
South Korea is a major energy importer, importing nearly all of its oil needs and ranking as the second-largest importer of liquefied natural gas in the world. Electricity generation in the country mainly comes from conventional thermal power, which accounts for more than two thirds of production, and from nuclear power.[1]
Energy producers were dominated by government enterprises, although privately operated coal mines and oil refineries also existed. The National Assembly enacted a broad electricity sector restructuring program in 2000, but the restructuring process was halted amid political controversy in 2004 and remains a topic of intense political debate.[2]
South Korea has no proven oil reserves.[1] Exploration until the 1980s in the Yellow Sea and on the continental shelf between Korea and Japan did not find any offshore oil. Coal supply in the country is insufficient and of low quality. The potential for hydroelectric power is limited because of high seasonal variations in the weather and the concentration of most of the rainfall in the summer. As of 2017, South Korean President Moon Jae-in has vowed to end the country’s reliance on coal and also said the nation would move away from nuclear energy. He has taken a major step in that direction in June, saying his country would not try to extend the life of its nuclear plants, would close existing coal-fired plants, and would not build any new coal plants.[3]
In recent years, South Korea has set a new direction for its energy sector, with significant decarbonization goals, aiming to raise the share of electricity from renewable sources from 6% in 2019 to 35% by 2030.[4][5]
Overview
Final energy consumption by source (2010):[6]
- Coal: 27.6 Mtoe (million tonne of oil equivalent) (14.2%)
- Petroleum: 100.5 Mtoe (51.6%)
- LNG: 21.9 Mtoe (11.3%)
- Electricity: 37.3 Mtoe (19.2%)
- Heat: 1.7 Mtoe (0.9%)
- Renewable: 5.8 Mtoe (3%)
| Capita | Prim. energy | Production | Import | Electricity | CO2-emission | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Million | TWh | TWh | TWh | TWh | Mt | |
| 2004 | 48.08 | 2,478 | 442 | 2,140 | 355 | 462 |
| 2007 | 48.46 | 2,584 | 494 | 2,213 | 412 | 489 |
| 2008 | 48.61 | 2,639 | 520 | 2,269 | 430 | 501 |
| 2009 | 48.75 | 2,665 | 515 | 2,304 | 438 | 515 |
| 2010 | 48.88 | 2,908 | 522 | 2,571 | 481 | 563 |
| 2012 | 49.78 | 3,029 | 546 | 2,644 | 506 | 588 |
| 2012R | 50.00 | 3,064 | 538 | 2,659 | 517 | 593 |
| 2013 | 50.22 | 3,068 | 507 | 2,723 | 524 | 572 |
| Change 2004-10 | 1.7% | 17.3% | 18.1% | 20.1% | 35.5% | 21.9% |
| Mtoe = 11.63 TWh, Prim. energy includes energy losses that are 2/3 for nuclear power[8]
2012R = CO2 calculation criteria changed, numbers updated | ||||||
Electric power
History
The Korea Electric Power Corporation (KEPCO) provided electricity in the country. When KEPCO's predecessor, KECO, was founded in 1961, annual power production was 1,770 GWh. Production reached 73,992 GWh in 1987. In that year, residential customers used 17.9% of total production, public and service businesses used 16.2%, and the industrial sector used 65.9%. Sources of power generation were primarily nuclear power, coal, oil, and liquefied natural gas. Of the 54,885 GWh of electricity generated in 1985, 22% came from nuclear plants then in operation, 74% from non-nuclear thermal plants (oil and coal), and 4% from hydroelectric sites. It was predicted in 1988 that the generation structure by the year 2000 would be 10.2% hydroelectric, 12.2% oil, 22.9% coal, 10.2% LNG, and 44.5% nuclear.
Statistics
| Source | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 |
| Thermal | 264,747 (62.7%) | 278,400 (64.2%) | 315,608 (66.5%) | 324,354 (65.3%) |
| Nuclear | 150,958 (35.7%) | 147,771 (34.1%) | 148,596 (31.3%) | 154,723 (31.1%) |
| Hydro | 5,561 (1.3%) | 5,641 (1.3%) | 6,472 (1.4%) | 7,831 (1.6%) |
| Other | 1,090 (0.3%) | 1,791 (0.4%) | 3,984 (0.8%) | 9,985 (2.0%) |
| Total | 422,355 | 433,604 | 474,660 | 496,893 |
Sources
Thermal
- KEPCO (한국전력공사) controls 5 regional gencos who sell via KPX to the grid:
- Korea East-West Power (한국동서발전㈜)
- Korea Midland Power (한국중부발전㈜)
- Korea South-Eastern Power (한국남동발전㈜)
- Korea Southern Power (한국남부발전㈜)
- Korea Western Power (한국서부발전㈜)
KOGAS (한국가스공사) acts as importer of LNG for the power generators.
Cogeneration and steam-heating
- Korea District Heating Corporation (KDHC, 한국지역난방공사㈜) supplies steam and CHP to the Seoul area and Daegu. GS Power and SH Corp are local providers. KDHC is the world's largest district heating company.
Nuclear Power
South Korea placed a heavy emphasis on nuclear power generation. The country's first nuclear power plant, the Kori Number One located near Pusan, which opened in 1977. Eight plants operated in 1987 when atomic power generation was an estimated 71,158 million kilowatts, or 53.1% of total electric power.
Renewable energy
After years of incremental policy changes and investments, the country has set ambitious targets and announced major projects.[9] In 2021, President Moon Jae-in announced a planned 8.2GW offshore wind farm that will be the largest in the world.[10]
The country's national Renewable Portfolio Standard (RPS) previously required a gradual increase of the renewable share of electricity generation from 2% in 2012 to 10% in 2023.[11] The 9th Basic Plan for Long-term Electricity Supply and Demand 2020–2034, released in 2021, now targets 35% by 2030.[12]
South Korea is fast-growing gigawatt-market for photovoltaics (PV) and plans to install 31 GW of solar power by 2030.
Hydro also comes under Korea Hydro & Nuclear Power Ltd. (한국수력원자력㈜)
Storage
In December 2017, Hyundai Electric announced a plan to build a 150MW grid storage battery near Ulsan for Korea Zinc.[13]
Global warming
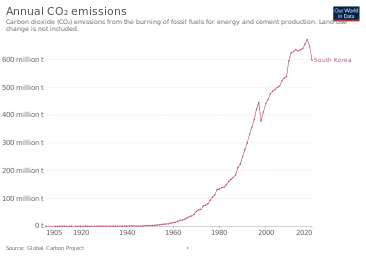
According to the Carbon Dioxide Information Analysis Center CDIAC South Korea is among the top ten, namely ninth, highest country in carbon dioxide emissions in the period 1950-2005. The United States (25%), China (10%) and Russia (8%) are the countries with the highest carbon dioxide emissions from 1950 to 2005.[14]
See also
References
- 1 2 "Korea, South". US Energy Information Administration. Retrieved 25 July 2013.
- ↑ "Which Direction for South Korean Electricity Policy?" (PDF). Korean Energy Economic Review 13 (2014) 145-178. Retrieved 6 June 2014.
- ↑ "South Korean President Details Phase-out of Coal, Nuclear Power". 1 August 2017.
- ↑ Lee, Kyeongho (Ken) (2021-03-02). "South Korea's 9th Basic Plan for electricity – a step closer to carbon neutrality?". www.woodmac.com. Retrieved 2021-09-27.
- ↑ "International - U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA)". www.eia.gov. Retrieved 2021-09-27.
- ↑ http://www.polsoz.fu-berlin.de/polwiss/forschung/systeme/ffu/veranstaltungen_aktuell/veranstaltungen_downloads/11_salzburg/Leem.pdf%5B%5D
- ↑ IEA Key World Energy Statistics Statistics 2015 Archived 2016-03-13 at WebCite, 2014 (2012R as in November 2015 Archived 2015-05-05 at WebCite + 2012 as in March 2014 is comparable to previous years statistical calculation criteria, 2013 Archived 2014-09-02 at the Wayback Machine, 2012 Archived 2013-03-09 at the Wayback Machine, 2011 Archived 2011-10-27 at the Wayback Machine, 2010 Archived 2010-10-11 at the Wayback Machine, 2009 Archived 2013-10-07 at the Wayback Machine, 2006 Archived 2009-10-12 at the Wayback Machine IEA October, crude oil p.11, coal p. 13 gas p. 15
- ↑ Energy in Sweden 2010 Archived October 16, 2013, at the Wayback Machine, Facts and figures, The Swedish Energy Agency, Table 8 Losses in nuclear power stations Table 9 Nuclear power brutto
- ↑ "Greentech Media | South Korea Boosts Renewable-Energy Investments by 60%". Archived from the original on 2008-12-16. Retrieved 2016-02-05.
- ↑ "South Korea announces ambitious 8.2GW wind complex". Renewable Energy World. 2021-02-17. Retrieved 2021-09-27.
- ↑ International Trade Administration (August 13, 2021). "South Korea - Country Commercial Guide". Retrieved September 26, 2021.
- ↑ Lee, Kyeongho (Ken) (2021-03-02). "South Korea's 9th Basic Plan for electricity – a step closer to carbon neutrality?". www.woodmac.com. Retrieved 2021-09-27.
- ↑ Graham, Karen (7 December 2017). "Hyundai building 150 MW energy storage battery in South Korea". Digital Journal. Retrieved 21 February 2018.
- ↑ State of the world 2009, Worldwatch institute 2009, statistics 219-223, CDIAC Carbon dioxide information analysis center (http://www.cdiac.ornl.gov/trends%5B%5D)