| Designations | |
|---|---|
| Official name | Partie camerounaise du fleuve Sangha |
| Designated | 2 February 2008 |
| Reference no. | 1739[1] |
| Official name | Sangha-Nouabalé-Ndoki |
| Designated | 4 March 2009 |
| Reference no. | 1858[2] |
| Official name | Riviere Sangha située en République Centrafricaine |
| Designated | 5 November 2009 |
| Reference no. | 1889[3] |

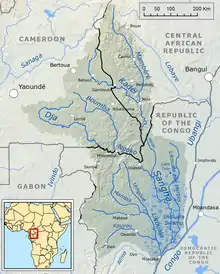
The Sangha River (Kikongo: Nzâdi Sangha, French: Rivière Sangha), a tributary of the Congo River, is located in Central Africa.
Geography
The Sangha River is formed at the confluence of the Mambéré River and the Kadéï River at Nola in the western Central African Republic. (3°30′55″N 16°2′50″E / 3.51528°N 16.04722°E) The Sangha flows along the border of Cameroon, with the Central African Republic, and then the Republic of Congo. It joins the Congo River at 1°12′45″S 16°49′40″E / 1.21250°S 16.82778°E
The tributaries of the Sangha River include the Ngoko River (Dja river). Its river mouth and confluence with the Sangha is at Ouésso, in the Republic of the Congo. (1°39′5″N 16°3′25″E / 1.65139°N 16.05694°E).
Ecology
The Sangha River is a Freshwater ecoregion of Africa. Its wetlands in the Central African Republic, Cameroon and Congo are protected Ramsar sites.
References
- ↑ "Partie camerounaise du fleuve Sangha". Ramsar Sites Information Service. Retrieved 25 April 2018.
- ↑ "Sangha-Nouabalé-Ndoki". Ramsar Sites Information Service. Retrieved 25 April 2018.
- ↑ "Riviere Sangha située en République Centrafricaine". Ramsar Sites Information Service. Retrieved 25 April 2018.
External links