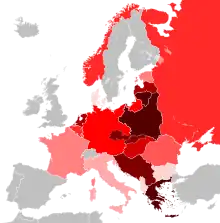
The World War II Portal Clockwise from top left: Commonwealth troops in the desert; Chinese civilians being buried alive by Japanese soldiers; Soviet forces during a winter offensive; Carrier-borne Japanese planes readying for take off; Soviet troops fighting in Berlin; A German submarine under attack. World War II, or the Second World War, was a global military conflict. It began as the joining of what had initially been two separate conflicts, with the first beginning in Asia in 1937 (the Second Sino-Japanese War) and the other beginning in Europe in 1939 (the German and Soviet invasion of Poland). The war split the majority of the world's nations into two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis. It involved the mobilization of over 100 million military personnel, making it the most widespread war in history, and placed the participants in a state of "total war", which erased the distinction between civil and military resources and resulted in the complete activation of a nation's economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities for the purposes of the war effort. Over 70 million people, the majority of them civilians, were killed, making it the deadliest conflict in human history. The Allies won the war, and as a result, the Soviet Union and the United States emerged as the world's leading superpowers. This set the stage for the Cold War, which lasted for the next 45 years. The United Nations was formed in the hope of preventing another such conflict. The self-determination spawned by the war accelerated decolonization movements in Asia and Africa, while Europe itself began moving toward integration. Featured article -
Selected equipment -
Selected battle -_low_in_the_water_on_30_January_1943.jpg.webp)
General imagesThe following are images from various World War II-related articles on Wikipedia.
Selected picture -
The mushroom cloud caused by the detonation of the "Fat Man" bomb during the atomic bombing of Nagasaki, Japan in 1945, rising approximately 18 kilometres (11 mi) above the hypocenter.
Selected biography -
Did you know...? -
CategoriesCategory puzzle World War II World War II by continent World War II by country Lists of World War II topics World War II-related lists Chronology of World War II Aftermath of World War II Battles and operations of World War II World War II casualties Collaboration during World War II World War II commemorations Cultural history of World War II Military deception during World War II Economic history of World War II Escapes and rescues during World War II Historiography of World War II The Holocaust Intelligence of World War II World War II legislation World War II and the media Military animals of World War II Military discipline and World War II Military equipment of World War II Military medicine in World War II Military units and formations of World War II World War II non-governmental organizations People of World War II Politics of World War II World War II propaganda World War II resistance movements Science and technology during World War II World War II sites Sociology of World War II Transport in World War II Unfree labor during World War II World War II crimes Works about World War II World War II stubs Selected quote -"This morning the British Ambassador in Berlin handed the German Government a final note, stating that, unless we heard from them by 11 o'clock that they were prepared at once to withdraw their troops from Poland, a state of war would exist between us. I have to tell you now that no such undertaking has been received and that consequently this country is at war with Germany."
TopicsRelated portalsThings you can doFrom the World War II task force of the Military history WikiProject:
Associated WikimediaMore portalsDiscover Wikipedia using portals
|







.svg.png.webp)












_3a.jpg.webp)



.jpg.webp)






.jpg.webp)











_burning_after_the_Japanese_attack_on_Pearl_Harbor_-_NARA_195617_-_Edit.jpg.webp)



.jpg.webp)