 Clementine image | |
| Coordinates | 62°42′S 110°24′W / 62.7°S 110.4°W |
|---|---|
| Diameter | 90 km |
| Depth | Unknown |
| Colongitude | 113° at sunrise |
| Eponym | Joseph von Petzval |

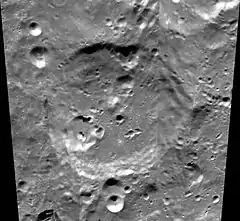
Petzval is a lunar impact crater that lies in the southern latitudes of the Moon's far side. This crater is located to the south of the larger Lippmann and to the north of Doerfel. It was namer after the Hungarian-German inventor Joseph Petzval.
This is a moderately worn crater formation with features that have become rounded and less well defined due to impact erosion. There are only a few small craterlets along parts of the rim and inner wall. Some faded terrace structures appear along parts of the inner wall to the east and south. Within the interior are small craters in the southwest and northeast sections of the floor. Near the midpoint is a worn central peak.
Petzval lies to the southwest of the Mendel-Rydberg Basin, a 630 km wide impact basin of Nectarian age, and it is on the southeast margin of the Pre-Nectarian South Pole-Aitken Basin.
Satellite craters
By convention, these features are identified on lunar maps by placing the letter on the side of the crater midpoint that is closest to Petzval.
| Petzval | Latitude | Longitude | Diameter |
|---|---|---|---|
| C | 60.3° S | 107.8° W | 52 km |
| D | 60.2° S | 105.9° W | 23 km |
References
- Andersson, L. E.; Whitaker, E. A. (1982). NASA Catalogue of Lunar Nomenclature. NASA RP-1097.
- Blue, Jennifer (July 25, 2007). "Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature". USGS. Retrieved 2007-08-05.
- Bussey, B.; Spudis, P. (2004). The Clementine Atlas of the Moon. New York: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-81528-4.
- Cocks, Elijah E.; Cocks, Josiah C. (1995). Who's Who on the Moon: A Biographical Dictionary of Lunar Nomenclature. Tudor Publishers. ISBN 978-0-936389-27-1.
- McDowell, Jonathan (July 15, 2007). "Lunar Nomenclature". Jonathan's Space Report. Retrieved 2007-10-24.
- Menzel, D. H.; Minnaert, M.; Levin, B.; Dollfus, A.; Bell, B. (1971). "Report on Lunar Nomenclature by the Working Group of Commission 17 of the IAU". Space Science Reviews. 12 (2): 136–186. Bibcode:1971SSRv...12..136M. doi:10.1007/BF00171763. S2CID 122125855.
- Moore, Patrick (2001). On the Moon. Sterling Publishing Co. ISBN 978-0-304-35469-6.
- Price, Fred W. (1988). The Moon Observer's Handbook. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-33500-3.
- Rükl, Antonín (1990). Atlas of the Moon. Kalmbach Books. ISBN 978-0-913135-17-4.
- Webb, Rev. T. W. (1962). Celestial Objects for Common Telescopes (6th revised ed.). Dover. ISBN 978-0-486-20917-3.
- Whitaker, Ewen A. (1999). Mapping and Naming the Moon. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-62248-6.
- Wlasuk, Peter T. (2000). Observing the Moon. Springer. ISBN 978-1-85233-193-1.