Wildeck | |
|---|---|
 Coat of arms | |
Location of Wildeck within Hersfeld-Rotenburg district 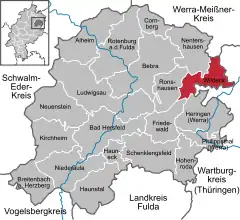 | |
 Wildeck  Wildeck | |
| Coordinates: 50°57′N 09°59′E / 50.950°N 9.983°E | |
| Country | Germany |
| State | Hesse |
| Admin. region | Kassel |
| District | Hersfeld-Rotenburg |
| Subdivisions | 5 districts |
| Government | |
| • Mayor (2020–26) | Alexander Wirth[1] (Ind.) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 39.86 km2 (15.39 sq mi) |
| Highest elevation | 465 m (1,526 ft) |
| Lowest elevation | 208 m (682 ft) |
| Population (2022-12-31)[2] | |
| • Total | 4,971 |
| • Density | 120/km2 (320/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| Postal codes | 36208 |
| Dialling codes | 06626 |
| Vehicle registration | HEF |
| Website | www.wildeck.de |
Wildeck is a municipality in Hersfeld-Rotenburg district in northeastern Hesse, Germany lying right at the boundary with Thuringia, 54 km southeast of Kassel.
Geography
Location
The community lies partly in the middle Werra valley, in the Berka-Gerstunger-Becken (basin) with its small side basins, the Obersuhler Becken and the Kleinenseer Bucht. This basin is surrounded by heights. In the southwest lies the Seulingswald, in the south the outliers of the Anterior Rhön, in the east the outliers of the Thuringian Forest and in the north the Richelsdorfer Hills, which belongs to the southern Werra Upland. The community lies partly in this last-named range.
The nearest major centres are Bad Hersfeld (some 25 km to the southwest) and Eisenach (some 25 km to the east). The lowest point in the community is In der Aue ("On the Floodplain") near Obersuhl at 208 m above sea level. The highest point is the Rotestock at 456 m above sea level.
Constituent communities
The community's five Ortsteile are Obersuhl, Bosserode, Hönebach, Richelsdorf and Raßdorf.
Neighbouring communities
Wildeck borders in the north on the community of Nentershausen (in Hersfeld-Rotenburg) and the town of Sontra (in the Werra-Meißner-Kreis), in the east on the community of Gerstungen, in the southeast on the town of Berka/Werra, in the south on the communities of Dankmarshausen and Großensee (all four in Thuringia's Wartburgkreis) and the town of Heringen, in the southwest on the community of Friedewald and in the west on the community of Ronshausen (all three in Hersfeld-Rotenburg).
History
The community's name stems from the Amt of Wildeck, to which some of today's constituent communities belonged, and which in the Middle Ages was under the Fulda Abbey's rule. The Amt seat lay at Wildeck Castle, which stood on the Schloßberg near Raßdorf.
In 1277, Richelsdorf had its first documentary mention when the Fulda Abbey temporarily relinquished the community to build a convent at St. Nicholas's Monastery (Nikolaikloster) in Eisenach, which was, however, never built. In 1325, the brothers Friedrich and Hermann von Colmatsch were enfeoffed with the Amt, in exchange for which today's constituent communities of Eisenach and Hötzelsroda went to St. Nicholas's Monastery. The fief passed in 1539 to the Landgraves of Hesse. After the family von Colmatsch had died out in 1562, the community passed to Hesse.
The craggy state boundary in the south and east still bears witness to the disputes between the Landgraves of Hesse and Thuringia and the Fulda Abbey, which lasted throughout the Middle Ages and on into modern times.[3]
Coppermining in Wildeck was mentioned for the first time in 1460. At the Richelsdorf foundry, cobalt was also mined beginning in 1708, which raised the foundry's importance, as well as another's in Iba (nowadays an outlying centre of Bebra), causing the mining office of Sontra to move to Richelsdorf.
Potash has been mined in the Wildeck region for over 100 years.[4]
From 1945 to 1990, the community found itself right near the Inner German border. The station in Hönebach, a component of Wildeck, served as West German border crossing for rail transport. The crossing was open for trains travelling between the Soviet Zone of occupation in Germany (till 1949, thereafter the East German Democratic Republic, or West Berlin and the American zone of occupation (till 1949) and thereafter the West German Federal Republic of Germany. The traffic was subject to the Interzonal traffic regulations, that between West Germany and West Berlin followed the special regulations of the Transit Agreement (1972).
Within the framework of municipal reform, the new community of Wildeck came into being on 31 December 1971 through the merger of the above-named communities.[3]
Population development
Data apply to community limits in each year named, and are in each case for 31 December[5]
| Year | 1971 | 1979 | 1984 | 1989 | 1994 | 1996 | 2001 | 2002 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inhabitants | 6314 | 5729 | 5809 | 5877 | 6095 | 6092 | 6046 | 6003 | 5247 | 5198 | 5136 |
By November 2020, the population had declined to 4,980.[6]
Politics
Community council
As of 2022, the municipal council is chaired by Egon Bachmann of the Social Democratic Party of Germany, with the following members:[7]
- Social Democratic Party of Germany: 10 members
- Christian Democratic Union of Germany: 4 members
- Free Voters: 6 members
- Alliance 90/The Greens: 2 members
- Free Democratic Party (Germany): 1 member
The municipal election held on 26 March 2006 yielded the following results:
| Parties and voter communities | % 2006 |
Seats 2006 |
% 2001 |
Seats 2001 | |
| CDU | Christian Democratic Union of Germany | 27.5 | 9 | 25.1 | 8 |
| SPD | Social Democratic Party of Germany | 49.0 | 15 | 56.8 | 17 |
| FDP | Free Democratic Party | 4.0 | 1 | 2.5 | 1 |
| FWG | Freie Wählergemeinschaft | 19.5 | 6 | 15.6 | 5 |
| Total | 100.0 | 31 | 100.0 | 31 | |
| Voter turnout in % | 62.1 | 69.1 | |||
Mayors
Mayoral elections are held every six years. The most recent mayors were:[1]
- 2020–present: Alexander Wirth (independent)[8]
- 2014-2020: Alexander Wirth (independent)
- 2003–2014: Jürgen Grau (independent)
- 1997–2003: Willi Müller (SPD)
Economy and infrastructure
Transport
The community lies on Autobahn A 4 (Aachen–Görlitz), at interchanges 34 and 35. Furthermore, the community has at its disposal three halts (Obersuhl, Bosserode and Hönebach) on the Thüringer Bahn (railway) from Eisenach to Bebra.
Established businesses
- alsecco Bauchemische Produkte GmbH & Co KG – construction chemistry products, and a successor business to the Richelsdorfer foundry
- Betten Malsch GmbH – a leading German maker of medical care beds
Culture and sightseeing
Buildings
- Rustic Baroque church in Richelsdorf
- Bosserode Evangelical church with winged altar and pietà
- Ruins of the Blumenstein hunting palace
- Remains of the palace's parklands with pond and obelisk
- Blumenstein hunting palace
 Blumenstein ruins
Blumenstein ruins Gate
Gate Obelisk
Obelisk Pond
Pond
Nature
- Rhäden nature and bird conservation area with information centre in Obersuhl
There are also many hiking trails, especially by way of the Blumenstein ruins around the Wildeck valley, by which one crosses the Bellers Estate. Quite a few forests can be visited on these hikes, leading by the Franzoseneiche ("Frenchman's Oak").
Famous people
Sons and daughters of the town
- Werner Heckmann, trumpet soloist at the Staatstheater Stuttgart and member of German Brass
- Margrit Klinger, German track and field athlete. Winner of bronze medal at the 1982 European Championships in Athletics in Athens
Nice to know
- Wildecker Herzbuben, German Volksmusik group (Wolfgang Schwalm and Wilfried Gliem)
References
- 1 2 "Ergebnisse der letzten Direktwahl aller hessischen Landkreise und Gemeinden" (XLS) (in German). Hessisches Statistisches Landesamt. 5 September 2022.
- ↑ "Bevölkerung in Hessen am 31.12.2022 nach Gemeinden" (XLS) (in German). Hessisches Statistisches Landesamt. June 2023.
- 1 2 "Die Geschichte einer Region". www.wildeck-hessen.de. Retrieved 2022-06-24.
- ↑ "Startseite". www.wildeck-hessen.de. Retrieved 2022-06-24.
- ↑ Data for 1971 to 1996 come from "Gemeinde Wildeck". Archived from the original on 2011-07-19. Retrieved 2010-11-27.; Data for 2004 to 2006 come from "Statistik-Hessen.de: Landesdaten". Archived from the original on 2012-09-11. Retrieved 2008-06-21..
- ↑ "Die Gemeinde". www.wildeck-hessen.de. Retrieved 2022-06-24.
- ↑ "Gemeindevertretung". www.wildeck-hessen.de. Retrieved 2022-06-24.
- ↑ "Veröffentlichung des Wahlergebnisses der Bürgermeisterwahl 2020". www.wildeck-hessen.de. Retrieved 2022-06-24.
External links
- Wildeck (in German)
- Richelsdorf (in German)
- Obersuhl (in German)
- Wildeck at Curlie (in German)