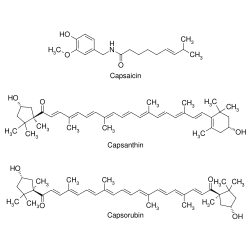
 Major chemical components of paprika oleoresin | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC names
(3R,3′S,5′R)-3,3′-dihydroxy-β,κ-caroten-6′-one (capsanthin) (3S,5R,3′S,5′R)-3,3′-dihydroxy-κ,κ-carotene-6,6′-dione (capsorubin) | |
| Other names
Paprika extract; Paprika color | |
| Identifiers | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| E number | E160c (colours) |
PubChem CID |
|
| Properties | |
| C40H56O3 (capsanthin)
C40H56O4 (capsorubin) | |
| Molar mass | 584.87 g/mol (capsanthin)
600.85 g/mol (capsorubin) |
| Appearance | Reddish viscous liquid |
| Insoluble | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Paprika oleoresin (also known as paprika extract and oleoresin paprika) is an oil-soluble extract from the fruits of Capsicum annuum or Capsicum frutescens, and is primarily used as a colouring and/or flavouring in food products. It is composed of vegetable oil (often in the range of 97% to 98%), capsaicin, the main flavouring compound giving pungency in higher concentrations, and capsanthin and capsorubin, the main colouring compounds (among other carotenoids).[1] It is much milder than capsicum oleoresin, often containing no capsaicin at all.
Extraction is performed by percolation with a variety of solvents, primarily hexane, which are removed prior to use. Vegetable oil is then added to ensure a uniform color saturation.[2]
Uses
Foods colored with paprika oleoresin include cheese, orange juice, spice mixtures, sauces, sweets, ketchup, soups, fish fingers, chips, pastries, fries, dressings, seasonings, jellies, bacon, ham, ribs, and among other foods even cod fillets.[3] In poultry feed, it is used to deepen the colour of egg yolks.
In the United States, paprika oleoresin is listed as a color additive “exempt from certification”.[4] In Europe, paprika oleoresin (extract), and the compounds capsanthin and capsorubin are designated by E160c.
Names and CAS nos
| Trivial Name | Preferred Name | AutoNom Name | Cas No. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capsaicin | 8-Methyl-N-vanillyl-trans-6-nonenamide | (E)-8-Methyl-non-6-enoic acid 4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-benzylamide | 404-86-4 |
| Capsanthin | (all-E,3R,3'S,5'R)-3,3'-dihydroxy-β,κ-caroten-6'-one | (2E,4E,6E,8E,10E,12E,14E,16E,18E)-19-((R)-4-Hydroxy-2,6,6-trimethyl-cyclohex-1-enyl)-1-((1R,4S)-4-hydroxy-1,2,2-trimethylcyclopentyl)-4,8,13,17-tetramethyl-nonadeca-2,4,6,8,10,12,14,16,18-nonaen-1-one | 465-42-9 |
| Capsorubin | (all-E,3S,3'S,5R,5'R)-3,3'-dihydroxy-κ,κ-carotene-6,6'-dione | (2E,4E,6E,8E,10E,12E,14E,16E,18E)-1,20-Bis-((1R,4S)-4-hydroxy-1,2,2-trimethyl-cyclopentyl)-4,8,13,17-tetramethyl-icosa-2,4,6,8,10,12,14,16,18-nonaene-1,20-dione | 470-38-2 |
References
- ↑ Pérez-Gálvez A, Martin HD, Sies H, Stahl W (2003). "Incorporation of carotenoids from paprika oleoresin into human chylomicrons". Br. J. Nutr. 89 (6): 787–93. doi:10.1079/BJN2003842. PMID 12828795.
- ↑ Jarén-Galán M, Nienaber U, Schwartz SJ (1999). "Paprika (Capsicum annuum) Oleoresin Extraction with Supercritical Carbon Dioxide". J. Agric. Food Chem. 47 (9): 3558–64. doi:10.1021/jf9900985. PMID 10552685.
- ↑ "Paprika Extract (E160c) – Overview, Uses, Side Effects & More". HealthKnight. Retrieved 2022-04-13.
- ↑ "Title 21 Code of Federal Regulations, part 73". Archived from the original on 2009-05-09. Retrieved 2008-08-12.