 A standard 4-pin S-Video male connector on a cable | |||
| Type | Analog video connector | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Production history | |||
| Designed | 1987 | ||
| General specifications | |||
| Hot pluggable | Yes | ||
| External | Yes | ||
| Video signal | NTSC, PAL, or SECAM video | ||
| Pins | 4, 7, or 9 | ||
| Connector | Mini-DIN connector | ||
| Pinout | |||
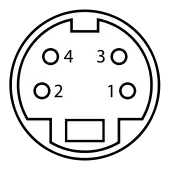 | |||
| Looking at the female connector. | |||
| Pin 1 | GND | Ground (Y) | |
| Pin 2 | GND | Ground (C) | |
| Pin 3 | Y | Intensity (Luminance) | |
| Pin 4 | C | Color (Chrominance) | |
|
The shells should be connected together by an overall screen/shield. However, the shield is often absent in low-end cables, which can result in picture degradation. Same connector as Apple Desktop Bus. | |||
S-Video (also known as separate video, Y/C, and erroneously Super-Video)[1] is an analog video signal format that carries standard-definition video, typically at 525 lines or 625 lines. It encodes video luma and chrominance on two separate channels, achieving higher image quality than composite video which encodes all video information on one channel. It also eliminates several types of visual defects such as dot crawl which commonly occur with composite video. Although it improved over composite video, S-Video has lower color resolution than component video, which is encoded over three channels.[2]
The Atari 800 was the first to introduce separate Chroma/Luma output in late 1979.[3] However, S-Video did not get widely adopted until JVC's introduction of the S-VHS (Super-VHS) format in 1987, which is why it is sometimes incorrectly referred to as Super-Video.[4] Before the shift towards digital video the S-video format was widely used by consumers, but it was rarely used in professional studios where YPbPr or component was generally preferred.[5]
Background
Standard analog television signals go through several processing steps on their way to being broadcast, each of which discards information and lowers the quality of the resulting images.
The image is originally captured in RGB form and then processed into three signals known as YPbPr. The first of these signals is called Y, which is created from all three original signals based on a formula that produces an overall brightness of the image, or luma. This signal closely matches a traditional black and white television signal and the Y/C method of encoding was key to offering backward compatibility. Once the Y signal is produced, it is subtracted from the blue signal to produce Pb and from the red signal to produce Pr. To recover the original RGB information for display, the signals are mixed with the Y to produce the original blue and red, and then the sum of those is mixed with the Y to recover the green.
A signal with three components is no easier to broadcast than the original three-signal RGB, so additional processing is required. The first step is to combine the Pb and Pr to form the C signal, for chrominance. The phase and amplitude of the signal represent the two original signals. This signal is then bandwidth-limited to comply with requirements for broadcasting. The resulting Y and C signals are mixed together to produce composite video. To play back composite video, the Y and C signals must be separated, and this is difficult to do without adding artifacts.
Each of these steps is subject to deliberate or unavoidable loss of quality. To retain that quality in the final image, it is desirable to eliminate as many of the encoding/decoding steps as possible. S-Video is an approach to this problem. It eliminates the final mixing of C with Y and subsequent separation at playback time.
Signal
The S-video cable carries video using two synchronized signal and ground pairs, termed Y and C.
Y is the luma signal, which carries the luminance – or black-and-white – of the picture, including synchronization pulses.
C is the chroma signal, which carries the chrominance – or coloring-in – of the picture. This signal contains two color-difference components.
The luminance signal carries horizontal and vertical sync pulses in the same way as a composite video signal.
In composite video, the signals co-exist on different frequencies. To achieve this, the luminance signal must be low-pass filtered, dulling the image. As S-Video maintains the two as separate signals, such detrimental low-pass filtering for luminance is unnecessary, although the chrominance signal still has limited bandwidth relative to component video.
Compared with component video, which carries the identical luminance signal but separates the color-difference signals into Cb/Pb and Cr/Pr, the color resolution of S-Video is limited by the modulation on a subcarrier frequency of either 3.58 megahertz (NTSC) or 4.43 megahertz (PAL). This difference is meaningless on home videotape systems, as the chrominance is already severely constrained by both VHS and Betamax.
Carrying the color information as one signal means that the color has to be encoded in some way, typically in accord with NTSC, PAL, or SECAM, depending on the applicable local standard.
Physical connectors
Atari 800
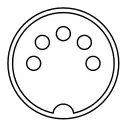
The Atari 800 introduced separate Chroma/Luma output in late 1979. The signals were put on pin 1 and 5 of a 5-pin 180-degree DIN connector socket. Atari did not sell a monitor for its 8-bit computer line, however.[3]
Commodore 64
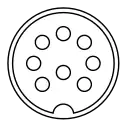
The Commodore 64 released in 1982 (with the exception of the earliest revisions using a 5-pin video port) also offers separate chroma and luma signals using a different connector. Although Commodore Business Machines did not use the term S-Video as the standard did not formally exist until 1987, a simple adapter connects the computer's LCA (luma-chroma-audio) 8-pin DIN socket to a S-Video display, or an S-Video device to the Commodore 1702 monitor's LCA jacks.[6]
4-pin mini-DIN
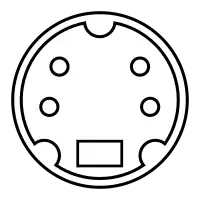
The four-pin mini-DIN connector is the most common of several S-Video connector types. The same mini-DIN connector is used in the Apple Desktop Bus for Macintosh computers. Desktop Bus can be used for S-Video in a pinch.[7][8][9] Other connector variants include seven-pin locking dub connectors used on many professional S-VHS machines, and dual Y and C BNC connectors, often used for S-Video patch panels. Early Y/C video monitors often used phono (RCA connector) that were switchable between Y/C and composite video input. Though the connectors are different, the Y/C signals for all types are compatible.
The mini-DIN pins, being weak, sometimes bend. This can result in the loss of color or other corruption (or loss) in the signal. A bent pin can be forced back into shape, but this carries the risk of the pin breaking off.
These plugs are usually made to be plug-compatible with S-video, and include optional features, such as component video using an adapter. They are not necessarily S-video, although they can be operated in that mode.
7-pin mini-DIN

Non-standard 7-pin mini-DIN connectors (termed 7P) are used in some computer equipment (PCs and Macs). A 7P socket accepts, and is pin compatible with, a standard 4-pin S-Video plug.[10] The three extra sockets may be used to supply composite (CVBS), an RGB or YPbPr video signal, or an I²C interface. The pinout usage varies among manufacturers.[10][11] In some implementations, the remaining pin must be grounded to enable the composite output or disable the S-Video output.
Some Dell laptops have a digital audio output in a 7-pin socket. [12]
8-pin mini-DIN
 The 8-pin mini-DIN connector is used in some ATI Radeon video cards[13]
The 8-pin mini-DIN connector is used in some ATI Radeon video cards[13]
9-pin Video In/Video Out


9-pin connectors are used in graphics systems that feature the ability to input video as well as output it.[14][15] Again, there is no standardization between manufacturers as to which pin does what, and there are two known variants of the connector in use. As can be seen from the diagram above, although the S-Video signals are available on the corresponding pins, neither variant of the connector will accept an unmodified 4-pin S-Video plug, though they can be made to fit by removing the key from the plug. In the latter case, it becomes all too easy to misalign the plug when inserting it with consequent damage to the small pins.
Comparison with SCART
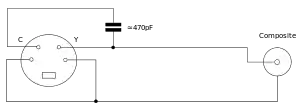
In many European countries, S-Video was less common because of the dominance of SCART connectors, which were present on televisions until the advent of HDMI. It is possible for a player to output S-Video over SCART, but televisions' SCART connectors are not always wired to accept it, and if not the display would show only a monochrome image.[16] In this case it is sometimes possible to modify the SCART adapter cable to allow full S-Video compatibility.
See also
References
- ↑ S-Video – Definition Archived 2016-03-01 at the Wayback Machine About.com
- ↑ Poynton, Charles (2002). Digital Video and HD: Algorithms and Interfaces (PDF) (First ed.). Morgan Kaufmann. p. 107. ISBN 1558607927.
- 1 2 Current, Michael. "Atari 8-bit FAQ". Retrieved 2018-02-23.
- ↑ "Definition of S-VHS".
- ↑ Poynton, Charles (2002). Digital Video and HD: Algorithms and Interfaces (PDF) (First ed.). Morgan Kaufmann. p. 107. ISBN 1558607927.
- ↑ Murray, David (2018-05-11). Commodore History Part 3 - The Commodore 64 (complete). The 8-Bit Guy. YouTube. Event occurs at 9:38. Archived from the original on 2021-12-11. Retrieved 2018-05-12.
- ↑ "Macintosh: S-Video Port Confused with the ADB Port". Archived from the original on 2016-05-12. Retrieved 2015-04-27.
- ↑ Waggoner, Ben (2002). Compression for Great Digital Video: Power Tips, Techniques, and Common Sense. ISBN 9781578201112.
- ↑ Wootton, Cliff (28 April 2005). A Practical Guide to Video and Audio Compression: From Sprockets and Rasters to Macro Blocks. ISBN 9781136036101.
- 1 2 Keith Jack (2007). Video demystified: a handbook for the digital engineer. Newnes. ISBN 9780750678223.
- ↑ ATI Radeon 7 pin SVID pinout.
- ↑ Dell (2009). "S-Video to TV-Composite Cable and SPDIF Adapter for Dell Inspiron".
- ↑ Pinouts.Ru (2017). "ATI Radeon 8-pin audio / video VID IN connector pinout".
- ↑ ATI Radeon: Using Video in and Video out.
- ↑ "ATI Radeon 9 pin VIVO pinout".
- ↑ S-Video drama :(. camp0s.com