Prešov Region
Prešovský Kraj | |
|---|---|
From the top to bottom-left; High Tatras, Levoča, Stará Ľubovňa, Co-Cathedral of Saint Nicholas in Prešov, Spišská Kapitula, Stužica primeval forest, Bodružal | |
 Flag  Coat of arms | |
 Prešov Region | |
| Country | |
| Capital | Prešov |
| Government | |
| • Governor | Milan Majerský (KDH) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 8,973.69 km2 (3,464.76 sq mi) |
| Highest elevation | 2,654 m (8,707 ft) |
| Lowest elevation | 105 m (344 ft) |
| Population (2017 estimate) | |
| • Total | 822,946 |
| • Density | 92/km2 (240/sq mi) |
| GDP | |
| • Total | €7.451 billion (2016) |
| • Per capita | €9,070 (2016) |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) |
| ISO 3166 code | SK-PV |
| Website | www |
The Prešov Region, also Priashiv Region[2] (Slovak: Prešovský kraj, pronounced [ˈpreʂɔwskiː ˈkraj]; Hungarian: Eperjesi kerület; Ukrainian: Пряшівський край) is one of the eight Slovak administrative regions and consists of 13 districts (okresy) and 666 municipalities, 23 of which have town status. The region was established in 1996 and is the most populous of all the regions in Slovakia.[3] Its administrative center is the city of Prešov.
Geography
It is located in the north-eastern Slovakia and has an area of 8,975 km2. The region has a predominantly mountainous landscape. The subdivisions of Tatras – High Tatras and Belianske Tatras lie almost entirely in the region and include the highest point of Slovakia – Gerlachovský štít (2,654 ASL). Other mountain ranges and highlands in the region are Šarišská vrchovina, Čergov, Ondavská vrchovina, Slanské vrchy, Pieniny, Levoča Hills, Laborecká vrchovina, Bukovské vrchy, Vihorlat Mountains and Eastern Slovak Lowland. The basins in Prešov Region are Podtatranská kotlina, Hornadská kotlina and Košice Basin.
Major rivers in the region include the Poprad in the west, which is the only major Slovak river in the Baltic Sea watershed, a small part of Hornád in the south-west, a small part of Dunajec in the north, the Torysa in the centre and the Ondava and Laborec in the east. As for administrative divisions, the region borders on the Lesser Poland and Subcarpathian voivodeships in Poland in the north, Zakarpattia Oblast of Ukraine in the east, Košice Region in the south, Banská Bystrica Region in the south-west and Žilina Region in the west.
Demographics
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1980 | 678,386 | — |
| 1991 | 739,264 | +9.0% |
| 2001 | 789,968 | +6.9% |
| 2011 | 814,527 | +3.1% |
| 2021 | 808,931 | −0.7% |
| Source:[4] | ||
The population density in the region is 92.13/km2 (238.6/sq mi) (2020-06-30/-07-01),[5] which is below the country's average (110 per km2). The largest towns are Prešov, Poprad, Humenné, Bardejov and Snina. According to the 2011 census, there were 814,527 inhabitants in the region, with a majority of Slovaks (90.7%), with minorities of Roma (4.0%), Rusyns (2.7%) and there are small minorities of Ukrainians (<1%) and Czechs (<0.5%).[6]
Politics
Current governor of Prešov region is Milan Majerský (KDH). He won with 42,0 %. In election 2017 was elected also regional parliament :
County Council of Prešov region | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Type | |
| Type | |
| Houses | County Council |
| Leadership | |
Governor | |
| Structure | |
| Seats | 65 |
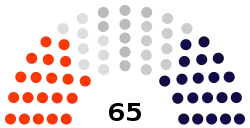 | |
Political groups |
|
| Elections | |
Last election | 29 October 2022 |
| Meeting place | |
| Prešov | |
| Website | |
| Council of Prešov region | |
Administrative division
The Prešov Region consists of 13 districts. There are 666 municipalities, of which 23 are towns, where about half of the region's population live.
List of districts
See also
References
- ↑ Regions and Cities > Regional Statistics > Regional Economy > Regional GDP per Capita, OECD.Stats. Accessed on 16 November 2018.
- ↑
- Magocsi, Paul R. (1999). Of the Making of Nationalities There is No End: Speeches, debates, bibliographic works. East European Monographs. p. 130. ISBN 9780880334389.
- Horbal, Bogdan; Krafcik, Patricia Ann; Rusinko, Elaine (2006). Carpatho-Rusyns and Their Neighbors: Essays in Honor of Paul Robert Magocsi. Eastern Christian Publications. p. 82. ISBN 9781892278630.
- Liber, George O. (2016). Total Wars and the Making of Modern Ukraine, 1914-1954. University of Toronto Press. p. 269. ISBN 9781442627086.
- ↑ "Demografia Prešovského samosprávneho kraja - VÚC Prešov" (in Slovak). Po-kraj.sk. Archived from the original on 2013-09-25. Retrieved 2013-08-19.
- ↑ "SLOVAKIA: Regions and Major Cities". Citypopulation. Retrieved 22 January 2021.
- ↑ "Statistic of Slovak places by Dušan Kreheľ – Export". Retrieved 2021-07-05.
- ↑ "POPULATION AND HOUSING CENSUS 2001 - Tab. 3a". 2006-11-29. Archived from the original on November 29, 2006. Retrieved 2013-08-19.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ↑ SaS, KDH, ZĽ
- ↑
Independet (8)
STANK (1) - ↑
Independet (8) - ↑
Independet (4)
Chance, PS, DS, ODS, Together (1)
Direction (1)
Republic (1)
Dawn (1)
Further reading
- Kopa, Ľudovít; et al. (2006). The Encyclopaedia of Slovakia and the Slovaks. Bratislava, Slovakia: Encyclopaedic Institute of the Slovak Academy of Sciences. ISBN 80-224-0925-1.
External links
- Prešovský samosprávny kraj Official website

.jpg.webp)



.jpg.webp)
.jpg.webp)