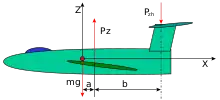
Parallel vertical forces acting on an airplane in straight and level flight. Lift from the main wing (Pz) is balanced by the weight of the airplane (mg) and the down-force on the horizontal stabilizer (Pzh).
In mechanical engineering, a parallel force system is a situation in which two forces of equal magnitude act in the same direction within the same plane, with the counter force in the middle. An example of this is a see saw. The children are applying the two forces at the ends, and the fulcrum in the middle gives the counter force to maintain the see saw in neutral position. Another example are the major vertical forces on an airplane in flight (see image at right).
References
- Kumar, K.L. (2003). Engineering Mechanics,3e (in Dutch). McGraw-Hill Education (India) Pvt Limited. p. 90. ISBN 978-0-07-049473-2. Retrieved September 10, 2017.
- Blake, Alexander (1985). Handbook of Mechanics, Materials, and Structures. John Wiley & Sons. p. 128. ISBN 9780471862390.
- R.K. Bansal (December 2005). A Textbook of Engineering Mechanics. Laxmi Publications. p. 25. ISBN 978-81-7008-305-4.
- M. N. Shesha Prakash; Ganesh B. Mogaveer (30 July 2014). Elements of Civil Engineering and Engineering Mechanics. PHI Learning Pvt. Ltd. p. 25. ISBN 978-81-203-5001-4.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.