 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
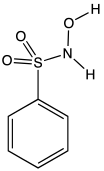
| Preferred IUPAC name
N-Hydroxybenzenesulfonamide | |
| Other names
benzenesulfohydroxamic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.009.068 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H7NO3S | |
| Molar mass | 173.19 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Melting point | 186 °C (367 °F; 459 K) |
| Acidity (pKa) | 9.29[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Piloty's acid is an organic compound with the formula C6H5SO2N(H)OH. A white solid, it is the benzenesulfonyl derivative of hydroxylamine. It is one of the main reagents used to generate nitroxyl (HNO), a highly reactive species that is implicated in a some chemical and biochemical reactions.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ Lester Packer (1999). Nitric Oxide: Biological and antioxidant activities. Gulf Professional Publishing. p. 286. ISBN 978-0-12-182202-6.
- ↑ Hughes, Martin N.; Cammack, Richard (1999). "Synthesis, chemistry, and Applications of Nitroxyl Ion Releasers Sodium Trioxodinitrate or Angeli's Salt and Piloty's Acid". Nitric Oxide, Part C: Biological and Antioxidant Activities. Methods in Enzymology. Vol. 301. pp. 279–287. doi:10.1016/S0076-6879(99)01092-7. PMID 9919577.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.