| Siege of Smolensk(1613-1617) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Polish–Muscovite War (1605–1618) | |||||||
 | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
Dmitry Cherkassky Ivan Khovansky |
Alexander Gonsevsky Alexander Lisovsky | ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
|
Up to 12,000 (the largest number) 5,000–6,000 (average number) |
Up to 2,000 (garrison) Up to 2,500 (troops outside the fortress) | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| Light | Light | ||||||
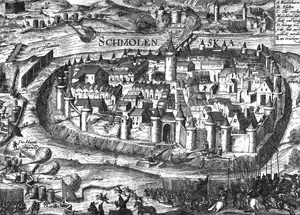
The siege of Smolensk (1613–1617) is an episode of the Polish–Muscovite War (1605–1618).
Prelude
After the tactical victory in the Battle of Moscow (1612), the Russian government made an attempt to repulse the Poles from the strategically important fortress of Smolensk. Russian troops without a fight retook Vyazma (July 7, 1613), Dorogobuzh, and Bely, an important outpost on the Lithuanian frontier.[1]
Siege
Russian troops for almost four years led a protracted and unsuccessful siege of the city, which consisted mainly of blockade of the garrison. During the siege, no attempt was made to assault. In the beginning of 1617, with the onset of the offensive of Polish–Lithuanian troops on Moscow (Wladislaw III campaign), the siege was lifted.[1]
Aftermath
The unsuccessful siege of Smolensk predetermined the unsuccessful completion of the Polish–Muscovite War (1605–18). According to the Truce of Deulino, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth retained the Smolensk lands, which were captured by Russians only in 1654 at the beginning of the next Russo-Polish War (1654-67).[2]
References
- 1 2 Velikai︠a︡ russkai︠a︡ smuta : prichiny vozniknovenii︠a︡ i vykhod iz gosudarstvennogo krizisa v XVI-XVII vv. Strizhova, I. M., Стрижова, И. М. Moskva: Dar. 2007. ISBN 9785485001230. OCLC 230750976.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: others (link) - ↑ Željko, Fajfrić (2008). Ruski carevi (1. izd ed.). Sremska Mitrovica: Tabernakl. ISBN 9788685269172. OCLC 620935678.