| Bern S-Bahn | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 | |||
 A BLS S-Bahn train at Thun in 2013 | |||
| Overview | |||
| Locale | Bern, Switzerland | ||
| Transit type | S-Bahn | ||
| Number of lines | 13 | ||
| Daily ridership | 175,000 (weekdays) | ||
| Website | S-Bahn Bern (in German) | ||
| Operation | |||
| Began operation | 1974 (Bern) 1995 (regional) | ||
| Operator(s) | BLS AG Regionalverkehr Bern-Solothurn (RBS) | ||
| Technical | |||
| Track gauge | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in) (BLS) 1,000 mm (3 ft 3+3⁄8 in) (RBS) | ||
| |||
The Bern S-Bahn (German: S-Bahn Bern; French: RER Berne) is an S-Bahn commuter rail network focused on Bern, the capital city of Switzerland. The network is roughly coterminous with Bern's urban agglomeration.
With approximately 9 million train kilometres per year, the Bern S-Bahn is the second-largest S-Bahn in Switzerland. It handles around 100,000 passengers daily (175,000 on weekdays), and thus carries the majority of the agglomeration's regional public transport traffic.
History
As early as 1974, Vereinigte Bern–Worb-Bahnen (VBW), forerunner of Regionalverkehr Bern-Solothurn (RBS), began operating S-Bahn-style clock-face schedule services in the Bern area.[1] The next step came in 1987, when Swiss Federal Railways (SBB) began running trains from Thun through Bern to Laupen BE or Fribourg on a half-hourly schedule.[2]
The second line began operation on 28 May 1995, operating from Schwarzenburg to Trubschachen.[3] At this time the "S"-style designations were introduced to differentiate the lines.
The next expansion occurred in 1998, with the commissioning of the S3 (Biel/Bienne−Belp) and the S4 (Bern–Bern Bümpliz Nord−Burgdorf and beyond). The S33 and S44 supplemented service on the S3 and S4, while the S5 designation was applied to regional services between Bern and Neuchâtel. Also introduced was the S55 for services from Bern to Murten/Morat via Kerzers.[4][5]
2005
The December 2004 timetable change saw major expansions of the Bern S-Bahn concept. This was partly enabled by infrastructure improvements carried out under the Rail 2000 program. The three RBS lines were formally incorporated into the network, SBB transferred the operation of the S1 and S3 to the Bern-Lötschberg-Simplon-Bahn (BLS). [6] The network now consisted of the following services:[7]
| Number | Route | Frequency | Operator |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | Fribourg/Laupen BE–Flamatt–Bern–Thun | Every 30 minutes | BLS |
| S11 | Bern–Fribourg | Rush-hour | BLS |
| S2 | Schwarzenburg–Bern–Langnau i.E. | Every 30 minutes | BLS |
| S22 | Schwarzenburg–Bern | Rush-hour | BLS |
| S3 | Biel/Bienne–Bern–Belp | Every 30 minutes | BLS |
| S33 | Bern–Belp–Thun | Every 30 minutes | BLS |
| S4 | Rosshäusern–Bern–Burgdorf–Affoltern-Weier | Every 60 minutes | RM |
| S44 | Rosshäusern–Bern–Burgdorf–Langnau i.E./Wiler | Every 60 minutes | RM |
| S5 | Bern–Kerzers–Neuchâtel/Murten (–Payerne) | Every 60 minutes | BLS |
| S51 | Bern–Bern Bümpliz Nord | Rush-hour | BLS |
| S7 | Bern–Bolligen–Worb Dorf | Every 15 minutes | RBS |
| S8 | Bern–Jegenstorf | Every 15 minutes | RBS |
| S9 | Bern–Unterzollikofen | Every 15 minutes | RBS |
2009
The December 2008 timetable change saw several major alterations to the standard gauge part of the network. On the Lausanne–Bern line, the S11 was eliminated, and the S1 began operating half-hourly between Flamatt and Fribourg and skipping most local stops between Flamatt and Niederwangen. The S2's western terminus was changed from Schwarzenburg to Laupen BE. On the Bern–Schwarzenburg railway line, the new S6 replaced the S2 and S22, offering a half-hourly service between Schwarzenburg and Bern. On the Bern–Neuchâtel line, the new S52 replaced the S4 and S44 between Bern and Rosshäusern, and was extended to Kerzers, while the S51 was increased to half-hourly service and extended to the new station at Bern Brünnen Westside. The S4 and S44 were re-routed over the Bern–Belp–Thun line to Thun via Belp, in place of the S33.[8]
| Number | Route | Frequency | Operator |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | Fribourg–Bern–Thun | Every 30 minutes | BLS[lower-alpha 1] |
| S2 | Laupen BE–Bern–Langnau i.E. | Every 30 minutes | BLS |
| S3 | Biel/Bienne–Bern–Belp (–Thun) | Every 30 minutes | BLS |
| S4 | Thun–Bern–Burgdorf–Affoltern-Weier | Every 60 minutes | BLS[lower-alpha 1] |
| S44 | Thun–Bern–Burgdorf–Langnau i.E./Wiler | Every 60 minutes | BLS |
| S5 | Bern–Kerzers–Neuchâtel/Murten (–Payerne) | Every 60 minutes | BLS |
| S51 | Bern–Bern Brünnen Westside | Every 30 minutes | BLS |
| S52 | Bern–Kerzers (–Neuchâtel) | Every 30 minutes | BLS |
| S6 | Schwarzenburg–Bern | Every 30 minutes | BLS |
| S7 | Bern–Bolligen–Worb | Every 15 minutes | RBS |
| S8 | Bern–Jegenstorf | Every 15 minutes | RBS |
| S9 | Bern–Unterzollikofen | Every 15 minutes | RBS |
2010–2012
The December 2009 timetable change saw a limited number of changes. The most significant involved the S4 and S44. Service on the Ramsei–Huttwil line was cut back from Affoltern-Weier to Sumiswald-Grünen, and the S4 and S44 swapped termini, with the S4 now going to Sumiswald-Grünen and the S44 going to Langnau i.E.[9] The December 2011 addition of the S31 between Münchenbuchsee and Belp (via Bern) increased the service frequency between those two stations to every fifteen minutes.[10]
Operations
The Bern S-Bahn Bern is operated, under a joint commission from the Canton of Bern, its neighbouring cantons and the Federal Government, by the following railway companies:
- BLS AG (BLS);
- Regionalverkehr Bern-Solothurn (RBS).
Upon the timetable change on 12 December 2004, the Swiss Federal Railways (SBB-CFF-FFS) withdrew from its previous involvement in the operation of the Bern S-Bahn, but also took over all of the long-distance services previously operated by the BLS.
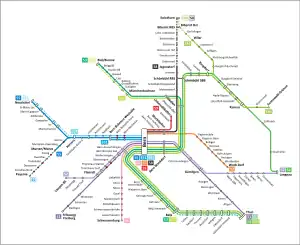
Lines
As of May 2022, the network consists of the following lines. Unless otherwise stated, the lines are 1,435 mm or 4 ft 8+1⁄2 in standard gauge.[11]
| # | Route | Notes | Operator |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | Fribourg–Flamatt–Bern–Thun | BLS AG | |
| S2 | Laupen–Flamatt–Bern–Konolfingen–Langnau im Emmental | BLS AG | |
| S3 | Biel/Bienne–Bern–Belp | BLS AG | |
| S31 | Biel/Bienne–Bern–Belp | Rush-hour service | BLS AG |
| S4 | Thun–Belp–Bern–Burgdorf–Hasle-Rüegsau–Zollbrück–Langnau im Emmental | BLS AG | |
| S44 | Thun–Belp–Bern–Burgdorf–Solothurn/Hasle-Rüegsau–Zollbrück-Sumiswald-Grünen | Operates as a single train between Thun and Burgdorf[12] | BLS AG |
| S5 | Neuchâtel–Ins/Payerne–Murten/Morat–Kerzers–Bern Brünnen Westside–Bern | Operates as a single train between Bern and Kerzers[13] | BLS AG |
| S51 | Bern Brünnen Westside–Bern | BLS AG | |
| S52 | (Ins–)Kerzers–Bern Brünnen Westside–Bern | Operates between Ins and Kerzers only during rush hour | BLS AG |
| S6 | Schwarzenburg–Bern | BLS AG | |
| S7 | Bern–Worb Dorf | Operates over the metre (3 ft 3+3⁄8 in) gauge Worb Dorf–Worblaufen line | RBS |
| S8 | Bern–Jegenstorf/Bätterkinden | Operates over the metre (3 ft 3+3⁄8 in) gauge Solothurn–Worblaufen line | RBS |
| S9 | Bern–Unterzollikofen | Operates over the metre (3 ft 3+3⁄8 in) gauge Zollikofen–Bern line | RBS |
Network map
Rolling stock
The normal rolling stock rosters for the Bern S-Bahn are:
- S1 BLS RABe 515 ("MUTZ"): up to two units per train (2 x 4- double-decker car EMU).
- S2 BLS RBDe 565 ("NPZ") with two "B6 Jumbo" intermediate cars.
- S3 BLS RABe 515 ("MUTZ"): up to two units per train (2 x 4- double-decker car EMU).
- S31 BLS RABe 515 ("MUTZ"): up to two units per train (2 x 4- double-decker car EMU).
- S4 BLS RABe 528 ("MIKA") (up to two units per train (2 x 6 cars EMU)) or BLS RBDe 565 or BLS RBDe 566 II ("NPZ") with "B6 Jumbo" and "B Lego" intermediate cars.
- S44 BLS RABe 525 ("NINA"): 1-2 units per train (4 cars EMU).
- S5 BLS RABe 525 ("NINA"): 1–3 units per train (3 cars EMU).
- S51 BLS RABe 515 ("MUTZ")
- S52 BLS RBDe 565 or RBDe 566 II
- S6 BLS RABe 515 ("MUTZ")
- S7 RBS Be 4/10 ("Worbla"): in peak times 2 x Be 4/10,
- S7 supplementary trains Bern–Bolligen RBS Be 4/10 ("Worbla")
- S8 RBS Be 4/12 ("Seconda"): 2 EMU per train in peak hours, 1 EMU outside of peak hours.
- S9 RBS Be 4/12 ("Seconda") or RBS Be 4/10 ("Worbla")
See also
Notes
- 1 2 BLS Lötschbergbahn and Regionalverkehr Mittelland merged in 2006 to form BLS AG, also commonly known as BLS.
Footnotes
- ↑ Bützer & Jeker 1980, p. 149.
- ↑ "Berner S-Bahn fährt ab 1995 auf zwei Linien". Der Bund (in German). 14 July 1993. p. 21. Retrieved 20 December 2022.
- ↑ "Neue S-Bahn-Linie Langnau-Schwarzenburg". Thuner Tagblatt (in German). 22 May 1995. p. 3. Retrieved 20 December 2022.
- ↑ "Berner S-Bahn: Täglich 400 Züge für 40 000 Reisende". Thuner Tagblatt (in German). 20 May 1998. p. 24. Retrieved 20 December 2022.
- ↑ Aebischer, Pascal (20 May 1998). "Murten hat S-Bahn-Anschluss". Freiburger Nachrichten (in German). p. 7. Retrieved 21 December 2022.
- ↑ Bern 2004, p. 70.
- ↑ Bern 2004, p. 21.
- ↑ "Der Fahrplan 2009" (PDF) (in German). 10 November 2008. p. 6. Retrieved 23 December 2022.
- ↑ "Veränderungen beim öffentlichen Verkehr mit dem Fahrplanwechsel vom 13. Dezember 2009" (PDF) (in German). Canton of Bern. 13 December 2009. p. 1. Retrieved 23 December 2022.
- ↑ "Fahrplanwechsel 11. Dezember 2011". Berner Zeitung (in German). 22 November 2011. Retrieved 23 December 2022.
- ↑ "Liniennetz S-Bahn Bern" (PDF). S-Bahn Bern (in German). 15 December 2019. Retrieved 23 May 2020.
- ↑ "S44: Thun–Belp–Bern–Burgdorf–Solothurn + Sumiswald-Grünen" (PDF). BLS AG. Retrieved 23 May 2020.
- ↑ "S5: Bern–Kerzers–Neuchâtel + Murten/Morat (–Payerne)" (PDF). BLS AG. Retrieved 23 May 2020.
References
- "Angebotskonzept Des Kantons Bern Für Den Öffentlichen Orts - Und Regionalverkehr 2005 - 2008" (PDF) (in German). December 2004.
- Bützer, Hans-Peter; Jeker, Mark (1980). Grosser Eisenbahn-Atlas Schweiz (in German). Bern: Kümmerly & Frey. ISBN 3-259-03234-6. OCLC 1222543836.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: ignored ISBN errors (link)