in Schizophrenia 1 Interactome: evidence for the close connectivity of risk genes and a potential synaptic basis for schizophrenia". Mol. Psychiatry. 12 (1): 74–86. doi:10.1038/sj.mp.4001880. PMID 17043677. S2CID 25119660.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: overridden setting (link)