| Posterior communicating artery | |
|---|---|
 Schematic representation of the arterial circle and arteries of the brain (inferior view). Blood flows up to the brain through the vertebral arteries and the internal carotid arteries. | |
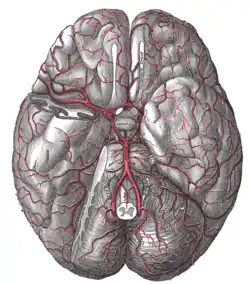 The brain and the arteries of the base of the brain, viewed from below, with the front of the brain at the top of the image. The temporal pole of the cerebrum and a portion of the cerebellar hemisphere have been removed on the right side. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | arteria cerebri communicans posterior |
| TA98 | A12.2.06.018 |
| TA2 | 4521 |
| FMA | 50084 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
In human anatomy, the left and right posterior communicating arteries are small[1]: 471 arteries at the base of the brain that form part of the circle of Willis.
Anteriorly, it unites with the internal carotid artery (ICA) (prior to the terminal bifurcation of the ICA into the anterior cerebral artery and middle cerebral artery); posteriorly, it unites with the posterior cerebral artery.
With the anterior communicating artery, the posterior communicating arteries establish a system of collateral circulation in cerebral circulation.
Anatomy
The arteries contribute to the blood supply of the optic tract.[1]: 465
The two posterior communicating arteries often differ in size.[1]: 472
Relations
Each posterior communicating artery is situated within the interpeduncular cistern, superolateral to the pituitary gland.[2]: 450 Each are is situated upon the medial surface of the ipsilateral cerebral peduncle[1]: 477 and adjacent to the anterior perforated substance.[1]: 471
The ipsilateral oculomotor nerve (CN III) passes inferolaterally to the artery[1]: 494 (pathology of the artery may thus compress the CN III[3]: 407 ).
Development
The development of the posterior cerebral artery (PCA) in the fetal brain occurs relatively late and arises from the fusion of several embryonic vessels near the caudal end of the posterior communicating artery.
The PCA begins as a continuation of the posterior communicating artery in 70-90% of fetuses with the remainder of PCAs having a basilar origin. The fetal carotid origin of the PCA usually regresses as the vertebral and basilar arteries become dominant and it finds a new origin in the basilar artery. About 20% of adults retain PCA origin from the posterior communicating artery, and in turn, the internal carotid arteries.[4]
Function
The brain is supplied with blood by the internal carotid arteries and also by the posterior cerebral arteries; the posterior communicating arteries connects the two systems. This provides redundancies or collaterals in the cerebral circulation so that, if one system is blocked or narrowed, the other can take over.
Clinical significance
Aneurysms of the posterior communicating artery are the third most common circle of Willis aneurysm[5] (the most common are anterior communicating artery aneurysms) and can lead to oculomotor nerve palsy.[6]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Sinnatamby, Chummy S. (2011). Last's Anatomy (12th ed.). ISBN 978-0-7295-3752-0.
- ↑ Sinnatamby, Chummy S. (2011). Last's Anatomy (12th ed.). ISBN 978-0-7295-3752-0.
- ↑ Sinnatamby, Chummy S. (2011). Last's Anatomy (12th ed.). ISBN 978-0-7295-3752-0.
- ↑ Osborn, Anne G.; Jacobs, John M. (1999), Diagnostic Cerebral Angiography, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, pp. 153
- ↑ Beck J, Rohde S, Berkefeld J, Seifert V, Raabe A. Size and location of ruptured and unruptured intracranial aneurysms measured by 3-dimensional rotational angiography. Surg Neurol. 2006 Jan;65(1):18-25; discussion 25-7. PMID 16378842.
- ↑ Dimopoulos VG, Fountas KN, Feltes CH, Robinson JS, Grigorian AA. Literature review regarding the methodology of assessing third nerve paresis associated with non-ruptured posterior communicating artery aneurysms. Neurosurg Rev. 2005 Oct;28(4):256-60. PMID 15947958.
External links
 Media related to Posterior communicating artery at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Posterior communicating artery at Wikimedia Commons- MedEd at Loyola Neuro/neurovasc/navigation/pcom.htm
- Anatomy photo:28:09-0209 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- "Anatomy diagram: 13048.000-1". Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator. Elsevier. Archived from the original on 2014-11-07.
- "Anatomy diagram: 13048.000-3". Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator. Elsevier. Archived from the original on 2012-07-22.