The Animals Portal Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, have myocytes and are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and grow from a hollow sphere of cells, the blastula, during embryonic development. As of 2022, around 2.16 million living animal species have been described—of which around 1.05 million are insects, over 85,000 are molluscs, and around 65,000 are vertebrates. It has been estimated there are as many as 7.77 million animal species on Earth. Animals' body lengths range from 8.5 μm (0.00033 in) to 33.6 m (110 ft). They have complex ecologies and interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology, and the study of animal behaviors is known as ethology. Most living animal species belong to the infrakingdom Bilateria, a highly proliferative clade whose members have a bilaterally symmetric body plan. Extant bilaterians include the basal group Xenacoelomorpha, but the vast majority belong to two large superphyla: the protostomes, which include phyla such as arthropods, molluscs, flatworms, annelids and nematodes, etc.; and the deuterostomes, which include the three phyla echinoderms, hemichordates and chordates, the latter with the vertebrates being its most successful subphylum. Precambrian life forms interpreted as early complex animals were already present in the Ediacaran biota of the late Proterozoic, but fossils of primitive sponge and other speculative early animals have been dated to as early as the Tonian period. Nearly all modern animal phyla became clearly established in the fossil record as marine species during the Cambrian explosion, which began around 539 million years ago (Mya), and most classes during the Ordovician radiation 485.4 Mya. 6,331 groups of genes common to all living animals have been identified; these may have arisen from a single common ancestor that lived 650 Mya during the Cryogenian period. (Full article...) Zoology (/zoʊˈɒlədʒi/) is the scientific study of animals. Its studies include the structure, embryology, classification, habits, and distribution of all animals, both living and extinct, and how they interact with their ecosystems. Zoology is one of the primary branches of biology. The term is derived from Ancient Greek ζῷον, zōion ('animal'), and λόγος, logos ('knowledge', 'study'). (Full article...)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phylum | Example | No. of Species |
Land | Sea | Fresh water |
Free- living |
Parasitic |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annelids |  |
17,000[1] | Yes (soil)[3] | Yes[3] | 1,750[2] | Yes | 400[4] |
| Arthropods |  |
1,257,000[1] | 1,000,000 (insects)[9] |
>40,000 (Malac- ostraca)[10] |
94,000[2] | Yes[3] | >45,000[lower-alpha 2][4] |
| Bryozoa | .jpg.webp) |
6,000[1] | Yes[3] | 60–80[2] | Yes | ||
| Chordates |  |
65,000[1] 45,000[11] |
23,000[11] |
13,000[11] |
18,000[2] 9,000[11] |
Yes | 40 (catfish)[12][4] |
| Cnidaria |  |
16,000[1] | Yes[3] | Yes (few)[3] | Yes[3] | >1,350 (Myxozoa)[4] | |
| Echinoderms |  |
7,500[1] | 7,500[1] | Yes[3] | |||
| Molluscs |  |
85,000[1] 107,000[13] |
35,000[13] |
60,000[13] |
5,000[2] 12,000[13] |
Yes[3] | >5,600[4] |
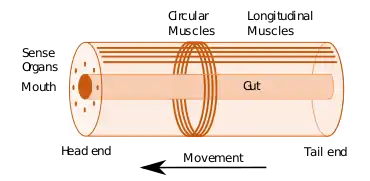
| Nematodes |  |
25,000[1] | Yes (soil)[3] | 4,000[5] | 2,000[2] | 11,000[5] | 14,000[5] |
| Platyhelminthes |  |
29,500[1] | Yes[14] | Yes[3] | 1,300[2] | Yes[3] 3,000–6,500[15] |
>40,000[4] 4,000–25,000[15] |
| Rotifers |  |
2,000[1] | >400[16] | 2,000[2] | Yes | ||
| Sponges |  |
10,800[1] | Yes[3] | 200-300[2] | Yes | Yes[17] | |
Total number of described extant species as of 2013: 1,525,728[1] | |||||||
Categories
WikiProjects
WikiProject family tree
- WikiProject Science
- WikiProject Biology
- WikiProject Tree of Life
- WikiProject Animals
- WikiProject Tree of Life
- WikiProject Biology
More projects |
|---|
|
Things you can do
|
|
Here are some Open Tasks :
|
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
 Commons
Commons
Free media repository -
 Wikibooks
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
 Wikidata
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
 Wikinews
Wikinews
Free-content news -
 Wikiquote
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
 Wikisource
Wikisource
Free-content library -
 Wikispecies
Wikispecies
Directory of species -
 Wikiversity
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
 Wiktionary
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
References
- ↑ The application of DNA barcoding to taxonomy further complicates this; a 2016 barcoding analysis estimated a total count of nearly 100,000 insect species for Canada alone, and extrapolated that the global insect fauna must be in excess of 10 million species, of which nearly 2 million are in a single fly family known as gall midges (Cecidomyiidae).[8]
- ↑ Not including parasitoids.[4]
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Zhang, Zhi-Qiang (2013-08-30). "Animal biodiversity: An update of classification and diversity in 2013. In: Zhang, Z.-Q. (Ed.) Animal Biodiversity: An Outline of Higher-level Classification and Survey of Taxonomic Richness (Addenda 2013)". Zootaxa. 3703 (1): 5. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.3703.1.3. Archived from the original on 24 April 2019. Retrieved 2 March 2018.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Balian, E. V.; Lévêque, C.; Segers, H.; Martens, K. (2008). Freshwater Animal Diversity Assessment. Springer. p. 628. ISBN 978-1-4020-8259-7.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Hogenboom, Melissa. "There are only 35 kinds of animal and most are really weird". BBC Earth. Archived from the original on 10 August 2018. Retrieved 2 March 2018.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Poulin, Robert (2007). Evolutionary Ecology of Parasites. Princeton University Press. p. 6. ISBN 978-0-691-12085-0.
- 1 2 3 4 Felder, Darryl L.; Camp, David K. (2009). Gulf of Mexico Origin, Waters, and Biota: Biodiversity. Texas A&M University Press. p. 1111. ISBN 978-1-60344-269-5.
- ↑ "How many species on Earth? About 8.7 million, new estimate says". 24 August 2011. Archived from the original on 1 July 2018. Retrieved 2 March 2018.
- ↑ Mora, Camilo; Tittensor, Derek P.; Adl, Sina; Simpson, Alastair G.B.; Worm, Boris (2011-08-23). Mace, Georgina M. (ed.). "How Many Species Are There on Earth and in the Ocean?". PLOS Biology. 9 (8): e1001127. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1001127. PMC 3160336. PMID 21886479.
- ↑ Hebert, Paul D.N.; Ratnasingham, Sujeevan; Zakharov, Evgeny V.; Telfer, Angela C.; Levesque-Beaudin, Valerie; Milton, Megan A.; Pedersen, Stephanie; Jannetta, Paul; deWaard, Jeremy R. (1 August 2016). "Counting animal species with DNA barcodes: Canadian insects". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 371 (1702): 20150333. doi:10.1098/rstb.2015.0333. PMC 4971185. PMID 27481785.
- ↑ Stork, Nigel E. (January 2018). "How Many Species of Insects and Other Terrestrial Arthropods Are There on Earth?". Annual Review of Entomology. 63 (1): 31–45. doi:10.1146/annurev-ento-020117-043348. PMID 28938083. S2CID 23755007. Stork notes that 1m insects have been named, making much larger predicted estimates.
- ↑ Poore, Hugh F. (2002). "Introduction". Crustacea: Malacostraca. Zoological catalogue of Australia. Vol. 19.2A. CSIRO Publishing. pp. 1–7. ISBN 978-0-643-06901-5.
- 1 2 3 4 Reaka-Kudla, Marjorie L.; Wilson, Don E.; Wilson, Edward O. (1996). Biodiversity II: Understanding and Protecting Our Biological Resources. Joseph Henry Press. p. 90. ISBN 978-0-309-52075-1.
- ↑ Burton, Derek; Burton, Margaret (2017). Essential Fish Biology: Diversity, Structure and Function. Oxford University Press. pp. 281–282. ISBN 978-0-19-878555-2.
Trichomycteridae ... includes obligate parasitic fish. Thus 17 genera from 2 subfamilies, Vandelliinae; 4 genera, 9spp. and Stegophilinae; 13 genera, 31 spp. are parasites on gills (Vandelliinae) or skin (stegophilines) of fish.
- 1 2 3 4 Nicol, David (June 1969). "The Number of Living Species of Molluscs". Systematic Zoology. 18 (2): 251–254. doi:10.2307/2412618. JSTOR 2412618.
- ↑ Sluys, R. (1999). "Global diversity of land planarians (Platyhelminthes, Tricladida, Terricola): a new indicator-taxon in biodiversity and conservation studies". Biodiversity and Conservation. 8 (12): 1663–1681. doi:10.1023/A:1008994925673. S2CID 38784755.
- 1 2 Pandian, T. J. (2020). Reproduction and Development in Platyhelminthes. CRC Press. pp. 13–14. ISBN 9781000054903.
- ↑ Fontaneto, Diego. "Marine Rotifers | An Unexplored World of Richness" (PDF). JMBA Global Marine Environment. pp. 4–5. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2 March 2018. Retrieved 2 March 2018.
- ↑ Morand, Serge; Krasnov, Boris R.; Littlewood, D. Timothy J. (2015). Parasite Diversity and Diversification. Cambridge University Press. p. 44. ISBN 978-1-107-03765-6. Archived from the original on 12 December 2018. Retrieved 2 March 2018.
-
 List of all portals
List of all portals -

-

-

-

-

-

-
-

-

-
 Random portal
Random portal -
 WikiProject Portals
WikiProject Portals
.jpg.webp)






_caterpillars.jpg.webp)

.jpg.webp)




_on_a_tree_trunk.jpg.webp)






.png.webp)





.jpg.webp)


















.JPG.webp)





_Naggar%252C_Himachal_Pradesh%252C_2013_(cropped).JPG.webp)








