Buol Regency
Kabupaten Buol | |
|---|---|
 Coat of arms | |
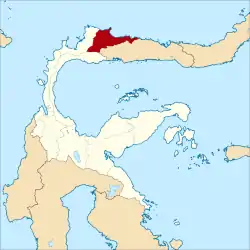 Location within Central Sulawesi | |
| Coordinates: 1°00′38″N 121°21′15″E / 1.010469°N 121.354250°E | |
| Country | Indonesia |
| Province | Central Sulawesi |
| Capital | Buol |
| Government | |
| • Regent | Amirudin Rauf |
| • Vice Regent | Abdullah Batalipu |
| Area | |
| • Total | 4,043.57 km2 (1,561.23 sq mi) |
| Population (mid 2022 estimate)[1] | |
| • Total | 148,246 |
| • Density | 37/km2 (95/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (ICST) |
| Area code | (+62) 445 |
| Website | buolkab |
Buol Regency (Indonesian: Kabupaten Buol) is a regency (second-level administrative division) of Central Sulawesi Province of Indonesia. It was created on 4 October 1999, having previously been the eastern half of a larger Buol Tolitoli Regency. It covers an area of 4,043.57 km2, and had a population of 132,330 at the 2010 Census;[2] and 145,254 (comprising 74,624 males and 70,630 females) at the 2020 Census;[3] the official estimate as at mid 2022 was 148,246 (comprising 75,250 males and 72,296 females).[1] The administrative centre is the town of Buol, in Biau District.
Administration
The Buol Regency was divided at 2020 into eleven districts (kecamatan), tabulated below with their areas and their populations at the 2010 Census[2] and 2020 Census,[3] together with the official estimates as at mid 2022.[1] The table includes the locations of the district administrative centres, the number of administrative villages in each district (108 rural desa and 7 urban kelurahan in total), and its postal code.
| Kode Wilayah | Name of District (kecamatan) | Area in km2 | Pop'n Census 2010 | Pop'n Census 2020 | Pop'n Estimate mid 2022 | Admin centre | No. of villages | Post code |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 72.05.02 | Lakea | 208.55 | 9,700 | 11,040 | 11,300 | Lakea II | 7 | 94573 |
| 72.05.06 | Biau | 217.80 | 27,567 | 29,516 | 29,950 | Leok II | 7 (a) | 94563 |
| 72.05.10 | Karamat | 153.10 | 8,296 | 9,734 | 9,963 | Busak I | 7 | 94572 |
| 72.05.01 | Momunu | 400.40 | 13,869 | 15,665 | 16,098 | Lamadong I | 16 | 94565 |
| 72.05.07 | Tiloan | 1,437.70 | 9,955 | 9,384 | 9,529 | Air Terang | 9 | 94566 |
| 72.05.03 | Bokat | 196.10 | 12,609 | 15,045 | 15,460 | Bokat | 15 | 94564 |
| 72.05.08 | Bukal | 355.52 | 13,485 | 14,746 | 15,123 | Unone | 14 | 94571 |
| 72.05.04 | Bunobogu | 327.15 | 8,814 | 9,764 | 9,955 | Bunobogu Selatan | 10 | 94568 |
| 72.05.09 | Gadung | 160.38 | 11,337 | 11,912 | 12,072 | Bulagidun | 11 | 94515 |
| 72.05.05 | Paleleh (b) | 386.19 | 11,323 | 12,342 | 12,583 | Paleleh | 12 | 94569 |
| 72.05.11 | Paleleh Barat (West Paleleh) | 200.68 | 5,375 | 6,106 | 6,213 | Timbulon | 7 | 94574 |
| Totals | 4,043.57 | 132,330 | 145,254 | 148,246 | Buol | 115 |
Notes: (a) comprising all 7 kelurahan (urban villages). (b) including seven offshore islands.
Demography
The Buol-speaking people live in the districts which now comprise the Buol regency (in Central Sulawesi Province) which borders the Gorontalo province. Formerly mountain dwellers, the Buol now live in scattered villages on the central part of the northern peninsula, to the north-west of the Gorontalo province. The history of the Buol region is one of the rise and fall of small kingdoms and their occasional confederation into larger entities for defense and conquest. Sometimes, the Buol people are treated as a subgroup of the Gorontalo people group due to cultural and linguistic similarities. The Buol language is part of a larger linguistic grouping called the Gorontalic family which also includes the Bintauna, Kaidipang, Bolango, Gorontalo, Lolak and Suwawa languages.[4]