Party of Functional Groups Partai Golongan Karya | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Abbreviation | Partai Golkar |
| General Chairman | Airlangga Hartarto[1] |
| Secretary-General | Lodewijk Freidrich Paulus[2] |
| Founded | 20 October 1964 |
| Headquarters | Jakarta |
| Newspaper | Suara Karya (1971–2016) |
| Youth wing | AMPG (Golkar Party Young Force) |
| Women's wing | KPPG (Golkar Party Women's Corps) |
| Labour wing | |
| Membership (2023) | 839,187[3] |
| Ideology | Pancasila National conservatism[4] Developmentalism[5] Economic liberalism[6] Indonesian nationalism[6] Secularism[6] Suhartoism[7][8] Catch-all party[9] During the New Order: Big tent[10] Right-wing authoritarianism[11][12] |
| Political position | Centre-right[13] to right-wing[lower-alpha 1][11][12] During the New Order: Far-right |
| National affiliation | Onward Indonesia Coalition Advanced Indonesia Coalition |
| Slogan | Suara Golkar, Suara Rakyat (Golkar's Voice, People's Voice) |
| Anthem | Mars Partai Golkar (Golkar Party March) |
| Ballot number | 4 |
| DPR seats | 85 / 575 |
| DPRD I seats | 309 / 2,232 |
| DPRD II seats | 2,412 / 17,340 |
| Website | |
| www | |
The Party of Functional Groups (Indonesian: Partai Golongan Karya), often known by its abbreviation Golkar, is a political party in Indonesia. It was founded as the Joint Secretariat of Functional Groups (Indonesian: Sekretariat Bersama Golongan Karya, Sekber Golkar) in 1964, and participated for the first time in national elections in 1971 as Functional Groups. Golkar was not officially a political party until 1999, when it was required to become a party in order to contest elections.
Golkar was the ruling political group from 1971 to 1999, under presidents Suharto and B. J. Habibie. It subsequently joined the ruling coalitions under presidents Abdurrahman Wahid, Megawati Sukarnoputri, and Susilo Bambang Yudhoyono. When President Joko Widodo of the Indonesian Democratic Party of Struggle was elected in 2014, Golkar initially joined an opposition coalition led by former general Prabowo Subianto but in 2016 switched its allegiance to Widodo's government.[14]
History
Origins
In 1959, President Sukarno introduced his concept of Guided Democracy, in which so-called functional groups would play a role in government in place of political parties. The Indonesian National Armed Forces supported its creation because it believed these groups would balance the growing strength of the Communist Party of Indonesia (PKI). In 1960, Sukarno awarded sectoral groups such as teachers, the Armed Forces and the Indonesian National Police, workers and artists seats in the Mutual Cooperation – People's Representative Council. As some of the members of these functional groups were linked to political parties, this gave political influence to the National Armed Forces. The TNI then established an anti-PKI trade union, the Central Organization of Indonesian Workers, or Soksi (Sentral Organisasi Karyawan Swadiri Indonesia), and used this as the core of an Armed Forces-led Joint Secretariat of Functional Groups, or Sekber Golkar, which was officially established on 20 October 1964.[15] By 1968 there were almost 250 organisations under the Sekber umbrella. On 22 November 1969 they were organized into seven main organizations, or Kino (Kelompok Induk Organisasi), namely Soksi, Kosgoro (Union of Mutual Cooperation Multifunction Organizations), MKGR (Mutual Assistance Families Association), Gerakan Karya Rakyat (People's Working Movement), Ormas Hankam (Defense and Security Mass Organizations), Professi (professional organizations), and Gerakan Pembangunan (Development Movement).[16][17] The Joint Secretariat was one of those organisations moblized against the PKI in the aftermath of the failure of the 30 September Movement in 1965.
Suharto and Golkar
In March 1968, General Suharto was officially elected by the People's Consultative Assembly (MPR) as Indonesia's second president. Because of his military background, Suharto was not affiliated with any political parties. Suharto had never expressed much interest in party politics. However, if he were to be elected for a second term as president, he needed to align himself with a political party. Originally, Suharto had shown interest in aligning with the Indonesian National Party (PNI) – the party of his predecessor, Sukarno.[18] But in seeking to distance himself from the old regime, Suharto settled on Golkar.
Suharto then ordered his closest associate, Ali Murtopo, to transform Golkar and turn it into an electoral machine. Under Murtopo, and with Suharto's supervision, Golkar was turned from a federation of NGOs into a political party. Under Suharto, Golkar continued to portray itself as a non-ideological entity, without favoritism or political agendas. It promised to focus on "economic development" and "stability" rather than a specific ideological goal.[19] Golkar also began identifying itself with the government, encouraging civil servants to vote for it as a sign of loyalty to the government.
Murtopo claimed that workers were a functional group, which by rights ought to be subsumed under Golkar: "thus all unions were united into a single body answerable to the state. The population was no longer there to be mobilised by political parties, rather, the people were the 'floating mass', or the 'ignorant mass', who needed firm guidance so they would not be lured into politics. In order to "Golkar-ize" the nation, Murtopo sometimes used the military and gangs of young thugs to eliminate political competition.[20]
Golkar was declared on 4 February 1970, that it would participate in the 1971 legislative elections. Suharto's alignment with Golkar paid dividends when Golkar won 62% of the votes and an overwhelming majority in the People's Representative Council (DPR). The members of the DPR also doubled as members of the MPR and thus Suharto was easily re-elected to a second term as president in March 1973.
The 1971 legislative election was a success for Golkar and Suharto. Strengthened by his re-election, Suharto quickly began tightening his grip on Golkar. Control was increased in October 1973 with the implementation of a less democratic and more centralized system headed by a chairman. In October 1978, after his re-election to a 3rd term, Suharto further consolidated his control of Golkar by being elected chairman of the executive board (Ketua Dewan Pembina), a position whose authority supersedes even the party chairman. From this position, Suharto had the supreme power in Golkar while leaving the day-to-day running of Golkar to the chairman.
Aside from being dominated by Suharto, Golkar was also an organization dominated by the Armed Forces. Out of the four people that served as Golkar Chairman during the New Order, three had a military background as officers. It was only in the last years of Suharto's rule that Harmoko, a civilian, was elected as Golkar chairman.
During the New Order, Golkar often offered a position to Suharto's supporters, such as Abdullah Nur, Ustaz Mil, and Zakaria bin Muhammad Amin.[21] But due to Golkar is not an Islamic party, Zakaria rejected the position, even though her daughter, Zaharah, would later served at People Representative Council in Bengkalis representing Golkar.[22]
Electoral dominance in the New Order
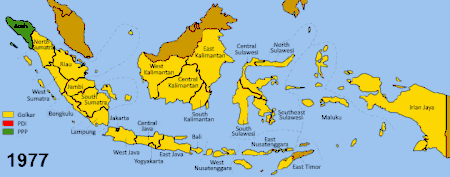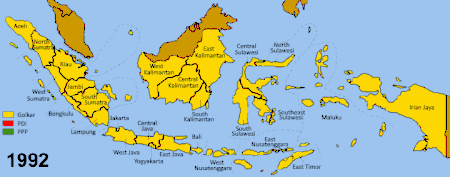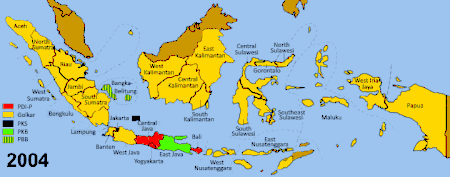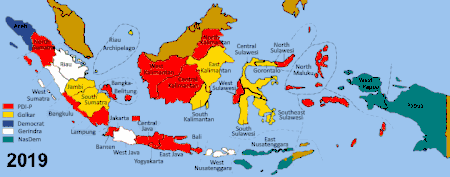
Golkar continued to dominate Indonesian politics well beyond the 1971 legislative elections. In subsequent New Order legislative elections, Golkar won 62% (1977), 64% (1982), 73% (1987), 68% (1992), and 74% (1997). Golkar's dominance was so absolute that for most of the Suharto era, Indonesia was effectively a one-party state. Suharto was able to pass bills without any meaningful opposition, and was able to form a Cabinet which consisted only of Golkar appointees.
After 1973, Suharto banned all political parties except for the Indonesian Democratic Party (PDI) and the United Development Party (PPP). These two parties were nominally permitted to contest the reign of Golkar. In practice, however, Golkar permitted only a semblance of competition. Elections were "exercises in controlled aggression", and were ritualized performances of "choice", in which local authorities were to obey directives about Golkar's electoral results in their area. A system of rewards, punishments, and violence meted out by thugs helped to guarantee cooperation across the archipelago, and the perpetual reelection of Golkar.[23]
After the 1977 and 1997 legislative elections, there were claims of electoral fraud launched by the party, who together with Golkar were the only legal political parties after 1973. There were also claims of Golkar members intimidating the electorate to vote for Golkar.
Organisation and factions
During the New Order Golkar was formally divided into seven (eight since 1971) organizations, called Main Organization Groups (Kelompok Induk Organisasi), or KINO. These were:[16][17]
- the Trikarya, consisting of:
- Central Indonesian Workers' Organization (Sentral Organisasi Karyawan Swadiri Indonesia, SOKSI/CIWO);
- Mutual Cooperation Multifunction Organizations' Union (Kesatuan Organisasi Serbaguna Gotong Royong, KOSGORO);
- Mutual Assistance Families Association (Musyawarah Kekeluargaan Gotong Royong, MKGR);
- Indonesian People's Working Movement (Gerakan Karya Rakyat Indonesia, GAKARI/IPWM);
- the Defense and Security Mass Organizations (Organisasi Kemasyarakatan Pertahanan dan Keamanan, Ormas Hankam/DSMOs);
- professional organizations (Golongan Profesi);
- the Development Movement (Gerakan Pembangunan);
- and, since its establishment by Presidential decree in 1971, the Employees' Corps of the Republic of Indonesia (Korps Pegawai Republik Indonesia, KORPRI).
However, Golkar during this era was also de facto divided into three factions:
- The ABRI faction: Consisted of members of the Indonesian armed forces (ABRI) who under Suharto played a dominant role in political affairs. This faction was headed by the ABRI Commander and was commonly known as the A faction. The Ormas Hankam was, as a general rule, supportive of the Armed Forces faction. It provided much of the military representation in the People's Consultative Assembly.
- The Bureaucrats (Birokrat) faction: Consisted of KORPRI members—which are de jure all civil servants; non-civil servant public officers; employees of state-, provincial- and municipal-owned enterprises; and ABRI members employed by the government. This faction was headed by the Home Affairs Minister and was commonly known as the B faction.
- The Groups (Utusan Golongan) faction: Consisted of Golkar members who were neither armed forces service personnel nor the bureaucracy. This faction was headed by the Golkar Chairman and was commonly known as the G faction. Its composition was made up of members of the other organizations that are part of the party.
These three factions worked closely together to gain consensus and in the case of nominating a presidential candidate it was the heads of these three factions who went to inform the candidate (which until 1998 was Suharto) that he had just been nominated as Golkar's presidential candidate. The three factions did not always work together however. In 1988, the ABRI faction was unable to nominate Sudharmono as vice president. The factions disappeared along with the fall of the New Order.
After Suharto: Reformasi and beyond
With the Fall of Suharto in May 1998, Golkar quickly sought to adapt and reform itself. In July 1998, a Special National Congress was held to elect the next chairman of Golkar. The congress was dogged by protests by both pro-Suharto and anti-Suharto groups. Suharto himself did not come to the congress. In the contest that followed, Akbar Tanjung emerged as the new chairman of Golkar after beating Army General Edi Sudrajat. It was the first time that a Golkar chairman was elected democratically rather than appointed by the chairman of the executive board. Under Akbar, the executive board was abolished and replaced by an advisory board which had considerably less authority.
In 1999, Golkar lost its first democratic legislative election to Megawati Sukarnoputri's PDI-P. Golkar won 20% of the votes and was the runner-up in the legislative elections. Despite losing these elections Golkar was still able to secure the Tanjung's election as Head of the DPR. October 1999 would see the MPR assemble for its General Session during which a president and a vice president would be elected. It was widely expected that Golkar would support Jusuf Habibie in his bid for a second term as president. Before Habibie could be nominated, however, he was required to deliver an accountability speech: a report delivered by the President to the MPR at the end of his term. The MPR would not ratify the accountability speech and it was revealed that some Golkar members had voted against ratifying the speech.
Although PDI-P had won the legislative elections, Golkar joined forces with the Central Axis, a political coalition put together by MPR Chairman Amien Rais, to nominate and successfully secure the election of Abdurrahman Wahid as president. Golkar, however, was unable to stop the election of Megawati as vice president.
Golkar was rewarded for its support of Wahid by having its members appointed to ministerial positions in Wahid's Cabinet. Much like those who had supported Wahid, Golkar would grow disillusioned with Wahid. In April 2000, Jusuf Kalla, a Golkar member who held position as Minister of Industries and Trade was sacked from his position. When Golkar inquired as to why this was done, Wahid alleged it was because of corruption. In July 2001, Golkar, along with its Central Axis allies, held an MPR Special Session to replace President Wahid with Megawati.
By 2004, the reformist sentiments that had led PDI-P to victory in the 1999 legislative elections had died down. Many Indonesians were disappointed with what Reformasi had achieved thus far and were also disillusioned with Megawati's presidency, enabling Golkar to emerge victorious in the 2004 legislative elections with 21% of the votes.
Unlike the other political parties who had one person as their presidential candidate from the start, Golkar had five. In April 2004, Golkar held a national convention to decide who would become Golkar's candidate for president. These five were Akbar Tanjung, General Wiranto, Lieutenant-General Prabowo, Aburizal Bakrie, and Surya Paloh. Akbar won the first round of elections but Wiranto emerged as the winner in the second round. Wiranto chose Solahuddin Wahid as his running mate.
The 2004 Presidential Election was held on 5 July. The first round was won by Susilo Bambang Yudhoyono and Yusuf Kalla who faced Megawati and Hasyim Muzadi in the September 2004 run-off. Wiranto/Wahid came second and there were allegations of disunity within the party with Akbar not fully supporting Wiranto after losing the nomination.
In August 2004 Golkar formed, with PDI-P, PPP, Reform Star Party (PBR) and Prosperous Peace Party (PDS), a national coalition to back Megawati. Further infighting would hamper Golkar in its bid to back Megawati. Fahmi Idris led a group of Golkar members in defecting and threw their support behind Yudhoyono and Kalla. At the Presidential Run-Off in September 2004, Yudhoyono emerged victorious over Megawati to become Indonesia's 6th president. Yusuf Kalla, who had gone his own way back in April 2004, became vice president.
2004 National Congress
Although he had overwhelmingly won the presidency, Yudhoyono was still weak in the DPR. His own Democratic Party had only won 7% in the legislative elections and even combined with other parties who had aligned themselves with the new government, they still had to contend with the legislative muscle of Golkar and PDI-P who now intended to play the role of opposition.
With a National Congress to be held in December 2004, Yudhoyono and Kalla had originally backed Head of DPR Agung Laksono to become Golkar chairman. When Agung was perceived to be too weak to run against Akbar, Yudhoyono and Kalla threw their weight behind Surya Paloh. Finally, when Paloh was perceived to be too weak to run against Akbar, Yudhoyono gave the green light for Kalla to run for the Golkar Chairmanship.
This was a widely controversial move. Up to that point, Yudhoyono had not let members of his administration hold a concurrent position in political parties to prevent the possible abuse of power. There were also complaints by Wiranto who claimed that some months earlier, Yudhoyono had promised to support him if he ran for the Golkar chairmanship.
On 19 December 2004, Kalla became the new Golkar chairman with over 50% of the votes. Akbar, who had expected to win a second term as Golkar chairman, was defeated with 30% of the votes. Agung and Surya, who Yudhoyono and Kalla had backed earlier, became the party vice chairman and the chairman of the advisory board, respectively.
Kalla's new appointment as chairman of Golkar significantly strengthened Yudhoyono's government in Parliament and left the PDI-P as the only major opposition party in the DPR.
2009 National Congress
At the 2009 Congress, held in Pekanbaru, Aburizal Bakrie was elected chairman, winning 269 out of 583 votes, and beating Surya Paloh into second place. Surya Paloh then went on to establish the National Democratic organization, which in turn established the National Democratic Party.[24][25]
Political identites
Ideology
The 2008 Law on Political Parties states that political parties are allowed to include specific characteristics that reflect their political aspirations, as long as they do not contradict Pancasila and the 1945 Constitution.[26] Outsider views on the party's political orientation vary. Academics and domestic observers classified it as a nationalist party,[27] while their international counterparts described it as a secular-nationalist party.[28] Its political leaning has been described as centrist[29] or centre-right.
Party platforms
Under chairman Aburizal Bakrie, the party has produced a blueprint known as "Vision Indonesia 2045: A Prosperous Nation" with the aim of making Indonesia a developed nation by the centenary of the country's independence in 2045. The plan comprises three stages each lasting a decade. The key strategies in the vision comprise developing Indonesia from the villages, strengthening the role of the state, quality economic growth, equalizing incomes, ensuring even development in all areas, quality education and healthcare, strengthening communities, sustained economic development, upholding the law and human rights, industrial development based on technology, and revitalization of agriculture and trade.
The first decade would lay the foundations for a developed nation, the second would accelerate development and the final decade would see Indonesia become a developed nation. Each stage would have targets for indicators such as economic growth, GDP, and levels of unemployment and poverty.[30]
| Indicator | 2015–2025 | 2025–2035 | 2035–2045 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Economic growth | 8–9% | 10–11% | 6–7% |
| Per capita income | US$10,000–12,000 | US$21,000–23,000 | US$41,000–43,000 |
| Unemployment | 4–6% | 4% | 4% |
| Poverty ratio | 5–8% | 2–3% | 1–2% |
| Life expectancy | 75 | 78 | 82 |
| Gini ratio | 0.35 | 0.31 | 0.28 |
| Human Development Index | 0.80 | 0.86 | 0.91 |
Chairpersons


- Brig. Gen. Djuhartono (1964–1969)
- Maj. Gen. Suprapto Sukowati (1969–1973)
- Maj. Gen. Amir Murtono (1973–1983)
- Lt. Gen. Sudharmono (1983–1988)
- Lt. Gen. Wahono (1988–1993)
- Harmoko (1993–1998)
- Akbar Tandjung (1998–2004)
- Jusuf Kalla (2004–2009)
- Aburizal Bakrie (2009–2014)
- Disputed between Aburizal Bakrie and Agung Laksono (2014–2016)
- Setya Novanto (2016–2017)
- Airlangga Hartarto (2017–present)
Election results
Legislative election results
| Election | Ballot number | Total seats won | Total votes | Share of votes | Outcome of election | Party leader |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1971 | 5 | 236 / 360 |
34,348,673 | 62.80%[31] | Suprapto Sukowati | |
| 1977 | 2 | 232 / 360 |
39,750,096 | 62.11%[32] | Amir Murtono | |
| 1982 | 2 | 242 / 360 |
48,334,724 | 64.34%[32] | Amir Murtono | |
| 1987 | 2 | 299 / 400 |
62,783,680 | 73.11%[32] | Sudharmono | |
| 1992 | 2 | 282 / 400 |
66,599,331 | 68.10%[32] | Wahono | |
| 1997 | 2 | 325 / 400 |
84,187,907 | 74.51%[32] | Harmoko | |
| 1999 | 33 | 120 / 500 |
23,741,749 | 22.46%[33] | Akbar Tandjung | |
| 2004 | 20 | 128 / 550 |
24,480,757 | 21.58%[34] | Akbar Tandjung | |
| 2009 | 23 | 106 / 560 |
15,037,757 | 14.45%[34] | Jusuf Kalla | |
| 2014 | 5 | 91 / 560 |
18,432,312 | 14.75%[35] | Governing coalition (since 2016)[36] |
Aburizal Bakrie |
| 2019 | 4 | 85 / 575 |
17,229,789 | 12,31%[37] | Airlangga Hartarto | |
| 2024 | 4 | Airlangga Hartarto |
Presidential election results
| Election | Ballot number | Pres. candidate | Running mate | 1st round (Total votes) |
Share of votes | Outcome | 2nd round (Total votes) |
Share of votes | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2004 | 1 | Wiranto | Salahuddin Wahid | 26,286,788 | 22.15% | Eliminated | Runoff[38] | ||
| 2009 | 3 | Jusuf Kalla | Wiranto | 15,081,814 | 12.41% | Lost | |||
| 2014 | 1 | Prabowo Subianto[39] | Hatta Rajasa | 62,576,444 | 46.85% | Lost | |||
| 2019 | 01 | Joko Widodo | Ma'ruf Amin | 85,607,362 | 55.50% | Elected | |||
| 2024 | 02 | Prabowo Subianto | Gibran Rakabuming Raka | ||||||
Note: Bold text indicates Golkar Party member
See also
Notes
- ↑ Golkar is generally a centre-right to right-wing secular party. The Golkar has also been described as liberal, but has far-right[11][12] factions described as elitist and New Order revivalist.
- ↑ Ibrahim, Gibran Maulana (14 December 2017). "Jadi Ketum Golkar, Airlangga Serahkan Jabatan Menterinya ke Jokowi". detikcom. Retrieved 14 December 2017.
- ↑ Ramadhani, Nurul Fitri (23 January 2018). "Golkar eyes big prize in 2019 poll". The Jakarta Post. Retrieved 25 January 2018.
- ↑ "Info Pemilu - Partai GOLKAR". Komisi Pemilihan Umum RI. 6 January 2023. Retrieved 15 February 2023.
- ↑ "Indonesia's election". The Economist. 24 March 2009.
- ↑ "DINAMIKA PARTAI POLITIK DAN POSITIONING IDEOLOGI: STUDI TENTANG PERGESERAN POSITIONING IDEOLOGI PARTAI-PARTAI POLITIK PESERTA PEMILU 2014" (in Indonesian). Journal of Governance.
- 1 2 3 Bulkin, Nadia. "Indonesia's Political Parties". Carnegie Endowment for International Peace.
- ↑ "Golkar Ajak Loyalis Soeharto Pulang ke Partai". 2021.
- ↑ "Golkar Cari Suara Loyalis Soeharto?". 2021.
- ↑ "Partai Catch-all dan Kartel". 2012.
- ↑ Editorial of Suara Karya, 1 May 1971
- 1 2 3 Derbyshire, J. Denis (1990). Political Systems Of The World. Allied Publishers. p. 116.
- 1 2 3 Thomas Bohlken, Anjali (2016). Democratization from Above. Cambridge University Press. p. 221.
- ↑ The Report: Indonesia 2008. Oxford Business Group. 2008. p. 13.
- ↑ "Golkar declares support for Jokowi". The Jakarta Post. 28 July 2016 – via PressReader.com.
- ↑ "Sejarah Partai Golkar". Golkar official site.
- 1 2 Nishihara 1972, p. 17-19.
- 1 2 Ricklefs 2008, p. 243.
- ↑ Elson 2001, p. 186.
- ↑ Elson 2001, p. 187.
- ↑ Vickers 2005, p. 162.
- ↑ Saputra 2020, p. 156.
- ↑ Saputra 2020, p. 146, 156.
- ↑ Vickers 2005, p. 175.
- ↑ "Aburizal Bakrie Elected New Golkar Party Chairman; Tommy Suharto Gets No Votes". Jakarta Globe.
- ↑ "Surya Paloh told to choose between Golkar, National Democratic". Jakarta Post. 29 July 2011. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016.
- ↑ Saifulloh 2016, pp. 178: "Akan tetapi, dalam Undang-Undang No.2 Tahun 2008 Tentang Partai Politik kembali dipertegas bahwa asas dan ciri partai politik merupakan penjabaran dari Pancasila dan UUD 1945." Translation: In Law No. 2 of 2008 on Political Parties, it is emphasized that the principles and characteristics of political parties derive from Pancasila and the 1945 Constitution.
- ↑ Lee & Paath 2019: "So-called nationalist parties such as the Indonesian Democratic Party of Struggle (PDI-P), Prabowo Subianto's political machine the Great Indonesia Movement Party (Gerindra), Golkar Party, National Democratic Party (NasDem) and the Democratic Party are still the dominant forces in Indonesian politics."
- ↑ Bulkin 2013: "Golkar, a large secular-nationalist party, is the oldest operating party in Indonesia."
- ↑ Mietzner 2013, p. 46: "Moreover, Indonesia has now three pivotal center parties — parties that are deeply rooted in the political center and against whose combined strength it would be difficult to govern. These are PDIP, Golkar, and Partai Demokrat (Democratic Party, PD)."
- ↑ "Visi Negara Kesejahteraan 2045" (PDF) (in Indonesian). Golkar Party. Archived from the original (PDF) on 21 April 2015.
- ↑ "Pemilu 1971 – KPU" (in Indonesian). Komisi Pemilihan Umum Republik Indonesia. 21 February 2008. Retrieved 1 August 2018.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Pemilu 1977–1997 – KPU" (in Indonesian). Komisi Pemilihan Umum Republik Indonesia. 21 February 2008. Retrieved 1 August 2018.
- ↑ "Pemilu 1999 – KPU" (in Indonesian). Komisi Pemilihan Umum Republik Indonesia. 21 February 2008. Retrieved 1 August 2018.
- 1 2 "Bab V – Hasil Pemilu – KPU" (PDF) (in Indonesian). Komisi Pemilihan Umum Republik Indonesia. Retrieved 1 August 2018.
- ↑ "KPU sahkan hasil pemilu, PDIP nomor satu" (in Indonesian). BBC. 10 May 2014. Retrieved 1 August 2018.
- ↑ "New Golkar Chairman Confirms Support for Jokowi in 2019 Presidential Election". Jakarta Globe.
- ↑ Zunita Putri (21 May 2019). "KPU Tetapkan Hasil Pileg 2019: PDIP Juara, Disusul Gerindra-Golkar". Detik.com (in Indonesian). Retrieved 31 May 2019.
- ↑ "Koalisi Parpol Pendukung Mega-Hasyim Dideklarasikan". Liputan6.com (in Indonesian). 19 August 2004. Retrieved 4 August 2018.
- ↑ Wardah, Fathiyah (19 May 2014). "6 Parpol Dukung Pasangan Prabowo-Hatta dalam Pilpres". Voice of America Indonesia (in Indonesian). Retrieved 1 August 2018.
Sources
- Elson, Robert (2001), Suharto: A Political Biography, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 0-521-77326-1
- Nishihara, Masashi (1972), Golkar and the Indonesian elections of 1971, Modern Indonesia Project, Cornell University, ISBN 978-0877630043
- Ricklefs, MC (2008), A History of Modern Indonesia Since c. 1200 (revised ed.), Palgrave Macmillan, ISBN 978-1137052018
- Vickers, Adrian (2005), A History of Modern Indonesia, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-1139447614
- Bulkin, Nadia (24 October 2013). "Indonesia's Political Parties". Carnegie Endowment for International Peace. Archived from the original on 14 August 2021. Retrieved 1 August 2019.
- Lee, Christian; Paath, Carlos K. Y. (31 May 2019). "How Different Are Political Parties in Indonesia From One Another?". Jakarta Globe. Retrieved 16 December 2023.
- Mietzner, Marcus (2013). Money, Power, and Ideology: Political Parties in Post-Authoritarian Indonesia. Asian Studies Association of Australia (ASAA) - Southeast Asia. NUS Press. ISBN 978-997-1697-99-0.
- Saifulloh, Putra Perdana Ahmad (December 2016). "Kewajiban Partai Politik Berideologi Pancasila Ditinjau dari Prinsip-Prinsip Negara Hukum Indonesia" [The obligation of political parties to embrace the ideology of Pancasila: examined from the principles of the rule of law in Indonesia]. Pandecta Research Law Journal (in Indonesian). 11 (2). doi:10.15294/pandecta.v11i2.9276.
- Saputra, Amrizal, Wira Sugiarto, Suyendri, Zulfan Ikhram, Khairil Anwar, M. Karya Mukhsin, Risman Hambali, Khoiri, Marzuli Ridwan Al-bantany, Zuriat Abdillah, Dede Satriani, Wan M. Fariq, Suwarto, Adi Sutrisno, Ahmad Fadhli (15 October 2020). PROFIL ULAMA KARISMATIK DI KABUPATEN BENGKALIS: MENELADANI SOSOK DAN PERJUANGAN (in Indonesian). CV. DOTPLUS Publisher. ISBN 978-623-94659-3-3.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
External links
- Official site (in Indonesian)
- "Golkar Kembali Berkuasa Pasca-Orde Baru (article on the politicking leading up to Kalla's election as Golkar Chairman)" (in Indonesian). Suara Merdeka. 20 December 2004. Archived from the original on 2 April 2017.
- "Asam di Gunung, Garam di Laut". Tempo (in Indonesian). Archived from the original on 5 March 2016.