 | |
Former name | San Francisco State Normal School (1899–1921) San Francisco State Teachers College (1921–1935) San Francisco State College (1935–1972) California State University, San Francisco (1972–1974) |
|---|---|
| Motto | Experientia Docet (Latin) |
Motto in English | "Experience Teaches" |
| Type | Public research university |
| Established | 1899 |
Parent institution | California State University |
| Accreditation | WSCUC |
Academic affiliation | USU |
| Endowment | $140.8 million (2020)[1] |
| Budget | $354.6 million (2023)[2] |
| President | Lynn Mahoney |
| Provost | Amy Sueyoshi |
Academic staff | 1,905 (2022) [3] |
Administrative staff | 1,398 (2022) [3] |
| Students | 25,046 (2022)[3] |
| Undergraduates | 21,868 (2022)[3] |
| Postgraduates | 3,178 (2022)[3] |
| Location | , , United States |
| Campus | Large city, 141.1 acres (57.1 ha)[4] |
| Other campuses | |
| Newspaper | Golden Gate Xpress |
| Colors | Purple and gold[5] |
| Nickname | Gators |
Sporting affiliations | NCAA Division II – CCAA |
| Mascot | Gator |
| Website | www |
 | |
| Official name | San Francisco State Teacher's College |
| Designated | 1/7/2008 |
| Reference no. | N2378[6] |
San Francisco State University (San Francisco State, SF State and SFSU) is a public research university in San Francisco. It was established in 1899 as the San Francisco State Normal School and is part of the California State University system.
It offers 119 bachelor's degree programs, 105 master's degree programs, and 3 doctoral degree programs, along with 22 teaching credential programs among seven colleges.[7][8][9] The 144.1-acre main campus is located in the southwest part of the city, less than two miles from the Pacific coast.[10] The university has 12 varsity athletic teams which compete at the NCAA Division II level.
San Francisco State is classified among "R2: Doctoral Universities – High research activity."[11] It is also a Hispanic-serving institution (HSI) and is eligible to be designated as an Asian American Native American Pacific Islander serving institution (AANAPISI).
San Francisco State's past and present faculty and alumni include 21 Pulitzer Prize winners, 16 Academy Award winners, 49 Emmy Award winners, 10 Grammy Award winners, 12 Tony Award laureates, 4 billionaires, and 1 astronaut.[12]
History

19th Century
In 1857, the San Francisco Board of Education created the San Francisco Weekly Normal School,[13][14] also known as the Minns' Evening Normal School.[15] In 1862, it became the California State Normal School, the first postsecondary institution established by the state.[14] Only six students were enrolled on its first day. By 1866, enrollment had increased to 384.[16]
In 1867, the principal of Girls' High School and Normal School, Ellis Holmes, realized that the California State Normal School was not meeting the demand for teachers. The city approved the addition of a new year-long teacher-training program to his high school's curriculum, for girls who wanted to pursue a career in education. This program is what would eventually become San Francisco State University. When the California State Normal School was moved to San José in 1871, Girls' High became the only publicly-supported teacher-training institution.[16]
In 1895, the teaching program was split from the school and became San Francisco City Normal School.[16] Due to a lack of funding, the school closed in 1898.[13] A group of teachers, students, and supporters pressured the California State Legislature to convert it into a state-funded institution.[16]
On March 22, 1899,[17] the California State Legislature approved the creation of the San Francisco State Normal School, with an appropriation of $10,000. Frederic Lister Burk was appointed as the first president and chose the school's motto, Experientia Docet.[18] The school rented[16] space in a building on Powell Street between Clay and Sacramento Streets and 31 women were enrolled in the first year.[19][20]
20th Century
The 1906 earthquake and fire forced the school to relocate from Nob Hill to a temporary campus at the Grant School in Oakland.[20]
In 1921, the school began offering Bachelor's degree options and was renamed San Francisco State Teachers College.[16][21] Teachers Colleges in California received authorization to grant Bachelor of Arts degrees in 1923.[14]
Also in 1921, construction for a new campus started at a property bound by Laguna, Haight, Buchanan and Hermann Streets. The campus consisted of four Spanish Colonial Revival style buildings designed by George McDougall, a California state architect.[22][23]
In 1924, Burk died and Archibald B. Anderson took over as acting president.
There were three presidents of the teachers college in 1927. Anderson served until his death in the summer of that year. Then, Mary A. Ward, the Dean of Women, served as acting president until the fall, when Alexander C. Roberts was appointed president.
In the 1930s, overcrowding became an issue at the campus. It had been designed for 1500 students, but had to accommodate about 3000. When the Hetch Hetchy project was completed in 1934, the city no longer needed land near Lake Merced for a reservoir. By 1939, the land had been acquired to build a new campus, but plans were paused due to World War 2. Many students took part in the war, causing enrollment to decline.[24]
During the 1920s and '30s, State Teachers Colleges expanded beyond being only vocational schools to train teachers. They were formally authorized to offer four-year liberal arts curriculums and renamed State Colleges in 1935.[25] So, the school became known as San Francisco State College.[21]
When veterans started returning in 1945, the Vets Village, a housing complex, was built at the site of the new campus. Some students commuted from there to the campus at Buchanan and Haight Streets.[24] In the same year, J. Paul Leonard became president after Alexander C. Roberts retired.[18]
In 1949, Master's degrees were authorized to be offered.[10]
In 1951, the Gymnasium building was the first major building to be completed at the current campus near Lake Merced. The Creative Arts building was built second. The campus opened for classes for Fall 1953, before it was formally dedicated in October 1954.[17]
From 1957 to 1961, Glenn Dumke was president of San Francisco State.
San Francisco State College became part of the California State College system established under the Donahoe Higher Education Act in 1960.[16] Dumke resigned to become the vice chancellor for academic affairs, before becoming the second chancellor of the system for 20 years.
In Fall 1965, the Experimental College was started by students Cynthia Carlson, Donna Michaelson, Sharon Gold, and James Nixon, in an effort to teach untraditionally. In 1927, over 2000 students enrolled in courses offered by the Experimental College.[16] The original Experimental College stopped operating after 1969.[26]
Demonstrations of the 1960s
1967
On May 2, 1967, 60 students staged a sit-in protest in President John Summerskill's office, opposing the practice of providing students' academic standing to the Selective Service System. On June 22 of the same year, students and faculty picketed administrative offices to protest the California State College Chancellor Glenn S. Dumke's directive to continue providing students' academic standings.[27]
On November 6, James Vaszko, the campus editor of the Gater, the student newspaper at the time, was assaulted by members of the Black Student Union.[28] This event became known as the Gater Incident. In an interview the day after the assault, Vaszko said he had no idea why it happened, but something was said during the incident about the Gater not running a photo of the BSU candidate for homecoming queen. However, the Gater had included a photo of the candidate. The District Attorney's office issued arrest warrants on November 9 for Ben Stewart, George Murray and Jack H. Alexis.[29]
About 450 students participated in a protest on December 2, against President Summerskill and the Vietnam War.[27]
On December 6, students protested against the suspension of students in the Gater incident. During the protest, students broke into the Administration building.[27]
1968
President Summerskill announced his resignation, effective in September, on February 22.[27]
The Third World Liberation Front was a coalition of the Black Students Union, the Latin American Students Organization, the Filipino-American Students Organization, and El Renacimiento. They occupied the school's YMCA office on March 23.[27]
On May 21, in the Administration building, approximately 400 students held a sit-in protesting various issues, including an end to AFROTC on campus and the hiring of nine minority faculty members. After nine hours, police were called to remove the students. 26 people were arrested.[27]
Students protested again on May 23. On the following day, Chancellor Dumke asked President Summerskill to resign immediately. Robert Smith, a professor of education, was appointed president on June 1.[27][16]
On September 10, George Mason Murray, a graduate student in English and Black Panther Minister of Education, was hired as a teaching assistant to teach introductory English classes for 400 students.[27]
President Smith announced the creation of a Black Studies Department and named Dr. Nathan Hare, a professor of sociology, as acting chair on September 18.[27]
On September 26, after Murray allegedly made inflammatory remarks at Fresno State College and San Francisco State, the California State College Trustees voted to ask President Smith to reassign George Murray to a non-teaching position.
Smith refused, causing Chancellor Dumke to order him to suspend Murray on October 31. On the same day, the Black Student Union Third World Liberation Front threatened to strike on November 6 and presented their 15 demands.[27] The demands were not met, and a lengthy student strike erupted. It was the longest student strike in American history.
On November 13, 1968, the campus closed after a week of confrontations between students and police. On November 18, the California State College Trustees ordered Smith to reopen the campus. The faculty didn't want to reopen the campus, but met for a convocation to discuss the issues. On November 26, Black Student Union leaders confronted Smith and the faculty during the convocation. Smith resigned the same day.[30]
On December 2, S. I. Hayakawa was appointed president. On his first day, Hayakawa climbed onto a sound truck positioned at 19th and Holloway Aves. and pulled out the speaker wires. According to a student who was inside the truck, "he was so mad you could see the foam on his mouth."[31]
On December 10, Mayor Joseph Alioto organized a citizen's committee to help end the strike.[30]
The school closed for the holidays a week early, on December 13.[30]
Also during that month, two bombs were discovered on campus. One was in the Administration building and the other was in the Psychology building (now Ethnic Studies and Psychology building).[32]
1969
On January 4, 1969, President Hayakawa banned meetings and gatherings on campus and limited picketing activities to the perimeter of the campus.[30] Picketers ignored the ban.[33]
About 350 teachers who were part of the American Federation of Teachers picketed around the campus on January 6.[30]
On January 23, over 500 people had gathered on campus for a rally. Police surrounded the protestors and arrested hundreds of them, backing up San Francisco's court system for months.[33]
On March 5, Timothy Peebles, a freshman, set off a bomb in the Creative Arts building at night. The bomb injured his hands and face.[34][30]
The strike officially ended on March 20, after an agreement was signed by representatives of the Black Student Union, the Third World Liberation Front, and the school.[16][30][33] The school agreed to establish the first College of Ethnic Studies in the country, housing the departments of American Indian Studies, Asian American Studies, Black Studies, and La Raza Studies, and to accept almost all nonwhite applicants for the Fall 1969 semester.[33]
1970s and onwards
In 1972, the State Colleges system was designated "The California State University and Colleges." 14 colleges met the criteria established by the Board of Trustees and the Coordinating Council for Higher Education, including San Francisco State, which was renamed California State University, San Francisco.[14] This name was not popular with students, and the university was soon renamed San Francisco State University in 1974.[16]
Hayakawa resigned in 1973. This led to the appointment of Paul F. Romberg.[35]
The Student Union building (now Cesar Chavez Student Center) was opened in 1975.[16] It was designed by Paffard Keatinge-Clay.
President Romberg secured a permanent federal lease for 25 acres of shoreline in Tiburon for just $1 in 1978.[36] The Romberg Tiburon Campus would eventually expand to 53 acres.
In 1983, Chia-Wei Woo became the 11th president of the university. Woo was the first Chinese-American to head a major American university.[37]
On May 14, 1985, a pipe bomb in a purse was found in the Business/Ethnic Studies Building (now Business Building).[38][39] A US Army bomb disposal team removed it.[40] In September that year, Coy Ray Phelps was arrested and charged for the attempted bombing.[41] Phelps had also planted bombs in four other locations in San Francisco, but only one exploded at the offices of the local Humanist Party.[42][43] On September 17, 1986, Phelps was placed in a psychiatric facility after being found not guilty by reason of insanity. He was released in 1999, but after starting a website that advocated for murdering Black people and Jewish people, a panel of three judges ruled that he should not have been released in the first place, and he was rearrested in 2002.[43] He appealed the ruling, but his case was dismissed in 2004.[44] On September 23, 2015, he was released from the United States Medical Center for Federal Prisoners.[45][46]
In 1993, the College of Extended Learning (now College of Global and Professional Education) opened the Downtown Center in San Francisco's Multimedia Gulch, at 425 Market St. [16][47]

In 1994, a mural depicting Malcolm X was painted on the Student Union building, commissioned by the Pan-African Student Union and African Student Alliance. The mural's border contained yellow Stars of David and dollar signs mingled with skulls and crossbones and near the words "African Blood." The next week, after demonstrations on both sides, the university's administration had the mural painted over, and subsequently sand blasted.[48] Two years later, a new Malcolm X mural was painted, without the controversial symbols.[49]
In 1995, San Francisco State alumni Geoff Marcy and Paul Butler discovered two new Jupiter-sized planets within 35 light-years of Earth, including one that could contain elements for organic life. They discovered another planet about 40 light years away less than three months later.[50][51]
21st Century
In 2007, the Downtown Campus was opened at 835 Market Street, replacing the Downtown Center. The campus had nearly 47,000 square feet of classroom space in Westfield San Francisco Centre. The campus was used for courses in the College of Extended Learning and Lam Family College of Business.[52]
The first Rhythms Music Festival happened in March 2011.[53] The annual music festival is held in a building known as the Annex.[54]
In 2013, the Science Building was found to have "unsafe levels" of airborne mercury, lead and asbestos in the basement as a result of reports that pesticide-laden Native American artifacts were previously stored with a material now known to be highly hazardous. Over $3.6 million was spent for remediation of the pervasive contamination. University administration terminated several employees who reported the contamination, resulting in several wrongful termination and whistle-blower lawsuits, including one by the recently hired director. In July 2014, Cal/OSHA cited the university for various health and safety violations in the Science Building, which included SFSU failing to locate asbestos in the building and warn employees about the hazards of mercury.[55][56] SFSU previously ran into trouble with its Environmental Health and Safety program when the director prior, Robert Shearer, was accused of accepting bribes from a waste disposal firm in exchange for at least $4 million in university funds.[57]
In March 2016, a video of a student being attacked for having dreadlocks went viral and sparked discussions about cultural appropriation.[58][59]
In response to the College of Ethnic Studies being underfunded since 2008, four students held a ten-day hunger strike from May 2–11, 2016, resulting in one hospitalization. The strike ended when President Leslie Wong agreed to commit nearly $500,000 to the college and meet a portion of their demands.[60]
The Experimental College was revived in Fall 2017. One-unit courses are created and taught by students.[26][61]
Also in 2017, a group of Jewish students and local residents accused SFSU of encouraging antisemitism, and excluding Jewish student pro-Israel activist groups from campus activities.[62][63][64] The students filed two lawsuits focusing on the disruption of a speech by Jerusalem mayor Nir Barkat in 2016. One suit was dismissed by a federal judge in 2018.[65] Another lawsuit was settled in 2019 and included provisions for a $200,000 university fund to promote viewpoint diversity, a new coordinator of Jewish Student Life position for at least four years, and an independent consultant to review the university's non-discrimination policies.[66]
In May 2019, Lynn Mahoney became the first woman to become president of San Francisco State in a permanent capacity.[67] Mary Ward had served as an acting president in the summer of 1927, after the death of Archibald Anderson.[68]
On September 23, 2020, SFSU faculty Rabab Abdulhadi and Tomomi Kinukawa hosted a discussion on Zoom titled "Whose Narratives? Gender, Justice, and Resistance."[69] The event's speakers included Leila Khaled, a Palestinian political activist and plane hijacker, Laura Whitehorn, an American political activist and domestic bomber. Zoom and YouTube canceled the broadcast due to Khaled's history of violent actions towards civilians. Facebook also removed a page for the event.[65][70][71] President Lynn Mahoney wrote a letter about the incident. A second event titled "Whose Narratives? What Free Speech for Palestine?" was scheduled for April 23, 2021, and was also blocked. The event had nine speakers scheduled, including Khaled, Whitehorn, Sekou Odinga, an activist and former Black Panther, and Sean Malloy, an author and professor at UC Merced.[72][73]
In 2022, the new Downtown Campus opened on the fifth floor and a part of the 12th floor of 160 Spear St., replacing the Downtown Campus at 835 Market Street.[74] The campus now only occupies the fifth floor.
On April 6, 2023, former NCAA swimmer Riley Gaines visited SFSU for a Turning Point USA student chapter event and spoke publicly about her campaign against transgender athletes in women's sports.[75][76] Protesters attended the event and were peaceful. After the event concluded, more protesters arrived.[77][75] Gaines was escorted by university police officers to shelter in a classroom.[77][75] Video clips were posted to social media, including by Gaines, that appear to show protesters chanting, shouting, and holding signs.[77] After the event, Gaines said she had been physically struck twice by a person during the protest.[78][77] Soon after the event, the university police stated that no arrests have been made, and an investigation is ongoing.[78]
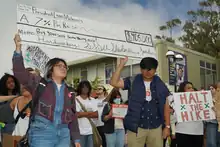
On September 11 of the same year, about 300 students rallied and marched against the CSU system's proposed tuition increase.[79] On September 15, CSU's Board of Trustees voted in favor of the plan to reduce the system's $1.5 billion deficit with annual tuition increases of 6%, starting from the 2024–2025 academic year to the 2028–2029 academic year.[80][81]
After years of declining enrollment, budget cuts were announced on August 31, totaling $11 million.[82] The university is also facing a $9 million budget deficit. A plan to eliminate the deficit calls for cutting the equivalent of 125 full-time positions.[83] The California Faculty Association said it would result in the layoff of about 325 part-time lecturers.[84] On October 11, the CFA held a practice rally against the tuition increase and possible layoffs.[85] On October 26, the CFA and the university Young Democratic Socialists of America chapter led about 300 students and faculty in a rally and march against layoffs and the tuition increase.[86] The CFA led another rally against layoffs on November 15.[87]

In response to the 2023 Israel–Hamas War, hundreds of students walked out and rallied on October 25, calling for a ceasefire.[88] It was part of a nationwide walkout organized by Students for Justice in Palestine.[89]
On November 14, Teamsters Local 2010 held a one-day strike across all 23 CSU campuses, seeking higher pay.[90] San Francisco State skilled laborers marched through the university before joining the picket line at the university's 19th Ave and Holloway entrance.[91]
Students walked out and protested on November 28, in response to 655 courses being cut and over 300 faculty members being laid off in the Spring 2024 semester.[92]
One-day strikes led by the CFA were held across four CSU campuses from December 4–7, including San Francisco State on December 5.[93] Faculty and students picketed against budget cuts and possible layoffs and are seeking a raise of 12%.[94]
In 2024, the Science & Engineering Innovation Center will open. The center includes a new 125,000 square-foot building and a renovated 54,000 square-foot building.[95]
Milestones
- 1901 – First graduating class consisting of 36 women.[20][10]
- 1923 – First Bachelor of Arts degree awarded[10]
- 1930 – Became four-year school[4]
- 1929 – Grace Hackett became the first known African-American to graduate from the school[20]
- 1949 – Master's degree first offered[10]
- 1972 – Received university status
- 1974 – Renamed San Francisco State University[21]
- 1975 – Cesar Chavez Student Center opened its doors to students[16]
- 1999 – Celebrated 100th birthday[96]
Governance
San Francisco State University is part of the California State University system. The CSU is governed by a 25-member Board of Trustees who oversee the system's chancellor.[97] The president of SF State reports to the chancellor. The president oversees six cabinet units. Cabinet units collaborate via 13 committees and work in conjunction with three semi-independent 501(c)(3) organizations that support the university.[98] Each cabinet, except the Office of the President, is led by a vice president.[99] The the vice president of Academic Affairs is also university's provost and oversees fifteen administrative units, including the university's seven colleges. Each college is led by a dean.[100] The colleges are comprised of departments, led by department chairs, and schools, led by directors.
Presidents
- Frederic Lister Burk (1899–1924)[101][102]
- Archibald B. Anderson (1924–1927)
- Mary A. Ward (1927)[103]
- Alexander C. Roberts (1927–1945)
- J. Paul Leonard (1945–1957)[104]
- Glenn Dumke (1957–1961)[105]
- Frank L. Fenton (1961–1962)
- Paul A. Dodd (1962–1965)
- Stanley F. Paulson (1965–1966)
- John Summerskill (1966–1968)
- Robert R. Smith (1968)
- S. I. Hayakawa (1968–1973)
- Paul F. Romberg (1973–1983)
- Chia-Wei Woo (1983–1988)
- Robert A. Corrigan (1988–2012)
- Leslie Wong (2012–2019)[106]
- Lynn Mahoney (2019–present)[107]
Academics

The university operates on a semester calendar. Students generally enroll in courses during the fall and spring semesters, but courses are also offered during the summer semester and winter session.[108] Winter courses are not eligible for financial aid.[109]
The university has a four-year graduation rate of 49% and a six-year graduation rate of 55%.[110][111] The student-faculty ratio at SFSU is 20:1.[110]
In Fall 2022, the university had 1,905 instructional faculty, of which 807 (or 42 percent) were tenured or on the tenure track.[10]
Colleges
The university's seven colleges are:
- College of Liberal & Creative Arts[112]
- Lam Family College of Business[113]
- College of Ethnic Studies[114]
- College Health and Social Sciences[115]
- College of Science and Engineering[116]
- Graduate College of Education[117]
- College of Professional & Global Education (formerly College of Extended Learning)[118]
Undergraduate programs
SFSU offers 119 bachelor's degree programs across its seven colleges.
The most popular undergraduate majors are Business Administration, Biology, Kinesiology, Engineering, English, Communication Studies, Psychology, Criminal Justice Studies, Sociology, and Cinema.[119]
The College of Health and Social Sciences also offers accelerated Bachelor of Science degrees in nursing in partnership with the City College of San Francisco and College of San Mateo.[120]
Blended Master's programs
SFSU offers 34 blended bachelor's and master's degree programs, called San Francisco State Scholars programs.[121] The programs provide students an accelerated path to a graduate degree by allowing students to earn graduate credit while in their junior or senior years.
Graduate and professional programs
The university offers 105 master's degree programs across six colleges: College of Liberal & Creative Arts, Lam Family College of Business, College of Ethnic Studies, College Health and Social Sciences, College of Science and Engineering, and Graduate College of Education.[122]
The Graduate College of Education offers two doctoral programs: Ph.D in special education, in partnership with University of California, Berkeley and Ed.D in Educational Leadership.[123] The College of Health and Social Sciences offers a DPT program in partnership with University of California, San Francisco. The Graduate College of Education also offers 22 teaching credential programs.[9]
Other academic programs
Experimental College
The original Experimental College, known as E.C., was created in 1965 and lasted until 1969. The revived Experimental College, also known as EXCO, allows students to create curriculums and teach one-unit courses about any topic.[26] It is similar to Oberlin College's ExCo program and University of California, Berkeley's DeCal program. Recent course offerings include BDSM 101, Lucid Dreaming, Adventures in SF, Thematic Analysis of Studio Ghibli Films, and United States Foster System.[124][125] EXCO is part of the Department of Undergraduate Education and Academic Planning.[126]
Open University
People without formal admission to the university can enroll in undergraduate or graduate courses on a space available basis, through the College of Professional & Global Education's Open University program. Up to undergraduate 24 units can be applied towards a bachelor's degree or six units towards a master's degree at San Francisco State. The program costs $395 per unit and is open to everybody except SFSU students. This includes high school students, community college students, and international students. This program is the university's concurrent enrollment program.[127]
ElderCollege
ElderCollege is a noncredit program provided by the College of Professional & Global Education that allows people 50 and older to sit in on courses on a space available basis, with the approval of an instructor. There are no official records of enrollment, attendance, or grades as ElderCollege students participate only for their personal benefit.[128] ElderCollege students are expected to attend regularly and participate, but are not expected to take exams or write papers.[129]
Osher Lifelong Learning Institute
SFSU's Osher Lifelong Learning Institute, or OLLI, was founded in 2003. OLLIs are education organizations for older adults that are operated independently. SFSU's OLLI provides six-week courses and "mini courses" intended for people 50 and older, but people under 50 may join.[130][131] The courses are not for credit. OLLI does not use SFSU's semester calendar and has its own five-session academic calendar in which six-week courses are taught; the sessions are spring, summer, late summer, fall, and winter.[132] Membership is required to attend six-week courses, while mini courses are open to non-members. Mini courses consist of one to three class meetings.[133] Mini courses are offered six out of twelve months: January, March, May, July, September, and December.[132] Courses are not taught at the main campus, and instead are available over Zoom and in person at SFSU's Downtown Campus.[130] OLLI also offers interest groups and social events.[134]
Accreditation
The university is accredited by the Western Association of Schools and Colleges Commission for Senior Colleges and Universities.[135] The College of Business is accredited by the Association to Advance Collegiate Schools of Business (AACSB International).[136] The School of Engineering is accredited by the Accreditation Board for Engineering and Technology (ABET).[137]
Admissions and enrollment
In Fall 2022, SFSU's total enrollment was 25,046. This included 21,868 undergraduate students and 3,178 postgraduate students. In-state students were 96% of undergraduate students enrolled at the university.[138]
SFSU uses Cal State Apply, the centralized application system for all 23 CSU campuses. There is a $70 fee per application, but fee waivers are available.[139]
The university does not use school rank, personal statements and essays, letters of recommendation, legacy status, or standardized test scores in the admissions process.[140]
| 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Applicants | 31,924 | 30,966 | 27,777 | 31,429 | 34,631 | 35,605 | 34,521 | 36,220 | 35,121 | 31,963 | 34,929 | 31,461 | 30,096 | 29,395 |
| Admits | 28,719 | 28,180 | 25,782 | 26,431 | 23,310 | 25,550 | 24,327 | 24,703 | 23,841 | 21,088 | 20,889 | 20,070 | 19,569 | 18,401 |
| Admit rate | 90% | 91% | 92.8% | 84.1% | 67.3% | 71.8% | 70.5% | 68.2% | 67.9% | 66% | 59.8% | 63.8% | 65% | 62.6% |
| Enrolled | 2,984 | 3,339 | 3,148 | 2,779 | 3,689 | 4,286 | 4,323 | 3,570 | 4,259 | 3,751 | 3,611 | 3,785 | 3,537 | 3,659 |
Rankings and distinctions
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
In 2020, SFSU was ranked the 19th top university in the United States by PayScale and CollegeNET's Social Mobility Index university rankings.[148] In 2022, the Philosophical Gourmet Report listed San Francisco State University as one of the top eight universities to earn a terminal MA in philosophy.[149] SFSU was one of the first California State University campuses to offer a doctorate of education. It was also instrumental in the establishment of the International University of Kyrgyzstan (1993).[150] The university is the only one in California to offer a bachelor's degree in technical and professional writing.[150] It is also the only university in the California State University system to offer a master's degree in Classics.[151]
The Cinema Department, in the College of Liberal & Creative Arts, was named one of the world's best film schools by Variety in 2019.[152] SFSU was also listed as one of the nation's top 25 film schools by The Hollywood Reporter, having produced many leading filmmakers, with over 13 Academy Award wins among its alumni.[153][154]
The Sutro Library houses the largest collection of genealogical records west of Salt Lake City.[155]
Demographics
| Race and ethnicity | Total | |
|---|---|---|
| Hispanic | 38% | |
| Asian | 24% | |
| White | 15% | |
| Foreign national | 4% | |
| Black | 6% | |
| Pacific Islander | 1% | |
| Other[lower-alpha 1] | 10% | |
| Economic diversity | ||
| Low-income[lower-alpha 2] | 48% | |
| Affluent or middle-class[lower-alpha 3] | 52% | |
In 2021, SFSU was ranked fifth for diversity nationwide and third for diversity in the western U.S. by the Wall Street Journal.[156][157]
SFSU has the second largest Asian and Filipino American enrollment percentage in the CSU system.[158]
Main campus buildings
Academic buildings[159]

- Burk Hall (BH)
- Business (BUS)
- Creative Arts (CA)
- Ethnic Studies & Psychology (EP)
- Fine Arts (FA)
- Health & Social Sciences (HSS)
- Hensill Hall (HH)
- Humanities (HUM)
- Liberal and Creative Arts (LCA)
- J. Paul Leonard Library (LIB)
- Science (SCI)
- Science & Engineering Innovation Center (Under construction)[160]
- Sutro Library (in LIB)
- Thornton Hall (TH)
- Marcus Hall (MH)
Residence buildings, communities, and services[159]

- City Eats Dining Center (DC)[161][162]
- Manzanita Square (MZS)[163]
- Mary Park Hall (MPH)[164]
- Mary Ward Hall (MWH)[164]
- Towers Junior Suites (TJS)[165]
- The Towers at Centennial Square (TCS)[166]
- The Village at Centennial Square (VCS)[167]
- University Park North (UPN)[168]
- University Park South (UPS)[169]
- West Campus Green Residential Building (Under construction)[170]
A dormitory building, Verducci Hall, was imploded in 1999, having sustained damage from the 1989 Loma Prieta earthquake.[171]
Conference and event facilities[159]
Student and administrative services[159]

Athletic facilities[159]
- Cox Stadium
- Gymnasium (GYM)
- Maloney Field
Gallery
Satellite campuses
In addition to the main campus, the university also has three satellite campuses.
Downtown Campus (DTC)

The Downtown Campus located on the fifth floor of 160 Spear St., in San Francisco, California.[177] It is used and managed by the Lam Family College of Business and the College of Professional & Global Education (formerly College of Extended Learning).[177] The campus spans approximately 15,850 square feet.[10]
SF State has maintained facilities in Downtown San Francisco since the 1950s. The current Downtown Campus replaces the previous, underused campus that was located in the San Francisco Centre.[178] The old Downtown Campus was a replacement for the Downtown Center located at 425 Market Street.[179]
The campus has a student lounge, a computer lab, and study rooms.[180] A portion of 160 Spear St.'s 12th floor was part of the campus until 2024.[179]
Sierra Nevada Field Campus (SNFC)
The 7.1-acre Sierra Nevada Field Campus is located in Sierra County, near Yuba Pass and the Sierra Valley, at 35400 Hwy 49 in Calpine, California.[10] It is over 200 miles north of the main campus.[181] The current director of the campus is Darrow Feldstein.[182]
The campus offers three to seven-day courses and workshops to students as well as the general public.[183][184] Accredited, one-unit courses are processed by the College of Professional & Global Education. Workshops are not for credit and processed by the University Corporation.[184] The campus is also used for research by graduate students of the College of Science and Engineering.[185]
Due to its remote location, there is no cell service and extremely limited internet access at the campus. Accommodations at the campus consist of tents with mattresses. Students and visitors can to bring their own tents or vehicles to sleep in, or stay off campus.[186][187] The campus has a moderately high elevation of about 5522 feet or 1683 meters.[188][189]
The campus is supported by Friends of Sierra Nevada Field Campus, a non-profit organization.[190]
Buildings
There are three buildings at the campus.[191]
- Director's Cabin
- Staff Cabin
- Dining Hall
Romberg Tiburon Campus (RTC)

The Romberg Tiburon Campus is a 53.7-acre research campus located in Marin County, at 3150 and 3152 Paradise Drive in Tiburon, California. It is home to the only marine and environmental science lab on San Francisco Bay.[10][192] Katharyn Boyer is the interim executive director of the Estuary & Ocean Science Center and manages the campus.[193][194]
The Tiburon branch of the Smithsonian Environmental Research Center's Marine Invasions Lab[195] and the offices for the San Francisco Bay National Estuarine Research Reserve are also located there.[196]

The campus was a former U.S. Navy base. SF State has operated a marine lab on the site since 1978, when it began acquiring the land from the federal government for $1, under the condition that the site be used for education.[16][196]
A master plan is being currently being drafted for the campus. It has never had a master plan formally prepared and adopted by the campus or the CSU Board of Trustees. An approved master plan and certified environmental impact statement are required before the university can begin significant construction projects at the campus.[197][198]
The campus is at risk of closing due to financial struggles.[196][194]
Buildings

There are eight occupied buildings at the campus.[199][200]
- Bay Conference Center (BCC)[201]
- Delta Hall
- Estuary Hall
- Farallon Hall
- Greenhouse
- Ohrenschall Guest House
- N. Barracks
- S. Barracks
Athletics

The university's intercollegiate athletics teams, the Gators, compete in NCAA Division II and are a member of the California Collegiate Athletic Association (wrestling competes in the Rocky Mountain Athletic Conference). SF State fields twelve sports: men's and women's cross country, men's and women's soccer, women's volleyball, men's and women's basketball, men's baseball, wrestling, indoor track and field, outdoor track and field and softball.
The Gators have also produced thirteen National Football League players, including Billy Baird, Elmer Collett, Maury Duncan, Carl Kammerer, Douglas Parrish, and Floyd Peters. Mike Holmgren got his collegiate coaching start as the team's Offensive Coordinator in 1981. The football program ended in 1995.
SF State has produced three Major League Baseball players, two of which became All-Stars (former Mets shortstop Bud Harrelson, and former Brewers and Red Sox outfielder Tommy Harper). The soccer program has had one player enter the professional ranks. Jared MacLane played in the soccer Professional First Division in Santa Cruz, Bolivia.
SF State Wrestling sent a wrestler to a national championship meet every year from 1963–64 to 2016–17.[202]
As of 2019, the Gators have earned one NCAA team championship at the Division II level, a 1997 wrestling championship.[203][204]
Mascot
In the early 20th century, collegiate sports at SF State became more popular, creating a need for a team name, and the search for a mascot started in 1921.[205] The university's newspaper at the time, the Bay Leaf, asked for suggestions for a mascot.[206] Students suggested an alligator named "Golden Gater" in reference to the Golden Gate.[207][208] Students voted in favor of the name and the alligator choice was finalized in 1931,[205] but after numerous misspellings by the newspaper, use of "Golden Gator" stuck.[209] In the beginning, two female students were chosen each year as alligator mascots.[205] The mascot's name was eventually shortened to the Gator.[208] In 2023, the Gator became Alli Gator and was redesigned.[210]
Intramural Sports
Intramural sports at SF State include indoor soccer, costume dodgeball, and badminton.[211]
Student life and traditions
As of December 2023, SFSU has 248 formally recognized student organizations.[212] In order to receive funding, student organizations must be formally recognized by the Office of Student Activities & Events.[213]
49 Greek life organizations are formally recognized[214] and include chapters of Alpha Phi, Sigma Pi Alpha, and Phi Sigma Sigma.
Housing
SFSU has three on-campus housing neighborhoods: the Central Neighborhood, the North Neighborhood, and the South Neighborhood. These neighborhoods are further divided into housing communities.[215] Also Parkmerced, a planned neighborhood consisting of high-rise and low-rise apartments, is located to the south of the university.[216]
First-year student accommodations

The Central Neighborhood consists of housing for first-year students. There are two residence halls available: Mary Ward Hall and Mary Park Hall. They are colloquially known as the Maries. In the Fall 2024 semester, a new residence hall will be completed and open to students.[170] The Towers at Centennial Square has full and partial high-rise suites. The Village at Centennial Square has apartments. The difference between suites and apartments is that apartments are available to be leased year-round, but suites are only available during the academic year. The Central Neighborhood is the closest housing neighborhood to the university's dining center, City Eats.[217]
Non-first-year student accommodations
The North Neighborhood has high-rise and low-rise garden apartments in the University Park North community. This neighborhood is closest to Stonestown Galleria, a shopping mall.
The South Neighborhood consists of University Park South and Manzanita Square. University Park South offers townhome-style apartments. Manzanita Square is a LEED Gold certified apartment building.[218] It is owned and operated by American Campus Communities.[219]
Health
Student Health Services
Student Health Services, or SHS, operates out of the Student Health Center.[220][221] Primary care, vaccinations, x-rays, pharmacy services, gynecology services, and STI testing are some of the services provided.[220][222][223] Many of the services are low-cost or provided at no charge to students.[222][224] In 2023, state law required abortion services to be provided at all SHS locations, which are located at all CSU campuses.[225] SHS is accredited by the Accreditation Association for Ambulatory Health Care.[222]
Recreation
The main recreation facility at SF State, Mashouf Wellness Center, opened in 2017.[226] It is named after Manny Mashouf, who donated $10 million towards the $86.5 million construction costs.[227] The LEED Platinum certified, 118,700-square-foot facility features two heated pools, a hot tub, a sauna, a 41-foot climbing wall, fitness studios, exercise equipment, an indoor running track, a racquetball court, a two basketball courts, a multipurpose activities court.[226][228][229] It was also the university's first LEED rated building.[230]
In addition, the university's Gymnasium building has a pool and multi-use spaces. The building is mostly used for basketball, volleyball, badminton, and indoor soccer events.[231]
The Campus Recreation department hosts student-led camping, hiking, and climbing trips, called Gator Outdoor Adventures. The trips are one to four days long and have varying levels of difficulty.[232][233]
Associated Students

The student government of San Francisco State is known as Associated Students Inc. of SF State.[234] Associated Students provides funding for student organizations and operates the Cesar Chavez Student Center, the Early Childhood Education Center, two food pantry programs, a weekly farmers' market, and many other programs.[234][235]
Cesar Chavez Student Center
The Cesar Chavez Student Center was built in the mid-1960s with a capacity of 12,000 students.[236] Around 2002, it was renovated and expanded to 142,160 square feet across five floors with a capacity of over 30,000.[236] The building includes staff and student offices, a 500-seat auditorium, conference rooms, an art gallery, a multi-cultural center, student lounges, restaurants, a bookstore, and additional restrooms.[236] In 2003, the Filipino American Community Mural at the center was unveiled, becoming the first Filipino-American mural on a CSU campus.[237]
Project Rebound
Project Rebound is a special admissions and support program for formerly incarcerated people.[238][239] It was founded by John Irwin, a professor of sociology, in 1967.[240][241] After Irwin served five years at Soledad State Prison in the 1950s for armed robbery, he wanted to create a program that provided educational support to people like him.[242] The program has grown since its founding at SFSU, with 15 CSU campuses now having Project Rebound programs.[243][244]
Rhythms Music Festival
Associated Students hosts the Rhythms Music Festival annually. Before the main show, there are two competitions: one for DJs and one for bands. The winners of each competition then open for the main show.[245]
The annual event started as a joke when a student, Franko Ali, made a Facebook group called “If 15,000 people join this group then the campus will let us have a rave in the Annex.” Over 5,000 people joined. In 2010, a year after Ali made the group, he was elected to the student government. Inspired by Ali's group, the Associated Students Board of Directors voted to hire Travie McCoy for a performance, but couldn't afford his booking fees after one of his songs was used in Glee. Ali proposed a three-day music festival instead and it was approved. The first festival took place in March 2011.[246]
| Year | Headliners |
|---|---|
| 2011 | Grieves, Budo, The Hood Internet, Toro y Moi[247] |
| 2012 | Toro y Moi[248] |
| 2013 | Big Boi[249] |
| 2014 | Timeflies[250] |
| 2015 | G-Eazy[251] |
| 2016 | Kehlani[252][253] |
| 2017 | Vince Staples[254] |
| 2018 | T-Pain[250] |
| 2019 | Hayley Kiyoko[255] |
| 2020 | Bishop Briggs[256] |
| 2021 | Jane Handcock[257] |
| 2023 | Lupe Fiasco[258][259] |
Del the Funky Homosapien, and K Theory also performed in 2012.[247][248][247] In 2020, the event was held at the Fort Mason Festival Pavilion instead of the Annex.[256] In 2021, the festival was held over Zoom.[257]
Annual Folk Festival
Associated Students hosted the annual San Francisco State College Folk Festival from 1962 to 1970.[260][261][262][263] The 2nd Annual Folk Festival included performances by Jerry Garcia and Robert Hunter.[264]
OneCard
Since 2017, each student has been issued an ID card called a OneCard.[265] The cards also function as university library cards, Clipper cards, meal plan cards, and campus payment cards.[266] When the cards' Clipper functions are used during the fall and spring semesters, students can use Muni (excluding cable cars) and SamTrans for free and receive a 50% discount on BART trips to and from Daly City station. Students are charged a "Gator Pass" transit fee each semester, which pays for the transit benefits.[267]
Media
Golden Gate Xpress
Golden Gate Xpress is the university's daily online student newspaper.[59][268][269] The university's newspaper has changed names several times, but its history can be traced back to 1927.[270] Golden Gate Xpress has been awarded by the Associated Collegiate Press, College Media Association, and the Hearst Journalism Awards Program.[271][272][273]
Xpress Magazine
Xpress Magazine is a student magazine published during the fall and spring semesters. Four issues are published per semester, two of which are also printed. The magazine was originally known as Prism and dates back December 1969. In October 1999, the magazine was published for the first time under its current name.[274] Xpress Magazine has been awarded by the Associated Collegiate Press.[272][275]
Alumni Magazine
SF State Magazine is published by the university's Strategic Marketing and Communications department. The semiannual publication is mailed to over 80,000 alumni.[276]
Fourteen Hills
Creative Writing graduate students have published Fourteen Hills, an international literary journal, since 1994.[277][278]
Transfer Magazine
Since 1950, undergraduate students in the Creative Writing department have published Transfer Magazine, featuring literature and art by SFSU students.[279][280][281]
Radio Station
KSFS is a college radio station run by Broadcast and Electronic Communication Arts (BECA) students, streaming online, at 100.7 on Comcast Cable radio in San Francisco, and at 88.1 FM near or at the main campus.[282][283]
Notable faculty and alumni
 Stanley Mazor, co-inventor of the microprocessor
Stanley Mazor, co-inventor of the microprocessor Yvonne Cagle, NASA astronaut
Yvonne Cagle, NASA astronaut.jpg.webp) Willie Brown, 41st Mayor of San Francisco
Willie Brown, 41st Mayor of San Francisco Annette Bening, actress
Annette Bening, actress Manny Mashouf, founder, bebe Stores, Inc.
Manny Mashouf, founder, bebe Stores, Inc. Anne Rice, author of the Vampire Chronicles
Anne Rice, author of the Vampire Chronicles Ron Dellums, 48th Mayor of Oakland
Ron Dellums, 48th Mayor of Oakland Danny Glover, actor
Danny Glover, actor.jpg.webp)
 Melba Pattillo Beals, journalist and member of the Little Rock Nine
Melba Pattillo Beals, journalist and member of the Little Rock Nine George Miller, U.S. Congressman, 1975–2015
George Miller, U.S. Congressman, 1975–2015
.jpg.webp) Kevin Mullin, U.S. Congressman, 2022–present
Kevin Mullin, U.S. Congressman, 2022–present Jonas Rivera, producer, Pixar Animation Studios
Jonas Rivera, producer, Pixar Animation Studios BD Wong, actor
BD Wong, actor Mohammad Javad Zarif, Former Iranian Minister of Foreign Affairs
Mohammad Javad Zarif, Former Iranian Minister of Foreign Affairs John Patitucci, jazz bassist
John Patitucci, jazz bassist Dana Carvey, comedian and actor
Dana Carvey, comedian and actor Kirk Hammett, lead guitarist for Metallica
Kirk Hammett, lead guitarist for Metallica Oscar Zeta Acosta, attorney, politician, novelist and activist
Oscar Zeta Acosta, attorney, politician, novelist and activist Jeffrey Tambor, actor
Jeffrey Tambor, actor Kari Byron, television host and artist
Kari Byron, television host and artist.jpg.webp) Rob Schneider, actor and comedian
Rob Schneider, actor and comedian Johnny Mathis, singer
Johnny Mathis, singer Ronnie Schell, comedian and actor, co-starred as Duke on Gomer Pyle: USMC
Ronnie Schell, comedian and actor, co-starred as Duke on Gomer Pyle: USMC_(5272638037).jpg.webp)
 Michael Medved, author and radio talk show host
Michael Medved, author and radio talk show host Nina Hartley, pornographic actress, activist and educator
Nina Hartley, pornographic actress, activist and educator
See also
Notes
- ↑ Other consists of Multiracial Americans & those who prefer to not say.
- ↑ The percentage of students who received an income-based federal Pell grant intended for low-income students.
- ↑ The percentage of students who are a part of the American middle class at the bare minimum.
References
- ↑ As of June 30, 2020. U.S. and Canadian Institutions Listed by Fiscal Year 2020 Endowment Market Value and Change in Endowment Market Value from FY19 to FY20 (Report). National Association of College and University Business Officers and TIAA. February 19, 2021. Retrieved February 20, 2021.
- ↑ As of August 31, 2023. "University Budget Committee August 31, 2023 Presentation" (PDF). San Francisco State University. 2023.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "SF State Facts". San Francisco State University. 2022.
- 1 2 SF State Facts 2009–2010, San Francisco State University
- ↑ "Color System | Identity System Guidelines". Logo.sfsu.edu. July 14, 2015. Archived from the original on October 26, 2015. Retrieved October 20, 2015.
- ↑ "San Francisco State Teacher's College Historical landmark". California State Parks Office of Historic preservation. Retrieved September 20, 2023.
- ↑ "Search CSU Degrees". Degrees.calstate.edu. Retrieved February 5, 2014.
- ↑ "Doctoral Programs | Graduate College of Education". gcoe.sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 25, 2023.
- 1 2 "Credential Programs | Graduate College of Education". gcoe.sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 25, 2023.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 "SF State Facts | Strategic Marketing and Communications". marcomm.sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 23, 2023.
- ↑ "San Francisco State University". Indiana University. 2022. Retrieved February 18, 2022.
- ↑ "About the University". San Francisco State University. 2022. Retrieved April 26, 2022.
- 1 2 "Which Came First?: San Francisco State or San Jose State?". www.sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 25, 2023.
- 1 2 3 4 "History | CSU". www.calstate.edu. Retrieved November 25, 2023.
- ↑ Steffens, Kate. "SJSU Research Guides: San Jose State Normal Training School History: Minns' Evening Normal School, 1857-1862". libguides.sjsu.edu. Retrieved November 25, 2023.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 "SFSU Centennial History: Long Narrative of SF State". www.sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 23, 2023.
- 1 2 "San Francisco State University Celebrates 100 Years of Opportunity and Academic Innovation in the Bay Area". www.sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 25, 2023.
- 1 2 "SFSU Centennial history". www.sfsu.edu. Retrieved December 25, 2023.
- ↑ "SFSU Centennial History: 1899". www.sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 25, 2023.
- 1 2 3 4 Eliassen, Meredith (October 3, 2007). San Francisco State University. Arcadia Publishing. ISBN 978-1-4396-3589-6.
- 1 2 3 Pollak, Mark (November 16, 2018). The Playing Grounds of College Football: A Comprehensive Directory, 1869 to Today. McFarland. p. 346. ISBN 978-1-4766-3260-5.
- ↑ "National Register #07001391: San Francisco State Teacher's College in San Francisco, California". noehill.com. Retrieved November 25, 2023.
- ↑ "SAN FRANCISCO STATE TEACHER'S COLLEGE". CA State Parks. Retrieved November 25, 2023.
- 1 2 Project, Western Neighborhods. "Streetwise: Celebrating San Francisco State". www.outsidelands.org. Retrieved November 25, 2023.
- ↑ Gerth, Donald R. (2010). The People's University: A History of the California State University. Berkeley Public Policy Press. ISBN 978-0-87772-435-3.
- 1 2 3 "A Revised History of the Experimental College - 1960's to present | SF State's Experimental College". ueap.sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 26, 2023.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 "San Francisco State College Strike Collection-Bibliography of Secondary Source Materials". November 29, 2014. Archived from the original on November 29, 2014. Retrieved November 25, 2023.
- ↑ Anonymous (October 30, 2018). "San Francisco State University Black Student Union (BSU) Attack Gater campus newspaper editor, James Vaszko, San Francisco, CA, November 6, 1967". Cleveland Museum of Art. Retrieved November 25, 2023.
- ↑ "Interview with Jim Vaszko - Bay Area Television Archive". diva.sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 25, 2023.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 "S.F. STATE STRIKE 1968-69 CHRONOLOGY - FoundSF". www.foundsf.org. Retrieved December 25, 2023.
- ↑ "From semantics to the U.S. Senate, S.I. Hayakawa". oac.cdlib.org. Retrieved December 25, 2023.
- ↑ "Bombs at SF State - Bay Area Television Archive". diva.sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 30, 2023.
- 1 2 3 4 "Ethnic Studies: Born in the Bay Area from History's Biggest Student Strike". KQED. July 30, 2020. Retrieved December 25, 2023.
- ↑ "stdin: [sixties-l] SF State Bombings, Radical Campus Chaplains,". lists.village.virginia.edu. Retrieved December 25, 2023.
- ↑ "San Francisco State Faculty Protests Selection of Hayakawa's Successor | News | The Harvard Crimson". www.thecrimson.com. Retrieved December 25, 2023.
- ↑ "SFSU Centennial History: 1978". www.sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 25, 2023.
- ↑ "Centennial Historical Presidents: Chia Wei Woo". www.sfsu.edu. Retrieved December 25, 2023.
- ↑ Archives, L. A. Times (May 14, 1985). "Ticking Bomb Found on Campus in San Francisco". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved November 30, 2023.
- ↑ "San Francisco State College Campus Guide". Retrieved November 29, 2023.
- ↑ "Bomb at SF State College - Bay Area Television Archive". diva.sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 30, 2023.
- ↑ Archives, L. A. Times (September 21, 1985). "S.F. Man Held in One Bombing, Three Attempts". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved November 30, 2023.
- ↑ "United States of America, Plaintiff-appellee, v. Coy Ray Phelps, Defendant-appellant, 35 F.3d 573 (9th Cir. 1994)". Justia Law. Retrieved November 30, 2023.
- 1 2 Egelko, Bob (March 22, 2002). "Man's release a mistake, judge rules / Found insane, he escaped bomb charges". SF Gate. Retrieved November 29, 2023.
- ↑ "Phelps v. United States, 92 F. App'x 539 | Casetext Search + Citator". casetext.com. Retrieved November 30, 2023.
- ↑ "Inmate Locator". www.bop.gov. Retrieved November 30, 2023.
- ↑ Judge, EDWARD M. CHEN, District. "U.S. v. PHELPS | No. CR-85-00899 EMC. | By EDWARD... | 20151125994| Leagle.com". Leagle. Retrieved November 30, 2023.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ Adams, Gerald D. (December 16, 1999). "S.F. State trumpets downtown campus". CT Insider. Retrieved November 23, 2023.
- ↑ "Malcolm X Mural Is Marred Amid Dispute on Its Content". The New York Times. May 22, 1994.
- ↑ "The Chronicle of Higher Education". chronicle.com. Archived from the original on April 30, 2009.
- ↑ Lemonick, Michael D. (January 29, 1996). "IS SOMEONE OUT THERE?". Time. ISSN 0040-781X. Retrieved November 25, 2023.
- ↑ "Space Scientist: Geoff Marcy and Paul Butler". Discover Magazine. Retrieved November 25, 2023.
- ↑ Berlin, Kyran. "SF State evaluates new locations for Downtown Campus". Golden Gate Xpress. Retrieved November 25, 2023.
- ↑ Sheffer, Devery. "ASI-sponsored Rhythms Music Festival kicks off tomorrow in the Annex". Golden Gate Xpress. Retrieved December 29, 2023.
- ↑ "Rhythms". Associated Students. Retrieved December 29, 2023.
- ↑ "SFSU fired whistleblower who exposed Science Building scandal". The San Francisco Examiner. Retrieved October 26, 2018.
- ↑ "SFSU attorneys ordered to release Science Building scandal emails". The San Francisco Examiner. Retrieved October 26, 2018.
- ↑ "Contractor Pleads Guilty to 118 Counts of Bribery Involving Former SFSU Official". sfappeal.com. Retrieved October 26, 2018.
- ↑ "Roommate of woman in viral dreadlocks video at SF State speaks out". ABC7 San Francisco. Retrieved January 2, 2024.
- 1 2 "The white student who was harassed over his dreadlocks has spoken out". The Independent. March 31, 2016. Retrieved January 2, 2024.
- ↑ Herrera, Jack. "10-day hunger strike = victory for SFSU students". USA TODAY. Retrieved November 25, 2023.
- ↑ "Pilot Program Revives 1960s Experimental College at S.F. State". KQED. December 11, 2017. Retrieved November 26, 2023.
- ↑ Pine, Dan (August 5, 2017). "Investigation: SF Hillel 'improperly excluded' from student fair". J. Retrieved November 25, 2023.
- ↑ "A Reluctant Campus Acknowledges Zionism". Commentary Magazine. March 22, 2019. Retrieved November 25, 2023.
- ↑ Egelko, Bob (June 20, 2017). "Lawsuit says Jewish students 'intimidated' at SF State". San Francisco Chronicle. Retrieved November 25, 2023.
- 1 2 Egelko, Bob (March 15, 2022). "Tensions over ethnic studies continue at S.F. State as president vetoes faculty decision siding with professor". San Francisco Chronicle. Retrieved November 25, 2023.
- ↑ Martos, Shaylyn Cortney. "Protesters denounce CSU settlement over Zionism". Golden Gate Xpress. Retrieved November 25, 2023.
- ↑ "Lynn Mahoney | CSU". www.calstate.edu. Retrieved November 25, 2023.
- ↑ "Centennial Historical Presidents: Mary Ward". www.sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 25, 2023.
- ↑ "Whose Narratives? Gender, Justice, and Resistance - Event - Arab America". September 29, 2020. Archived from the original on September 29, 2020. Retrieved November 25, 2023.
- ↑ "Zoom refuses to stream university event featuring member of terrorist organization". September 27, 2020. Archived from the original on September 27, 2020. Retrieved November 25, 2023.
- ↑ Vincent, James (September 24, 2020). "Zoom cancels talk by Palestinian hijacker Leila Khaled at San Francisco State University". The Verge. Retrieved November 25, 2023.
- ↑ McLaughlin, Sarah (April 22, 2021). "Zoom cancels another academic event with Leila Khaled, again raising questions about company's role in the classroom". www.thefire.org. Retrieved November 25, 2023.
- ↑ Greschler, Gabriel (September 4, 2020). "Palestinian hijacker Leila Khaled to speak at S.F. State". J. Retrieved November 25, 2023.
- ↑ "New Downtown Campus - We Moved! | College of Professional & Global Education". cpage.sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 23, 2023.
- 1 2 3 Hernandez, Adriana (April 7, 2023). "Riley Gaines visit to SF State results in trans-rights activist protest". Golden Gate Xpress. Archived from the original on April 8, 2023. Retrieved April 8, 2023.
- ↑ Ross, Alexandra (March 28, 2023). "'Spiritual warfare': Riley Gaines speaks against trans women in women's sports at on-campus event". The Pitt News. Archived from the original on April 5, 2023. Retrieved April 8, 2023.
- 1 2 3 4 Regimbal, Alec (April 7, 2023). "Anti-Lia Thomas activist whisked away by police amid protest at San Francisco State". SFGATE. Archived from the original on April 7, 2023. Retrieved April 8, 2023.
- 1 2 "Former college swimmer says she was assaulted at an event opposing the inclusion of trans women in women's sports". CNN. April 7, 2023.
- ↑ Hernandez, Adriana. "'Stop the hike,' SFSU students oppose tuition increase". Golden Gate Xpress. Retrieved November 25, 2023.
- ↑ "Multi-Year Tuition Proposal | CSU". www.calstate.edu. Retrieved November 25, 2023.
- ↑ "Facing $1.5B deficit, California State University to hike tuition 6% annually for next 5 years". AP News. September 13, 2023. Retrieved November 25, 2023.
- ↑ King, Stephanie. "Budget cuts hit all colleges totaling over $11 million". Golden Gate Xpress. Retrieved November 25, 2023.
- ↑ "University Budget Committee August 31, 2023 Presentation" (PDF). University Budget Committee. August 31, 2023. Retrieved November 25, 2023.
- ↑ Singh, Preetina (October 12, 2023). "Organizing Against Massive Layoffs at San Francisco State University". California Faculty Association. Retrieved November 25, 2023.
- ↑ Osborn, Sophia. "CFA rally against tuition increase and working conditions". Golden Gate Xpress. Retrieved November 25, 2023.
- ↑ Osborn, Sophia. "CFA rally at SFSU for a better contract amidst vote to strike". Golden Gate Xpress. Retrieved November 25, 2023.
- ↑ Pratap, Ishaan. "CFA hosts rally to save SFSU faculty jobs". Golden Gate Xpress. Retrieved November 25, 2023.
- ↑ Osborn, Sophia. "SFSU walkout of class to call ceasefire in Gaza". Golden Gate Xpress. Retrieved November 25, 2023.
- ↑ "Walkouts Protesting 'Gaza Genocide' Planned on Campuses Across U.S." Haaretz. Retrieved November 25, 2023.
- ↑ Arbona, Catie (November 16, 2023). "Teamsters Show our POWER on Strike!". Teamsters Local 2010. Retrieved November 25, 2023.
- ↑ Osborn, Sophia. "Teamsters 2010 Union goes on strike". Golden Gate Xpress. Retrieved November 25, 2023.
- ↑ Hernandez, Jason. "Gators bite back in latest walkout". Golden Gate Xpress. Retrieved November 30, 2023.
- ↑ "California Faculty Association Instagram Post". November 9, 2023. Retrieved November 25, 2023.
- ↑ Osborn, Sophia, The other side: Q&A With CFA-SFSU Brad Erickson, retrieved November 25, 2023
- ↑ "University raises $10 million for new science building | Catalyze the Future". catalyze.sfsu.edu. Retrieved December 21, 2023.
- ↑ Hoover, Ken (March 21, 1999). "1899–1999 '100 Years of Opportunity' A century and 185,020 degrees after its humble beginnings, San Francisco State University proudly celebrates its legacy of service, activism and diversity". San Francisco Chronicle. pp. SC-1. Retrieved December 10, 2009.
- ↑ "Board of Trustees | CSU". www.calstate.edu. Retrieved January 16, 2024.
- ↑ "About Campus Governance | Administration & Finance". adminfin.sfsu.edu. Retrieved January 16, 2024.
- ↑ "Administrative Officers < San Francisco State University". bulletin.sfsu.edu. Retrieved January 16, 2024.
- ↑ "About Academic Affairs | Academic Affairs and the Office of the Provost". academic.sfsu.edu. Retrieved January 16, 2024.
- ↑ Eliassen, Meredith (February 1, 2019). "San Francisco State University Archives". California History. 96 (1): 33–45. doi:10.1525/ch.2019.96.1.33. ISSN 0162-2897. S2CID 166317280.
- ↑ Centennial Historical Presidents, San Francisco State University
- ↑ "President Mary A. Ward". University Communications, SFSU.
- ↑ "J. Paul Leonard, 93, University President". The New York Times. March 1, 1995. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved August 4, 2022.
- ↑ "Dr. Glenn S. Dumke, 72, Is Dead; Was California Universities' Head". The New York Times. July 1, 1989. Retrieved November 23, 2008.
- ↑ Asimov, Nanette (May 11, 2012). "Leslie Wong is named president of S.F. State". SFGATE. San Francisco. Retrieved August 13, 2018.
- ↑ "Lynn Mahoney Appointed President of San Francisco State University". May 22, 2019.
- ↑ "Academic Calendar - SF State University". webapps.sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 23, 2023.
- ↑ "Office of Student Financial Aid | San Francisco State University". financialaid.sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 26, 2023.
- 1 2 "San Francisco State University". U.S. News & World Report. Retrieved September 21, 2017.
- ↑ "Student Right-to-Know | Institutional Research". ir.sfsu.edu. Retrieved January 16, 2024.
- ↑ "College of Liberal & Creative Arts | San Francisco State University". lca.sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 27, 2023.
- ↑ "Innovate Sustainably. Lead Responsibly. | Lam Family College of Business". cob.sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 27, 2023.
- ↑ "College of Ethnic Studies | San Francisco State University". ethnicstudies.sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 27, 2023.
- ↑ "College of Health & Social Sciences | San Francisco State University". chss.sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 27, 2023.
- ↑ "The College of Science & Engineering (CoSE) | College of Science & Engineering". cose.sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 27, 2023.
- ↑ "Graduate College of Education | San Francisco State University". gcoe.sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 27, 2023.
- ↑ "College of Professional and Global Education (CPaGE) | San Francisco State University | Bay Area, California Continuing Education / Extension Classes + Certificates". cpage.sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 27, 2023.
- ↑ "Visit SF State - Fast Facts". SFSU.edu. Archived from the original on September 3, 2017. Retrieved September 23, 2017.
- ↑ "ADN-BSN | School of Nursing". www.nursing.sfsu.edu. Retrieved December 21, 2023.
- ↑ "SF State Scholars (Blended Bachelor's +Master's) Programs | Division of Graduate Studies & Career Development". grad.sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 25, 2023.
- ↑ "Find Your Graduate Program | Division of Graduate Studies & Career Development". grad.sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 25, 2023.
- ↑ "Joint Doctorate in Special Education | Department of Special Education". sped.sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 25, 2023.
- ↑ "EXCO Courses". ueap.sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 26, 2023.
- ↑ "EXCO Past Courses Fall 2023 | SF State's Experimental College". ueap.sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 26, 2023.
- ↑ "Undergraduate Education and Academic Planning | Undergraduate Education and Academic Planning". ueap.sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 26, 2023.
- ↑ "Open University | San Francisco State University | College of Professional & Global Education". cpage.sfsu.edu. Retrieved December 28, 2023.
- ↑ "ElderCollege at San Francisco State University | San Francisco State University | Courses for Mature Learners | College of Professional & Global Education". cpage.sfsu.edu. Retrieved December 28, 2023.
- ↑ "eldercollege.pdf | Powered by Box". sfsu.app.box.com. Retrieved December 28, 2023.
- 1 2 "About OLLI | Osher Lifelong Learning Institute". olli.sfsu.edu. Retrieved December 28, 2023.
- ↑ "Frequently Asked Questions | Osher Lifelong Learning Institute". olli.sfsu.edu. Retrieved December 28, 2023.
- 1 2 "Session Dates | Osher Lifelong Learning Institute". olli.sfsu.edu. Retrieved December 28, 2023.
- ↑ "OLLI SF State Courses | Osher Lifelong Learning Institute". olli.sfsu.edu. Retrieved December 28, 2023.
- ↑ "Osher Lifelong Learning Institute". olli.sfsu.edu. Retrieved December 28, 2023.
- ↑ "SF State WASC Accreditation". Archived from the original on November 1, 2012. Retrieved November 8, 2012.
- ↑ "SF State AACSB Accreditation".
- ↑ "Abet-Accredited Programs: San Francisco State University".
- 1 2 "College Navigator - San Francisco State University". nces.ed.gov. Retrieved November 25, 2023.
- ↑ "How To Apply | Division of Graduate Studies & Career Development". grad.sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 25, 2023.
- ↑ "College Navigator - San Francisco State University". nces.ed.gov. Retrieved November 25, 2023.
- ↑ "Forbes America's Top Colleges List 2023". Forbes. Retrieved September 22, 2023.
- ↑ "Wall Street Journal/Times Higher Education College Rankings 2022". The Wall Street Journal/Times Higher Education. Retrieved July 26, 2022.
- ↑ "2023-2024 Best National Universities". U.S. News & World Report. Retrieved September 22, 2023.
- ↑ "2022 National University Rankings". Washington Monthly. Retrieved September 13, 2022.
- ↑ "2022-23 Best Global Universities Rankings". U.S. News & World Report. Retrieved February 25, 2023.
- ↑ "California State University - San Francisco Rankings". U.S. News & World Report. Retrieved September 12, 2022.
- ↑ "San Francisco - U.S. News Best Grad School Rankings". U.S. News & World Report. Retrieved September 24, 2020.
- ↑ "Social Mobility Index". Social Mobility Index. CollegeNET and PayScale. 2020. Retrieved November 12, 2021.
- ↑ "Graduate Philosophy Department Ranks #8 Nationwide". Archived from the original on May 21, 2018. Retrieved May 20, 2018.
- 1 2 "Programs - San Francisco State University". Sfsu.edu. Archived from the original on December 5, 2013. Retrieved February 5, 2014.
- ↑ "Schools & Departments". Retrieved May 24, 2018.
- ↑ "Entertainment Education Report: The Best Film Schools for 2019". Variety. 2019. Retrieved July 13, 2019.
- ↑ "The Top 25 American Film Schools, Ranked". The Hollywood Reporter. August 15, 2019.
- ↑ "University Impact Report 2023 | University Development". develop.sfsu.edu. Retrieved January 12, 2024.
- ↑ McGrane, Sally (August 26, 2001). "Family Matters / Learning about relatives -- near and far -- expands our sense of self". SFGATE. San Francisco. Retrieved September 23, 2017.
- ↑ "Wall Street Journal ranks SF State top 5 for diversity nationwide | SF State News". news.sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 26, 2023.
- ↑ "Top Colleges in the West for Diversity". Wall Street Journal. November 17, 2021. ISSN 0099-9660. Retrieved November 26, 2023.
- ↑ "Ethnicity Enrollment Profile". www.calstate.edu. Archived from the original on October 25, 2019. Retrieved July 9, 2019.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Welcome | Campus Maps". maps.sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 27, 2023.
- ↑ "Science & Engineering Innovation Center | School of Engineering". engineering.sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 23, 2023.
- ↑ "Welcome to DineOnCampus at San Francisco State University by Chartwells Higher Education". Dineoncampus.com. Retrieved November 4, 2011.
- ↑ "Dining Center – SF State University Property Management". Sfsu.edu. Archived from the original on September 7, 2011. Retrieved November 4, 2011.
- ↑ "Manzanita Square | University Housing". housing.sfsu.edu. Retrieved December 24, 2020.
- 1 2 "Mary Park and Mary Ward Residence Halls – SF State University Property Management". Sfsu.edu. Archived from the original on November 17, 2011. Retrieved November 4, 2011.
- ↑ "Towers at Centennial Square". Archived from the original on June 2, 2017. Retrieved June 4, 2017.
- ↑ "Towers at Centennial Square – SF State University Property Management". Sfsu.edu. Archived from the original on November 17, 2011. Retrieved November 4, 2011.
- ↑ "Village at Centennial Square – SF State University Property Management". Sfsu.edu. Archived from the original on November 17, 2011. Retrieved November 4, 2011.
- ↑ "University Park North". Archived from the original on June 3, 2008. Retrieved June 18, 2008.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ↑ "University Park South". Archived from the original on February 20, 2009. Retrieved June 18, 2008.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - 1 2 3 "West Campus Green Site Development | Capital Planning, Design and Construction". cpdc.sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 23, 2023.
- ↑ Levy, Dan (March 29, 1999). "Old Dorm Reduced To Dust / Thousands watch implosion at S.F. State". San Francisco Chronicle. Retrieved January 27, 2017.
- ↑ "Meeting and Conference Facilities- Seven Hills – SF State University Property Management". Sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 4, 2011.
- ↑ "Student Life Events Center | Student Activities & Events". activities.sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 27, 2023.
- ↑ "Meeting and Conference Facilities-Towers – SF State University Property Management". Sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 4, 2011.
- ↑ "Cesar Chavez Student Center". Associated Students. Retrieved November 27, 2023.
- ↑ "Early Childhood Education Center". Associated Students. Retrieved November 27, 2023.
- 1 2 "Downtown Campus | San Francisco State University | College of Professional & Global Education". cpage.sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 23, 2023.
- ↑ Berlin, Kyran. "SF State evaluates new locations for Downtown Campus". Golden Gate Xpress. Retrieved November 23, 2023.
- 1 2 Wong, Neal. "Xplainer: Downtown Campus". Golden Gate Xpress. Retrieved December 21, 2023.
- ↑ "San Francisco State University Downtown Campus | Lam Family College of Business". cob.sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 27, 2023.
- ↑ "February 13, 2023 | CampusMemo". campusmemo.sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 27, 2023.
- ↑ "Contact | Sierra Nevada Field Campus". sierra.sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 27, 2023.
- ↑ "Welcome to the San Francisco State Sierra Nevada Field Campus". SF State Sierra Nevada Field Campus. Retrieved December 15, 2021.
- 1 2 "Classes & Workshops | Sierra Nevada Field Campus". sierra.sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 27, 2023.
- ↑ "Scholarships | Sierra Nevada Field Campus". sierra.sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 27, 2023.
- ↑ "FAQs | Sierra Nevada Field Campus". sierra.sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 27, 2023.
- ↑ "Gallery | Sierra Nevada Field Campus". sierra.sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 27, 2023.
- ↑ "Sierra Nevada Field Campus | Sierra Nevada Field Campus". sierra.sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 27, 2023.
- ↑ "Worldwide Elevation Finder". elevation.maplogs.com. Retrieved November 27, 2023.
- ↑ "Friends of the Sierra Nevada Field Campus – photo by Sarah Rabkin". friendsofsnfc.org. Retrieved November 27, 2023.
- ↑ "Sierra Nevada Field Campus · 35400 CA-49, Sierra City, CA 96124". Sierra Nevada Field Campus · 35400 CA-49, Sierra City, CA 96124. Retrieved November 27, 2023.
- ↑ "Romberg Tiburon Campus". Estuary & Ocean Science Center. Retrieved September 15, 2021.
- ↑ Lang, Gretchen (June 29, 2022). "The Ark | Marine center's new director hopeful amid funding challenges". The Ark. Retrieved November 27, 2023.
- 1 2 "Director's Message | Estuary & Ocean Science Center". eoscenter.sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 27, 2023.
- ↑ Administrator, SI OCIO Web (August 24, 2015). "The Tiburon Branch of the Marine Invasions Lab - Conducting World-class research on the US West Coast Since 2000". Smithsonian Environmental Research Center. Retrieved December 25, 2023.
- 1 2 3 Alexander, Kurtis (June 10, 2023). "The only marine science lab on San Francisco Bay is at risk of closing. Here's what's at stake". San Francisco Chronicle. Retrieved November 23, 2023.
- ↑ "Campus Planning at San Francisco State University | Campus Planning". plan.sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 27, 2023.
- ↑ "Romberg Tiburon Campus Master Plan | Campus Planning". plan.sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 27, 2023.
- ↑ "Estuary & Ocean Science Center | Facilities Services". facilities.sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 27, 2023.
- ↑ "Visit Our Offices | San Francisco Bay National Estuarine Research Reserve". sfbaynerr.sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 27, 2023.
- ↑ "Bay Conference Center | Estuary & Ocean Science Center". eoscenter.sfsu.edu. Retrieved September 15, 2021.
- ↑ "WRE | Season concludes at NCAA Regionals". SF State Athletics. February 24, 2017. Retrieved March 28, 2017.
- ↑ "Championships Summary" (PDF). National Collegiate Athletic Association. Retrieved May 20, 2018.
- ↑ "Division II Wrestling Championships Records Book" (PDF). National Collegiate Athletic Association. Retrieved August 19, 2019.
- 1 2 3 Eliassen, Meredith (2007). San Francisco State University. Arcadia Publishing. p. 35. ISBN 9780738555669.
- ↑ Eliassen, Meredith. "LibGuides: SFSU Archives: Mascot". libguides.sfsu.edu. Retrieved January 1, 2024.
- ↑ "Alli the Gator | New Student & Family Programs". newstudentprograms.sfsu.edu. Retrieved January 1, 2024.
- 1 2 "Why is SF State's mascot a 'Gator?'". KRON4. February 15, 2023. Retrieved January 1, 2024.
- ↑ "Why is SF State's mascot a Gator? - Library Help". sfsu.libanswers.com. Retrieved January 1, 2024.
- ↑ "Alli Gator gets a glow up | SF State News". news.sfsu.edu. Retrieved January 1, 2024.
- ↑ "IMLeagues". www.imleagues.com. Retrieved November 28, 2023.
- ↑ "- GatorXperience". sfsu.campuslabs.com. Retrieved November 23, 2023.
- ↑ "Reregister a Club/Organization | Student Activities & Events". activities.sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 26, 2023.
- ↑ "Greek Life at SF State | Student Activities & Events". activities.sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 23, 2023.
- ↑ "Residential Community Overview | University Housing". housing.sfsu.edu. Retrieved January 1, 2024.
- ↑ "Student Living". Parkmerced. Retrieved January 1, 2024.
- ↑ Dorm Tour | SFSU Mary Ward Hall, retrieved January 1, 2024
- ↑ "San Francisco State University Manzanita Square". Multistudio. Retrieved January 1, 2024.
- ↑ "Welcome to Manzanita Square! | University Housing". housing.sfsu.edu. Retrieved January 1, 2024.
- 1 2 Making the most of the Health Center at SFSU, retrieved January 2, 2024
- ↑ "Student Health Services - San Francisco State University - LocalWiki". localwiki.org. Retrieved January 2, 2024.
- 1 2 3 "Student Health Services | San Francisco State University". health.sfsu.edu. Retrieved January 1, 2024.
- ↑ "Sexual Health Services at Student Health Services - San Francisco State University - LocalWiki". localwiki.org. Retrieved January 2, 2024.
- ↑ "Nutrition Clinic | Health Promotion & Wellness". wellness.sfsu.edu. Retrieved January 1, 2024.
- ↑ Alonso, Johanna. "Abortions on Campus". Inside Higher Ed. Retrieved January 1, 2024.
- 1 2 "Green-designed Mashouf Wellness Center opens its doors | SF State News". news.sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 26, 2023.
- ↑ Dunaway, Dayvon. "Future wellness center named after alumni donor". Golden Gate Xpress. Retrieved November 26, 2023.
- ↑ "Mashouf Wellness Center | Campus Recreation". campusrec.sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 26, 2023.
- ↑ "San Francisco State University Mashouf Wellness Center". WRNS Studio. Retrieved November 27, 2023.
- ↑ "San Francisco State University, Mashouf Wellness Center by WRNS Studio". www.dexigner.com. December 19, 2018. Retrieved January 1, 2024.
- ↑ "Gymnasium | Campus Recreation". campusrec.sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 27, 2023.
- ↑ "Search Programs - San Francisco State University Recreation Portal". member.campusrec.sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 28, 2023.
- ↑ "Gator Outdoor Adventures | Campus Recreation". campusrec.sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 28, 2023.
- 1 2 "Associated Students: Your Student Government | Dean of Students (DOS)". dos.sfsu.edu. Retrieved November 26, 2023.
- ↑ "Associated Students". Associated Students. Retrieved November 26, 2023.
- 1 2 3 Yee, Roger (2002). Educational Environments. HarperCollins.
- ↑ Allyson Tintiangco-Cubales, E.J.R. David, Kevin Leo Yabut Nadal, ed. (September 13, 2022). The SAGE Encyclopedia of Filipina/x/o American Studies. Sage Publications. p. 674. ISBN 9781071828977.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: editors list (link) - ↑ "Project Rebound | Associated Students SFSU". Associated Students. Retrieved January 2, 2024.
- ↑ "Project Rebound". January 2, 2024.
- ↑ Al-Khasib, Sabeen. "Road to Redemption: Project Rebound". The Pioneer. Retrieved January 1, 2024.
- ↑ "Project Rebound Celebrates 50 Years of Educating Former Prisoners". KQED. September 29, 2017. Retrieved January 1, 2024.
- ↑ Bates, Kristin A.; Swan, Richelle S. (March 28, 2023). Juvenile Delinquency in a Diverse Society. SAGE Publications. ISBN 9781071862278.
- ↑ "History of Project Rebound". www.csueastbay.edu. Retrieved January 2, 2024.
- ↑ "Project Rebound | CSU". www.calstate.edu. Retrieved January 2, 2024.
- ↑ "Rhythms". Associated Students. Retrieved December 29, 2023.
- ↑ Sheffer, Devery. "ASI-sponsored Rhythms Music Festival kicks off tomorrow in the Annex". Golden Gate Xpress. Retrieved December 29, 2023.
- 1 2 3 "Rhythms Music Festival - Franko Ali". cargocollective.com. Retrieved January 2, 2024.
- 1 2 Mulich, Hunter. "Rhythms Music Festival schedule". Golden Gate Xpress. Retrieved December 29, 2023.
- ↑ Ramos, Jonathan. "Costly Rhythms Music Festival attracts low student turnout". Golden Gate Xpress. Retrieved December 29, 2023.
- 1 2 Rhythms Just Got Bigger, retrieved December 29, 2023
- ↑ Ruidas, Kalani. "Rhythms Music Festival brings familiar faces and new Bay Area talent". Golden Gate Xpress. Retrieved December 29, 2023.
- ↑ Manson, Adrian Pintor, Connor Hunt, Ryan Zaragoza, and Madeline. "Math rock band opens for Kehlani at Rhythms Music festival". Golden Gate Xpress. Retrieved December 29, 2023.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ Clark, Trent (April 15, 2016). "Kehlani Headlines San Francisco State University Event". HipHopDX. Retrieved January 2, 2024.
- ↑ Rhythms Music Fest Archive 2017, retrieved December 29, 2023
- ↑ Hayley Kiyoko @ SFSU!, retrieved December 29, 2023
- 1 2 Bishop Briggs Coming to SF! | Rhythms Music Festival 2020, retrieved December 29, 2023
- 1 2 "RHYTHMS MUSIC FESTIVAL 2021: Opener Show". sfsu.campuslabs.com. Retrieved December 29, 2023.
- ↑ Pratap, Ishaan. "Lupe Fiasco headlines 12th Annual Rhythms Music Festival". Golden Gate Xpress. Retrieved December 29, 2023.
- ↑ "KALW Music programmers judge SFSU Battle of the DJs, Bands". KALW. May 22, 2023. Retrieved January 2, 2024.
- ↑ "San Francisco 1966 Folk Festival Photos and Premium High Res Pictures - Getty Images".
- ↑
- https://newspaperarchive.com/lowell-sun-may-02-1966-p-2/
- http://brunoceriotti.weebly.com/the-blues-project.html
- https://farinafiles1.tripod.com/timeline.htm
- https://www.diggers.org/chrono_notes.htm
- https://www.classicposters.com/poster/199/
- https://worldradiohistory.com/hd2/IDX-Business/Music/Billboard-Index/IDX/1966/Billboard-1966-03-19-II-Music-on-Campus-OCR-Page-0030.pdf
- https://woodyguthriecenter.org/archives/collections/ronald-d-cohen-folk-music-research-collection/
- http://sfmuseum.org/hist1/rock.html
- https://dc.library.northwestern.edu/items/d49eba42-a635-4b3b-8604-463070a23f6a
- https://www.gettyimages.com/detail/news-photo/american-songwriter-record-producer-and-musician-al-kooper-news-photo/1257223144
- ↑
- https://www.nicholasjennings.com/1968-the-year-of-lightfoot-s-u-s-breakthrough
- https://folkways.si.edu/vern-ray/san-francisco-1968/country-bluegrass/music/album/smithsonian
- https://kpsu.org/ankenytwang/way-west-maddox-brothers-vern-ray-classic-cowboys/
- http://www.deaddisc.com/GDFD_SF_State_College.htm
- ↑ "That Be-Bop-A-Lula Cat – Jungle Records".
- ↑ "Digital Collections - Libraries - Northwestern University".
- ↑ "S.F. State Students Approve $180 Per Semester Fee for New Transit Pass". KQED. April 21, 2016. Retrieved January 1, 2024.
- ↑ Wong, Neal. "Xplainer: OneCard". Golden Gate Xpress. Retrieved January 1, 2024.
- ↑ "Gator Pass Transit Fee | Vice President for Student Affairs & Enrollment Management". vpsaem.sfsu.edu. Retrieved January 1, 2024.
- ↑ "Golden Gate Xpress". Golden Gate Xpress. Retrieved January 2, 2024.
- ↑ "Department of Journalism | College of Liberal & Creative Arts". journalism.sfsu.edu. Retrieved January 2, 2024.
- ↑ "ABOUT". Golden Gate Xpress. Retrieved January 2, 2024.
- ↑ "ACP - Pacemaker 100". Retrieved January 2, 2024.
- 1 2 "Awards and Honors | Department of Journalism". journalism.sfsu.edu. Retrieved January 2, 2024.
- ↑ jstone (October 31, 2023). "CMA 2023 Pinnacle Award Winners". College Media Association. Retrieved January 2, 2024.
- ↑ "Xpress Magazine". Xpress Magazine. Retrieved January 2, 2024.
- ↑ "ACP - ACP names top student magazines". Retrieved January 2, 2024.
- ↑ "SF State Magazine | CASE". www.case.org. Retrieved January 2, 2024.
- ↑ "Alumni & Student Publications & Department Publications | Department of Creative Writing". creativewriting.sfsu.edu. Retrieved January 2, 2024.
- ↑ "Fourteen Hills: The SFSU Review". Poets & Writers. March 12, 2009. Retrieved January 2, 2024.
- ↑ "Transfer 119.pdf". Google Docs. Retrieved January 2, 2024.
- ↑ "Alumni & Student Publications & Department Publications | Department of Creative Writing". creativewriting.sfsu.edu. Retrieved January 2, 2024.
- ↑ "Arielle Jones; Fiction Editor of Transfer Magazine and Runway Model". April 28, 2012. Retrieved January 2, 2024.
- ↑
- "SF State News". www.sfsu.edu. Retrieved September 10, 2018.
- "KSFS Radio". KSFS Media. Retrieved September 10, 2018.
- "San Francisco Bay Area's Bounty of Independent Radio Offerings". radiosurvivor.com. March 12, 2012. Retrieved September 10, 2018.
- ↑
- "KSFS". sfsu.edu. April 6, 2005. Archived from the original on April 6, 2005. Retrieved September 10, 2018 – via archive.org.
- "radio Guide". baylindo.com. Retrieved September 10, 2018.
- "Media List". City of Berkeley. Retrieved September 10, 2018.
- "KSFS 100.7 F.M". facebook.com. Retrieved September 10, 2018.
- "RADIO WAVES". sfgate.com. December 4, 2005. Retrieved September 10, 2018.












