| PEPD | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | PEPD, PROLIDASE, peptidase D | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 613230 MGI: 97542 HomoloGene: 239 GeneCards: PEPD | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Xaa-Pro dipeptidase, also known as prolidase, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PEPD gene.[5][6][7]
Function
Xaa-Pro dipeptidase is a cytosolic dipeptidase that hydrolyzes dipeptides with proline or hydroxyproline at the carboxy terminus (but not Pro-Pro). It is important in collagen metabolism because of the high levels of imino acids.[7] Mutations at the PEPD locus cause prolidase deficiency. This is characterised by Iminodipeptidurea, skin ulcers, mental retardation and recurrent infections.
Structure
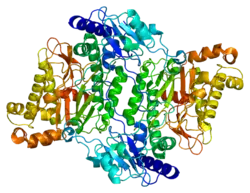
Prolidases fall under a subclass of metallopeptidases that involve binuclear active site metal clusters.[8] This metal cluster facilitates catalysis by serving as a substrate binding site, activating nucleophiles, and stabilizing the transition state. Furthermore, prolidases are classified under a smaller family called “pita-bread” enzymes, which cleave amido-, imido-, and amidino- containing bonds.[9] The “pita-bread” fold, containing a metal center flanked by two well-defined substrate binding pockets enabled prolidase to specifically cleave between any non-proline amino acid and proline.

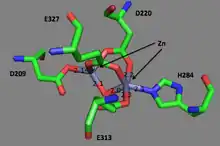
The first ever solved structure of prolidase came from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus (Pfprol).[8] This dimer has a crystal structure shows two approximately symmetrical monomers that both have an N-terminal domain, made up of a six-stranded mixed β-sheet flanked by five α-helices, a helical linker, and C-terminal domain, consisting of a mixed six-stranded β-sheet flanked by four α-helices. The curved β-sheet of Domain II has a “pita-bread” fold. The active site lies on the inner surface of the β-sheet of Domain II, with a notable dinuclear Co cluster anchored by the side chains of two aspartate residues (Asp209 and Asp220), two glutamate residues (Glu313 and Glu327), and a histidine residue (His284). Carboxylate groups of aspartate and glutamine residues serve as bridges between the two Co atoms. In the crystallization process, the Co atoms are replaced with Zn, which hinders enzymatic activity.
Unlike Pfprol, the structure of the human variant remains poorly understood. Sequence homology between human and Pfprol yield only 25% identity and 43% similarity.[10] The two available structures of human prolidase available on the Protein Data Bank are homodimers contain either Na or Mn, which bind to similar amino acids as those in Pfprol: Glu412 (Glu313 in Pfprol), binds to the first ion, Asp276 (Asp209 in Pfprol) binds to the second ion, and Asp287 and Glu452 bind to both (Asp220 and Glu327 in Pfprol).
Function
Due to proline’s cyclic structure, only few peptidases could cleave the bond between proline and other amino acids.[11] Along with prolinase, prolidase are the only known enzymes that can break down dipeptides to yield free proline. Prolidase serve to hydrolyze both dietary and endogenous Xaa-Pro dipeptides. More specifically, it is essential in catalyzing the last step of the degradation of procollagen, collagen, and other proline-containing peptides into free amino acids to be used for cellular growth.[12] Additionally, it also participates in the process of recycling proline from Xaa-Pro dipeptides for collagen resynthesis. Proline and hydroyxyproline make up a quarter of the amino acid residues in collagen, which is the most abundant protein in the body by mass and plays an important role in maintaining connective tissue in the body.[12][13]
Mechanism
The mechanism for prolidase catalytic activity remains largely uncharacterized.[14] However, biochemical and structural analyses of aminopeptidase (APPro), methionine aminopeptidase (MetAP), and prolidase, all members of the “pita-bread” metalloenzymes, suggest that they share a common mechanism scheme.[9] The main difference arises in the location of the carbonyl oxygen atom of the scissile peptide bond.

The following mechanism shows a proposed scheme for a metal-dependent “pita-bread” enzyme with residue numbering corresponding to those found in methionine aminopeptidase from E. coli.[9] As shown in Intermediate I of the figure, three potential acidic amino acid residues interact with the N-terminus of the substrate in a fashion that is yet to be determined. The carbonyl and amide groups of the scissile peptide bond interact with the first metal ion, M1, in addition to His178 and His79, respectively. M1 and Glu204 activate a water molecule to prepare it nucleophilic attack at the carbonyl carbon of the scissile peptide bond. Then, the tetrahedral intermediate (Intermediate II) becomes stabilized from interactions with M1 and His178. Lastly, Glu204 donates a proton to the amine of the leaving peptide (P1’). This leads to the breakdown of the intermediate (Intermediate III), which retains its interactions with M1 and His178.
Regulation
Post-translational modifications of prolidase regulate its enzymatic abilities. Phosphorylation of prolidase has been shown to increase its activity while dephosphorylation leads to a decrease in enzyme activity.[15] Analysis of known consensus sequence required for serine/threonine phosphorylation revealed that prolidase contains at least three potential sites for serine/threonine phosphorylation. Nitric oxide, both exogenously acquired and endogenously generated, was shown to increase prolidase activity in a time- and dose-dependent manner via phosphorylation at these serine and threonine sites.[16] Additionally, prolidase may also be regulated at tyrosine phosphorylation sites, which are mediated by FAK and MAPK signaling pathways.[15]
Disease relevance
Deficiency in prolidase leads to a rare, severe autosomal recessive disorder (prolidase deficiency) that causes many chronic, debilitating health conditions in humans.[17] These phenotypical symptoms vary and may include skin ulcerations, mental retardation, splenomegaly, recurrent infections, photosensitivity, hyperkeratosis, and unusual facial appearance. Furthermore, prolidase activity was found to be abnormal compared to healthy levels in various medical conditions including but limited to: bipolar disorder, breast cancer, endometrial cancer, keloid scar formation, erectile dysfunction, liver disease, lung cancer, hypertension, melanoma, and chronic pancreatitis.[11] In some cancers with increased levels of prolidase activity, such as melanoma, the differential expression of prolidase and its substrate specificity for dipeptides with proline at the carboxyl end suggests the potential of prolidase in becoming a viable, selective endogenous enzyme target for proline prodrugs.[18] Serum prolidase enzyme activity is also currently being explored as a possible, reliable marker for diseases including chronic hepatitis B and liver fibrosis.[19][20][21]
Other applications
Decontamination: Prolidase from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus (Pfprol) shows potential for application in decontamination of organophosphorus nerve agents in chemical warfare agents.[22] Additionally, prolidase could also serve to detect fluorine-containing organophosphorus neurotoxins, like the G-type chemical warfare agents, and could antagonize organophosphorous intoxication and protect against the effects of diisopropylfluorophosphate when encapsulated in liposomes.[23][24]
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000124299 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000063931 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Endo F, Tanoue A, Nakai H, Hata A, Indo Y, Titani K, Matsuda I (March 1989). "Primary structure and gene localization of human prolidase". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 264 (8): 4476–81. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)83768-1. PMID 2925654.
- ↑ Tanoue A, Endo F, Matsuda I (July 1990). "Structural organization of the gene for human prolidase (peptidase D) and demonstration of a partial gene deletion in a patient with prolidase deficiency". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 265 (19): 11306–11. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(19)38592-8. PMID 1972707.
- 1 2 "Entrez Gene: PEPD peptidase D".
- 1 2 Maher MJ, Ghosh M, Grunden AM, Menon AL, Adams MW, Freeman HC, Guss JM (March 2004). "Structure of the prolidase from Pyrococcus furiosus". Biochemistry. 43 (10): 2771–83. doi:10.1021/bi0356451. PMID 15005612.
- 1 2 3 4 Lowther WT, Matthews BW (December 2002). "Metalloaminopeptidases: common functional themes in disparate structural surroundings". Chemical Reviews. 102 (12): 4581–608. doi:10.1021/cr0101757. PMID 12475202.
- ↑ Lupi A, Tenni R, Rossi A, Cetta G, Forlino A (November 2008). "Human prolidase and prolidase deficiency: an overview on the characterization of the enzyme involved in proline recycling and on the effects of its mutations". Amino Acids. 35 (4): 739–52. doi:10.1007/s00726-008-0055-4. PMID 18340504. S2CID 925797.
- 1 2 Kitchener RL, Grunden AM (August 2012). "Prolidase function in proline metabolism and its medical and biotechnological applications". Journal of Applied Microbiology. 113 (2): 233–47. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2672.2012.05310.x. PMID 22512465. S2CID 22164798.
- 1 2 Surazynski A, Miltyk W, Palka J, Phang JM (November 2008). "Prolidase-dependent regulation of collagen biosynthesis". Amino Acids. 35 (4): 731–8. doi:10.1007/s00726-008-0051-8. PMID 18320291. S2CID 13025572.
- ↑ Phang JM, Donald SP, Pandhare J, Liu Y (November 2008). "The metabolism of proline, a stress substrate, modulates carcinogenic pathways". Amino Acids. 35 (4): 681–90. doi:10.1007/s00726-008-0063-4. PMID 18401543. S2CID 26081769.
- ↑ Graham SC, Lilley PE, Lee M, Schaeffer PM, Kralicek AV, Dixon NE, Guss JM (January 2006). "Kinetic and crystallographic analysis of mutant Escherichia coli aminopeptidase P: insights into substrate recognition and the mechanism of catalysis". Biochemistry. 45 (3): 964–75. doi:10.1021/bi0518904. PMID 16411772.
- 1 2 Surazyński A, Pałka J, Wołczyński S (April 2001). "Phosphorylation of prolidase increases the enzyme activity". Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry. 220 (1–2): 95–101. doi:10.1023/a:1010849100540. PMID 11451388. S2CID 25456347.
- ↑ Surazynski A, Liu Y, Miltyk W, Phang JM (December 2005). "Nitric oxide regulates prolidase activity by serine/threonine phosphorylation". Journal of Cellular Biochemistry. 96 (5): 1086–1094. doi:10.1002/jcb.20631. PMID 16167338. S2CID 33258991.
- ↑ Viglio S, Annovazzi L, Conti B, Genta I, Perugini P, Zanone C, et al. (February 2006). "The role of emerging techniques in the investigation of prolidase deficiency: from diagnosis to the development of a possible therapeutical approach". Journal of Chromatography B. 832 (1): 1–8. doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2005.12.049. PMID 16434239.
- ↑ Mittal S, Song X, Vig BS, Landowski CP, Kim I, Hilfinger JM, Amidon GL (2005). "Prolidase, a potential enzyme target for melanoma: design of proline-containing dipeptide-like prodrugs". Molecular Pharmaceutics. 2 (1): 37–46. doi:10.1021/mp049922p. PMID 15804176.
- ↑ Şen V, Uluca Ü, Ece A, Kaplan İ, Bozkurt F, Aktar F, et al. (November 2014). "Serum prolidase activity and oxidant-antioxidant status in children with chronic hepatitis B virus infection". Italian Journal of Pediatrics. 40 (1): 95. doi:10.1186/s13052-014-0095-1. PMC 4247636. PMID 25425101.
- ↑ Duygu F, Aksoy N, Cicek AC, Butun I, Unlu S (September 2013). "Does prolidase indicate worsening of hepatitis B infection?". Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis. 27 (5): 398–401. doi:10.1002/jcla.21617. PMC 6807447. PMID 24038226.
- ↑ Stanfliet JC, Locketz M, Berman P, Pillay TS (May 2015). "Evaluation of the utility of serum prolidase as a marker for liver fibrosis". Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis. 29 (3): 208–13. doi:10.1002/jcla.21752. PMC 6807100. PMID 24798655.
- ↑ Theriot CM, Du X, Tove SR, Grunden AM (August 2010). "Improving the catalytic activity of hyperthermophilic Pyrococcus prolidases for detoxification of organophosphorus nerve agents over a broad range of temperatures". Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology. 87 (5): 1715–26. doi:10.1007/s00253-010-2614-3. PMID 20422176. S2CID 1363629.
- ↑ Simonian AL, Grimsley JK, Flounders AW, Schoeniger JS, Cheng TC, DeFrank JJ, Wild JR (2001). "Enzyme-based biosensor for the direct detection of fluorine-containing organophosphates". Analytica Chimica Acta. 442: 15–23. doi:10.1016/S0003-2670(01)01131-X.
- ↑ Petrikovics I, Cheng TC, Papahadjopoulos D, Hong K, Yin R, DeFrank JJ, et al. (September 2000). "Long circulating liposomes encapsulating organophosphorus acid anhydrolase in diisopropylfluorophosphate antagonism". Toxicological Sciences. 57 (1): 16–21. doi:10.1093/toxsci/57.1.16. PMID 10966507.
Further reading
- Tanoue A, Endo F, Kitano A, Matsuda I (July 1990). "A single nucleotide change in the prolidase gene in fibroblasts from two patients with polypeptide positive prolidase deficiency. Expression of the mutant enzyme in NIH 3T3 cells". The Journal of Clinical Investigation. 86 (1): 351–5. doi:10.1172/JCI114708. PMC 296729. PMID 2365824.
- Boright AP, Scriver CR, Lancaster GA, Choy F (May 1989). "Prolidase deficiency: biochemical classification of alleles". American Journal of Human Genetics. 44 (5): 731–40. PMC 1715628. PMID 2705457.
- Friedrich U, Brunner H, Smeets D, Lambermon E, Ropers HH (March 1987). "Three-point linkage analysis employing C3 and 19cen markers assigns the myotonic dystrophy gene to 19q". Human Genetics. 75 (3): 291–3. doi:10.1007/BF00281077. PMID 2881880. S2CID 24376519.
- Maruyama K, Sugano S (January 1994). "Oligo-capping: a simple method to replace the cap structure of eukaryotic mRNAs with oligoribonucleotides". Gene. 138 (1–2): 171–4. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(94)90802-8. PMID 8125298.
- Ledoux P, Scriver C, Hechtman P (June 1994). "Four novel PEPD alleles causing prolidase deficiency". American Journal of Human Genetics. 54 (6): 1014–21. PMC 1918181. PMID 8198124.
- Ledoux P, Scriver CR, Hechtman P (November 1996). "Expression and molecular analysis of mutations in prolidase deficiency". American Journal of Human Genetics. 59 (5): 1035–9. PMC 1914827. PMID 8900231.
- Pałka JA (1997). "The role of prolidase as an enzyme participating in the metabolism of collagen". Roczniki Akademii Medycznej W Bialymstoku. 41 (2): 149–60. PMID 9020526.
- Palka JA, Phang JM (November 1997). "Prolidase activity in fibroblasts is regulated by interaction of extracellular matrix with cell surface integrin receptors". Journal of Cellular Biochemistry. 67 (2): 166–75. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-4644(19971101)67:2<166::AID-JCB2>3.0.CO;2-V. PMID 9328822. S2CID 30974724.
- Suzuki Y, Yoshitomo-Nakagawa K, Maruyama K, Suyama A, Sugano S (October 1997). "Construction and characterization of a full length-enriched and a 5'-end-enriched cDNA library". Gene. 200 (1–2): 149–56. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(97)00411-3. PMID 9373149.
- Muszyńska A, Pałka J, Gorodkiewicz E (May 2000). "The mechanism of daunorubicin-induced inhibition of prolidase activity in human skin fibroblasts and its implication to impaired collagen biosynthesis". Experimental and Toxicologic Pathology. 52 (2): 149–55. doi:10.1016/s0940-2993(00)80108-6. PMID 10965990.
- Surazyński A, Pałka J (2002). "FAK-independent regulation of prolidase activity and collagen biosynthesis in MCF-7 cells". Folia Histochemica et Cytobiologica. 39 (Suppl 2): 212–3. PMID 11820613.
- Harris RA, Yang A, Stein RC, Lucy K, Brusten L, Herath A, et al. (February 2002). "Cluster analysis of an extensive human breast cancer cell line protein expression map database". Proteomics. 2 (2): 212–23. doi:10.1002/1615-9861(200202)2:2<212::AID-PROT212>3.0.CO;2-H. PMID 11840567. S2CID 44946014.
- Forlino A, Lupi A, Vaghi P, Icaro Cornaglia A, Calligaro A, Campari E, Cetta G (October 2002). "Mutation analysis of five new patients affected by prolidase deficiency: the lack of enzyme activity causes necrosis-like cell death in cultured fibroblasts". Human Genetics. 111 (4–5): 314–22. doi:10.1007/s00439-002-0792-5. PMID 12384772. S2CID 40260709.
- Beausoleil SA, Jedrychowski M, Schwartz D, Elias JE, Villén J, Li J, et al. (August 2004). "Large-scale characterization of HeLa cell nuclear phosphoproteins". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 101 (33): 12130–5. Bibcode:2004PNAS..10112130B. doi:10.1073/pnas.0404720101. PMC 514446. PMID 15302935.
- Lupi A, De Riso A, Della Torre S, Rossi A, Campari E, Vilarinho L, et al. (2004). "Characterization of a new PEPD allele causing prolidase deficiency in two unrelated patients: natural-occurrent mutations as a tool to investigate structure-function relationship". Journal of Human Genetics. 49 (9): 500–6. doi:10.1007/s10038-004-0180-1. PMID 15309682.