| United States District Court for the Southern District of New York | |
|---|---|
| (S.D.N.Y.) | |
 | |
| Location | Daniel Patrick Moynihan U.S. Courthouse |
| Appeals to | Second Circuit |
| Established | April 9, 1814 |
| Judges | 28 |
| Chief Judge | Laura Taylor Swain |
| Officers of the court | |
| U.S. Attorney | Damian Williams |
| U.S. Marshal | Ralph Sozio |
| www.nysd.uscourts.gov | |
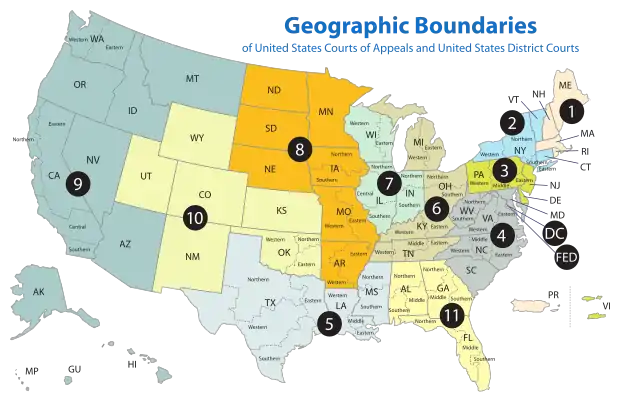
The United States District Court for the Southern District of New York (in case citations, S.D.N.Y.) is a federal trial court whose geographic jurisdiction encompasses eight counties of the State of New York. Two of these are in New York City: New York (Manhattan) and Bronx; six are in the Hudson Valley: Westchester, Putnam, Rockland, Orange, Dutchess, and Sullivan. Appeals from the Southern District of New York are taken to the United States Court of Appeals for the Second Circuit (except for patent claims and claims against the U.S. government under the Tucker Act, which are appealed to the Federal Circuit).
Because it covers Manhattan, the Southern District of New York has long been one of the most active and influential federal trial courts in the United States. It often has jurisdiction over America's largest financial institutions and prosecution of white-collar crime and other federal crimes.[1] Because of its age and influence, it is sometimes colloquially called the "Mother Court" or the "Sovereign District of New York."[2][3] The district has had several prominent judges on its bench, including Learned Hand, Michael Mukasey, and Sonia Sotomayor, and many of the U.S. attorneys for the district have been prominent American legal and political figures, such as Elihu Root, Henry L. Stimson, Robert Morgenthau, Rudy Giuliani, James Comey, Michael J. Garcia, and Preet Bharara.[4]
Jurisdiction
The United States District Court for the Southern District of New York encompasses the counties of New York, Bronx, Westchester, Rockland, Putnam, Orange, Dutchess, and Sullivan and draws jurors from those counties. The Court also shares jurisdiction over the waters of the counties of Kings, Nassau, Queens, Richmond, and Suffolk with the United States District Court for the Eastern District of New York.[5] The Court hears cases in Manhattan, White Plains, and Poughkeepsie, New York.[6]
The United States Attorney's Office for the Southern District of New York represents the United States in civil and criminal litigation in the Court. As of October 10, 2021 the United States Attorney is Damian Williams.[7]
The court sits in the Thurgood Marshall United States Courthouse and Daniel Patrick Moynihan United States Courthouse, both in Manhattan, and in the Charles L. Brieant Jr. Federal Building and Courthouse in White Plains.
History
The United States District Court for the District of New York was one of the original 13 courts established by the Judiciary Act of 1789, 1 Stat. 73, on September 24, 1789. It first sat at the old Merchants Exchange on Broad Street in November 1789, the first federal court to do so.[8][9][10] The Act of April 9, 1814, 3 Stat. 120, divided the District of New York into Northern and Southern Districts.[9][10]
The subdivision of the district was reportedly instigated by Matthias B. Tallmadge, out of antipathy for fellow district judge William P. Van Ness. These Districts were later further subdivided with the creation of the Eastern District on February 25, 1865 by 13 Stat. 438,[10] and the Western District on May 12, 1900, by 31 Stat. 175.[10] Public Law 95-408 (enacted October 2, 1978) transferred Columbia, Greene, and Ulster counties from the Southern to the Northern district.[11]
For the first hundred years of its existence, the case load of the district was dominated first by admiralty cases, and then by a mix of admiralty and bankruptcy cases. The primary responsibility for hearing bankruptcy cases has since been transferred to the United States Bankruptcy Court for the Southern District of New York, with the District Court only reviewing cases already decided by a bankruptcy judge.
Since its creation, the Southern District of New York has had over 150 judges, more than any other District. Twenty-one judges from the Southern District of New York have been elevated to the United States Court of Appeals for the Second Circuit—Samuel Blatchford, Charles Merrill Hough, Learned Hand, Julius Marshuetz Mayer, Augustus Noble Hand, Martin Thomas Manton, Robert P. Patterson, Harold Medina, Irving Kaufman, Wilfred Feinberg, Walter R. Mansfield, Murray Gurfein, Lawrence W. Pierce, Pierre N. Leval, John M. Walker Jr., Sonia Sotomayor, Denny Chin, Barrington Daniels Parker Jr., Gerard E. Lynch, Richard J. Sullivan, and Alison Nathan. Blatchford and Sotomayor, after being elevated from the Southern District of New York to serve as Circuit Judges for the Second Circuit, were later elevated to the Supreme Court of the United States. The longest serving judge, David Norton Edelstein, served as an active judge for 43 years to the day, and in senior status for an additional six years.
Judges of the court have gone on to other high governmental positions. Robert P. Patterson served as Under Secretary of War under President Franklin Roosevelt and was Secretary of War under President Harry S. Truman. Louis Freeh served as Director of the Federal Bureau of Investigation from September 1993 to June 2001. Michael Mukasey served as the 81st United States Attorney General under President George W. Bush.
Notable cases
- The injury and loss of life claims from the sinking of the Titanic,[12] the torpedo attack on the Lusitania[13] and the fire aboard the General Slocum[14] were heard in the S.D.N.Y.
- The espionage trial of Julius and Ethel Rosenberg[15] and the perjury trial of Alger Hiss[16] were heard in the S.D.N.Y.
- Judge John M. Woolsey of the S.D.N.Y. rejected government efforts to censor on obscenity grounds the distribution of James Joyce's Ulysses.[17]
- Judge Murray Gurfein of the Court rejected government efforts to enjoin The New York Times from publishing the Pentagon Papers.[18]
- Defamation suits were heard in the S.D.N.Y. against CBS and Time magazine by General William Westmoreland and Israeli General Ariel Sharon.
- Two former Attorneys General of the United States were indicted and tried in the S.D.N.Y. for crimes while in office – Harry Daugherty of the Teapot Dome era and John Mitchell of the Watergate era. Juries were unable to reach verdicts in the two trials against Daugherty; John Mitchell was acquitted.
- Financial frauds have been prosecuted in the S.D.N.Y., among them the cases against Bernard Madoff, Ivan Boesky, Michael Milken, and Sam Bankman-Fried.
- Bombings: the trials of those accused of the 1998 United States embassy bombings in East Africa; those alleged to have been responsible for the 1993 World Trade Center bombing; and Omar Abdel Rahman (known in the press as "The Blind Sheikh"), occurred in the District. More recently, the prosecution arising out of the 2010 Times Square car bombing attempt were each heard in the S.D.N.Y.
- Bridgeman v. Corel (1999) established that exact reproductions of public domain paintings were not subject to copyright protection.
- Viacom Inc. v. YouTube Inc., a $1 billion lawsuit against Google and YouTube on the grounds of alleged copyright infringement. The DMCA safe harbor law became the main argument in the case.
- Prosecution of Abduwali Muse, the so-called "Somali Pirate", was heard in the Court in 2010.[19]
- The criminal cases against Bess Myerson, Leona Helmsley and Martha Stewart were heard in the S.D.N.Y., as was the U.S. case against Imelda Marcos.
- The Deflategate controversy concerning the National Football League's Tom Brady was heard in the S.D.N.Y.
- Hosseinzadeh v. Klein, concerning the practice of fair use in online video content, was heard in the S.D.N.Y.[20]
- On December 12, 2018, Judge William H. Pauley III sentenced Michael Cohen – who had served as personal legal counsel to U.S. president Donald Trump for more than a decade – to "three years in prison and millions in forfeitures, restitution and fines",[21] after pleading guilty to charges including campaign finance violations, tax evasion and committing perjury while under oath before Congress.[22]
- In July 2022, Real Housewives of Salt Lake City star Jennifer Shah pleaded guilty to conspiracy to commit wire fraud in the S.D.N.Y. In January 2023, Shah was sentenced to six-and-a-half years in prison.[23]
- The E. Jean Carroll v. Donald J. Trump trial, presided over by Lewis Kaplan, was held in April and May of 2023 in which the jury reached a unanimous decision, after deliberating for less than three hours, that Donald J. Trump was liable for sexual abuse via forcible digital penetration and defamation. Carroll was awarded a total of $5 million in damages.[24]
Current judges
As of January 9, 2024:
| # | Title | Judge | Duty station | Born | Term of service | Appointed by | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Active | Chief | Senior | ||||||
| 125 | Chief Judge | Laura Taylor Swain | Manhattan | 1958 | 2000–present | 2021–present | — | Clinton |
| 110 | District Judge | John G. Koeltl | Manhattan | 1945 | 1994–present | — | — | Clinton |
| 129 | District Judge | Kenneth M. Karas | White Plains | 1964 | 2004–present | — | — | G.W. Bush |
| 132 | District Judge | Cathy Seibel | White Plains | 1960 | 2008–present | — | — | G.W. Bush |
| 135 | District Judge | J. Paul Oetken | Manhattan | 1965 | 2011–present | — | — | Obama |
| 136 | District Judge | Paul A. Engelmayer | Manhattan | 1961 | 2011–present | — | — | Obama |
| 139 | District Judge | Edgardo Ramos | Manhattan | 1960 | 2011–present | — | — | Obama |
| 140 | District Judge | Andrew L. Carter Jr. | Manhattan | 1969 | 2011–present | — | — | Obama |
| 141 | District Judge | Jesse M. Furman | Manhattan | 1972 | 2012–present | — | — | Obama |
| 142 | District Judge | Ronnie Abrams | Manhattan | 1968 | 2012–present | — | — | Obama |
| 143 | District Judge | Lorna G. Schofield | Manhattan | 1956 | 2012–present | — | — | Obama |
| 144 | District Judge | Katherine Polk Failla | Manhattan | 1969 | 2013–present | — | — | Obama |
| 145 | District Judge | Analisa Torres | Manhattan | 1959 | 2013–present | — | — | Obama |
| 146 | District Judge | Nelson S. Román | White Plains | 1960 | 2013–present | — | — | Obama |
| 147 | District Judge | Vernon S. Broderick | Manhattan | 1963 | 2013–present | — | — | Obama |
| 148 | District Judge | Gregory H. Woods | Manhattan | 1969 | 2013–present | — | — | Obama |
| 149 | District Judge | Valerie E. Caproni | Manhattan | 1955 | 2013–present | — | — | Obama |
| 150 | District Judge | Mary Kay Vyskocil | Manhattan | 1958 | 2019–present | — | — | Trump |
| 151 | District Judge | Lewis J. Liman | Manhattan | 1960 | 2019–present | — | — | Trump |
| 152 | District Judge | Philip M. Halpern | White Plains | 1956 | 2020–present | — | — | Trump |
| 153 | District Judge | John P. Cronan | Manhattan | 1976 | 2020–present | — | — | Trump |
| 154 | District Judge | Jennifer L. Rochon | Manhattan | 1970 | 2022–present | — | — | Biden |
| 155 | District Judge | Jennifer H. Rearden | Manhattan | 1970 | 2022–present | — | — | Biden |
| 156 | District Judge | Arun Subramanian | Manhattan | 1979 | 2023–present | — | — | Biden |
| 157 | District Judge | Jessica G. L. Clarke | Manhattan | 1983 | 2023–present | — | — | Biden |
| 158 | District Judge | Dale Ho | Manhattan | 1977 | 2023–present | — | — | Biden |
| 159 | District Judge | Margaret Garnett | Manhattan | 1971 | 2024–present | — | — | Biden |
| 160 | District Judge | vacant | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 79 | Senior Judge | Charles S. Haight Jr. | New Haven, CT[Note 1] | 1930 | 1976–1995 | — | 1995–present | Ford |
| 89 | Senior Judge | John F. Keenan | inactive | 1929 | 1983–1996 | — | 1996–present | Reagan |
| 91 | Senior Judge | Louis L. Stanton | Manhattan | 1927 | 1985–1996 | — | 1996–present | Reagan |
| 97 | Senior Judge | Kimba Wood | Manhattan | 1944 | 1988–2009 | 2006–2009 | 2009–present | Reagan |
| 102 | Senior Judge | Loretta Preska | Manhattan | 1949 | 1992–2017 | 2009–2016 | 2017–present | G.H.W. Bush |
| 108 | Senior Judge | Denise Cote | Manhattan | 1946 | 1994–2011 | — | 2011–present | Clinton |
| 109 | Senior Judge | Lewis A. Kaplan | Manhattan | 1944 | 1994–2011 | — | 2011–present | Clinton |
| 113 | Senior Judge | Sidney H. Stein | Manhattan | 1945 | 1995–2010 | — | 2010–present | Clinton |
| 115 | Senior Judge | Jed S. Rakoff | Manhattan | 1943 | 1996–2010 | — | 2010–present | Clinton |
| 117 | Senior Judge | Richard M. Berman | Manhattan | 1943 | 1998–2011 | — | 2011–present | Clinton |
| 118 | Senior Judge | Alvin Hellerstein | Manhattan | 1933 | 1998–2011 | — | 2011–present | Clinton |
| 119 | Senior Judge | Colleen McMahon | Manhattan | 1951 | 1998–2021 | 2016–2021 | 2021–present | Clinton |
| 121 | Senior Judge | Naomi Reice Buchwald | Manhattan | 1944 | 1999–2012 | — | 2012–present | Clinton |
| 122 | Senior Judge | Victor Marrero | Manhattan | 1941 | 1999–2010 | — | 2010–present | Clinton |
| 123 | Senior Judge | George B. Daniels | Manhattan | 1953 | 2000–2021 | — | 2021–present | Clinton |
| 126 | Senior Judge | P. Kevin Castel | Manhattan | 1950 | 2003–2017 | — | 2017–present | G.W. Bush |
| 130 | Senior Judge | Paul A. Crotty | Manhattan | 1941 | 2005–2015 | — | 2015–present | G.W. Bush |
| 133 | Senior Judge | Paul G. Gardephe | Manhattan | 1957 | 2008–2023 | — | 2023–present | G.W. Bush |
| 134 | Senior Judge | Vincent L. Briccetti | White Plains | 1954 | 2011–2023 | — | 2023–present | Obama |
- ↑ Judge Haight has sat with the District of Connecticut since taking senior status.
Vacancies and pending nominations
| Seat | Prior judge's duty station | Seat last held by | Vacancy reason | Date of vacancy | Nominee | Date of nomination |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | Manhattan | Paul G. Gardephe | Senior status | August 9, 2023 | — | — |
| 27 | Lorna G. Schofield | December 31, 2024[25] | — | — |
Former judges
| # | Judge | State | Born–died | Active service | Chief Judge | Senior status | Appointed by | Reason for termination |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | William P. Van Ness | NY | 1778–1826 | 1814–1826 | — | — | Madison/Operation of law[Note 1] | death |
| 2 | Samuel Rossiter Betts | NY | 1786–1868 | 1826–1867 | — | — | J.Q. Adams | resignation |
| 3 | Samuel Blatchford | NY | 1820–1893 | 1867–1878[Note 2] | — | — | A. Johnson | elevation to 2d Cir. |
| 4 | William Gardner Choate | NY | 1830–1920 | 1878–1881 | — | — | Hayes | resignation |
| 5 | Addison Brown | NY | 1830–1913 | 1881–1901[Note 3] | — | — | Garfield | retirement |
| 6 | George Bethune Adams | NY | 1845–1911 | 1901–1911[Note 4] | — | — | McKinley | death |
| 7 | George Chandler Holt | NY | 1843–1931 | 1903–1914 | — | — | T. Roosevelt | retirement |
| 8 | Charles Merrill Hough | NY | 1858–1927 | 1906–1916 | — | — | T. Roosevelt | elevation to 2d Cir. |
| 9 | Learned Hand | NY | 1872–1961 | 1909–1924 | — | — | Taft | elevation to 2d Cir. |
| 10 | Julius Marshuetz Mayer | NY | 1865–1925 | 1912–1921 | — | — | Taft | elevation to 2d Cir. |
| 11 | Augustus Noble Hand | NY | 1869–1954 | 1914–1927 | — | — | Wilson | elevation to 2d Cir. |
| 12 | Martin Thomas Manton | NY | 1880–1946 | 1916–1918 | — | — | Wilson | elevation to 2d Cir. |
| 13 | John C. Knox | NY | 1881–1966 | 1918–1955 | 1948–1955 | 1955–1966 | Wilson | death |
| 14 | Henry W. Goddard | NY | 1876–1955 | 1923–1954 | — | 1954–1955 | Harding | death |
| 15 | Francis A. Winslow | NY | 1866–1932 | 1923–1929 | — | — | Harding | resignation |
| 16 | William Bondy | NY | 1870–1964 | 1923–1956 | 1955–1956 | 1956–1964 | Harding | death |
| 17 | Thomas D. Thacher | NY | 1881–1950 | 1925–1930 | — | — | Coolidge | resignation |
| 18 | Frank Joseph Coleman | NY | 1886–1934 | 1927–1934[Note 5] | — | — | Coolidge | death |
| 19 | John M. Woolsey | NY | 1877–1945 | 1929–1943 | — | 1943–1945 | Hoover | death |
| 20 | Francis Gordon Caffey | NY | 1868–1951 | 1929–1947 | — | 1947–1951 | Hoover | death |
| 21 | Alfred Conkling Coxe Jr. | NY | 1880–1957 | 1929–1951 | — | 1951–1957 | Hoover | death |
| 22 | Robert P. Patterson | NY | 1891–1952 | 1930–1939 | — | — | Hoover | elevation to 2d Cir. |
| 23 | George Murray Hulbert | NY | 1881–1950 | 1934–1950 | — | — | F. Roosevelt | death |
| 24 | Vincent L. Leibell | NY | 1883–1968 | 1936–1954 | — | 1954–1968 | F. Roosevelt | death |
| 25 | John William Clancy | NY | 1888–1969 | 1936–1959 | 1956–1959 | 1959–1969 | F. Roosevelt | death |
| 26 | Samuel Mandelbaum | NY | 1884–1946 | 1936–1946 | — | — | F. Roosevelt | death |
| 27 | Edward Augustus Conger | NY | 1882–1963 | 1938–1954 | — | 1954–1963 | F. Roosevelt | death |
| 28 | John Bright | NY | 1884–1948 | 1941–1948 | — | — | F. Roosevelt | death |
| 29 | Simon H. Rifkind | NY | 1901–1995 | 1941–1950 | — | — | F. Roosevelt | resignation |
| 30 | Harold Medina | NY | 1888–1990 | 1947–1951 | — | — | Truman | elevation to 2d Cir. |
| 31 | Sylvester J. Ryan | NY | 1896–1981 | 1947–1973[Note 6] | 1959–1966 | 1973–1981 | Truman | death |
| 32 | Samuel H. Kaufman | NY | 1893–1960 | 1948–1955[Note 7] | — | 1955–1960 | Truman | death |
| 33 | Irving Kaufman | NY | 1910–1992 | 1949–1961[Note 8] | — | — | Truman | elevation to 2d Cir. |
| 34 | John F. X. McGohey | NY | 1894–1972 | 1949–1970[Note 9] | — | 1970–1972 | Truman | death |
| 35 | Gregory Francis Noonan | NY | 1906–1964 | 1949–1964[Note 10] | — | — | Truman | death |
| 36 | Sidney Sugarman | NY | 1904–1974 | 1949–1971[Note 11] | 1966–1971 | 1971–1974 | Truman | death |
| 37 | Edward Weinfeld | NY | 1901–1988 | 1950–1988 | — | — | Truman | death |
| 38 | Thomas Francis Murphy | NY | 1905–1995 | 1951–1970 | — | 1970–1995 | Truman | death |
| 39 | Edward Jordan Dimock | NY | 1890–1986 | 1951–1961 | — | 1961–1986 | Truman | death |
| 40 | David Norton Edelstein | NY | 1910–2000 | 1951–1994[Note 12] | 1971–1980 | 1994–2000 | Truman | death |
| 41 | Archie Owen Dawson | NY | 1898–1964 | 1954–1964 | — | — | Eisenhower | death |
| 42 | Lawrence Walsh | NY | 1912–2014 | 1954–1957 | — | — | Eisenhower | resignation |
| 43 | Alexander Bicks | NY | 1901–1963 | 1954–1963 | — | — | Eisenhower | death |
| 44 | Edmund Louis Palmieri | NY | 1907–1989 | 1954–1972 | — | 1972–1989 | Eisenhower | death |
| 45 | William Bernard Herlands | NY | 1905–1969 | 1955–1969[Note 13] | — | — | Eisenhower | death |
| 46 | John M. Cashin | NY | 1892–1970 | 1955–1965[Note 14] | — | 1965–1970 | Eisenhower | death |
| 47 | Richard Harrington Levet | NY | 1894–1980 | 1956–1966 | — | 1966–1976 | Eisenhower | retirement |
| 48 | Frederick van Pelt Bryan | NY | 1904–1978 | 1956–1972 | — | 1972–1978 | Eisenhower | death |
| 49 | Lloyd Francis MacMahon | NY | 1912–1989 | 1959–1982 | 1980–1982 | 1982–1989 | Eisenhower | death |
| 50 | Charles Miller Metzner | NY | 1912–2009 | 1959–1977 | — | 1977–2009 | Eisenhower | death |
| 51 | Thomas Francis Croake | NY | 1902–1978 | 1961–1972 | — | 1972–1978 | Kennedy | death |
| 52 | Dudley Baldwin Bonsal | NY | 1906–1995 | 1961–1976[Note 15] | — | 1976–1995 | Kennedy | death |
| 53 | Irving Ben Cooper | NY | 1902–1996 | 1961–1972[Note 16] | — | 1972–1996 | Kennedy | death |
| 54 | Wilfred Feinberg | NY | 1920–2014 | 1961–1966[Note 15] | — | — | Kennedy | elevation to 2d Cir. |
| 55 | Harold R. Tyler Jr. | NY | 1922–2005 | 1962–1975 | — | — | Kennedy | resignation |
| 56 | Edward Cochrane McLean | NY | 1903–1972 | 1962–1972 | — | — | Kennedy | death |
| 57 | Inzer Bass Wyatt | NY | 1907–1990 | 1962–1977 | — | 1977–1990 | Kennedy | death |
| 58 | John Matthew Cannella | NY | 1908–1996 | 1963–1977 | — | 1977–1996 | Kennedy | death |
| 59 | Charles Henry Tenney | NY | 1911–1994 | 1963–1979 | — | 1979–1994 | L. Johnson[Note 17] | death |
| 60 | Marvin E. Frankel | NY | 1920–2002 | 1965–1978 | — | — | L. Johnson | resignation |
| 61 | Walter R. Mansfield | NY | 1911–1987 | 1966–1971 | — | — | L. Johnson | elevation to 2d Cir. |
| 62 | Constance Baker Motley | NY | 1921–2005 | 1966–1986 | 1982–1986 | 1986–2005 | L. Johnson | death |
| 63 | Milton Pollack | NY | 1906–2004 | 1967–1983 | — | 1983–2004 | L. Johnson | death |
| 64 | Morris E. Lasker | NY | 1917–2009 | 1968–1983 | — | 1983–2009 | L. Johnson | death |
| 65 | Murray Gurfein | NY | 1907–1979 | 1971–1974 | — | — | Nixon | elevation to 2d Cir. |
| 66 | Lawrence W. Pierce | NY | 1924–2020 | 1971–1981 | — | — | Nixon | elevation to 2d Cir. |
| 67 | Charles L. Brieant | NY | 1923–2008 | 1971–2007 | 1986–1993 | 2007–2008 | Nixon | death |
| 68 | Arnold Bauman | NY | 1914–1989 | 1971–1974 | — | — | Nixon | resignation |
| 69 | Lee Parsons Gagliardi | NY | 1918–1998 | 1971–1985 | — | 1985–1998 | Nixon | death |
| 70 | Thomas P. Griesa | NY | 1930–2017 | 1972–2000 | 1993–2000 | 2000–2017 | Nixon | death |
| 71 | Whitman Knapp | NY | 1909–2004 | 1972–1987 | — | 1987–2004 | Nixon | death |
| 72 | Charles E. Stewart Jr. | NY | 1916–1994 | 1972–1985 | — | 1985–1994 | Nixon | death |
| 73 | Robert L. Carter | NY | 1917–2012 | 1972–1986 | — | 1986–2012 | Nixon | death |
| 74 | Kevin Duffy | NY | 1933–2020 | 1972–1998 | — | 1998–2016 | Nixon | retirement |
| 75 | Robert Joseph Ward | NY | 1926–2003 | 1972–1991 | — | 1991–2003 | Nixon | death |
| 76 | William C. Conner | NY | 1920–2009 | 1973–1987 | — | 1987–2009 | Nixon | death |
| 77 | Richard Owen | NY | 1922–2015 | 1973–1989 | — | 1989–2015 | Nixon | death |
| 78 | Henry Frederick Werker | NY | 1920–1984 | 1974–1984 | — | — | Nixon | death |
| 80 | Gerard Louis Goettel | NY | 1928–2011 | 1976–1993 | — | 1993–2011 | Ford | death |
| 81 | Vincent Lyons Broderick | NY | 1920–1995 | 1976–1988 | — | 1988–1995 | Ford | death |
| 82 | Pierre N. Leval | NY | 1936–present | 1977–1993 | — | — | Carter | elevation to 2d Cir. |
| 83 | Robert W. Sweet | NY | 1922–2019 | 1978–1991 | — | 1991–2019 | Carter | death |
| 84 | Leonard B. Sand | NY | 1928–2016 | 1978–1993 | — | 1993–2016 | Carter | death |
| 85 | Mary Johnson Lowe | NY | 1924–1999 | 1978–1991 | — | 1991–1999 | Carter | death |
| 86 | Abraham David Sofaer | NY | 1938–present | 1979–1985 | — | — | Carter | resignation |
| 87 | John E. Sprizzo | NY | 1934–2008 | 1981–2000 | — | 2000–2008 | Reagan | death |
| 88 | Shirley Wohl Kram | NY | 1922–2009 | 1983–1993 | — | 1993–2009 | Reagan | death |
| 90 | Peter K. Leisure | NY | 1929–2013 | 1984–1997 | — | 1997–2013 | Reagan | death |
| 92 | John M. Walker Jr. | NY | 1940–present | 1985–1989 | — | — | Reagan | elevation to 2d Cir. |
| 93 | Miriam Goldman Cedarbaum | NY | 1929–2016 | 1986–1998 | — | 1998–2016 | Reagan | death |
| 94 | Richard J. Daronco | NY | 1931–1988 | 1987–1988 | — | — | Reagan | death |
| 95 | Michael Mukasey | NY | 1941–present | 1987–2006 | 2000–2006 | 2006 | Reagan | retirement |
| 96 | Kenneth Conboy | NY | 1938–present | 1987–1993 | — | — | Reagan | resignation |
| 98 | Robert P. Patterson Jr. | NY | 1923–2015 | 1988–1998 | — | 1998–2015 | Reagan | death |
| 99 | John S. Martin Jr. | NY | 1935–present | 1990–2003 | — | 2003 | G.H.W. Bush | retirement |
| 100 | Lawrence M. McKenna | NY | 1933–2023 | 1990–2002 | — | 2002–2023 | G.H.W. Bush | death |
| 101 | Louis Freeh | NY | 1950–present | 1991–1993 | — | — | G.H.W. Bush | resignation |
| 103 | Sonia Sotomayor | NY | 1954–present | 1992–1998 | — | — | G.H.W. Bush | elevation to 2d Cir. |
| 104 | Allen G. Schwartz | NY | 1934–2003 | 1993–2003 | — | — | Clinton | death |
| 105 | Deborah Batts | NY | 1947–2020 | 1994–2012 | — | 2012–2020 | Clinton | death |
| 106 | Harold Baer Jr. | NY | 1933–2014 | 1994–2004 | — | 2004–2014 | Clinton | death |
| 107 | Denny Chin | NY | 1954–present | 1994–2010 | — | — | Clinton | elevation to 2d Cir. |
| 111 | Barrington D. Parker Jr. | NY | 1944–present | 1994–2001 | — | — | Clinton | elevation to 2d Cir. |
| 112 | Shira Scheindlin | NY | 1946–present | 1994–2011 | — | 2011–2016 | Clinton | retirement |
| 114 | Barbara S. Jones | NY | 1947–present | 1995–2012 | — | 2012–2013 | Clinton | retirement |
| 116 | Richard C. Casey | NY | 1933–2007 | 1997–2007 | — | — | Clinton | death |
| 120 | William H. Pauley III | NY | 1952–2021 | 1998–2018 | — | 2018–2021 | Clinton | death |
| 124 | Gerard E. Lynch | NY | 1951–present | 2000–2009 | — | — | Clinton | elevation to 2d Cir. |
| 127 | Richard J. Holwell | NY | 1946–present | 2003–2012 | — | — | G.W. Bush | resignation |
| 128 | Stephen C. Robinson | NY | 1957–present | 2003–2010 | — | — | G.W. Bush | resignation |
| 131 | Richard J. Sullivan | NY | 1964–present | 2007–2018 | — | — | G.W. Bush | elevation to 2d Cir. |
| 137 | Katherine B. Forrest | NY | 1964–present | 2011–2018 | — | — | Obama | resignation |
| 138 | Alison Nathan | NY | 1972–present | 2011–2022 | — | — | Obama | elevation to 2d Cir. |
- ↑ Initially appointed to the District of New York, reassigned by operation of law to the Southern District of New York on April 9, 1814.
- ↑ Recess appointment; formally nominated on July 13, 1867, confirmed by the United States Senate on July 16, 1867, and received commission the same day.
- ↑ Recess appointment; formally nominated on October 12, 1881, confirmed by the Senate on October 14, 1881, and received commission the same day.
- ↑ Recess appointment; formally nominated on December 5, 1901, confirmed by the Senate on December 17, 1901, and received commission the same day.
- ↑ Recess appointment; formally nominated on December 6, 1927, confirmed by the Senate on December 19, 1927, and received commission the same day.
- ↑ Recess appointment; formally nominated on November 24, 1947, confirmed by the Senate on December 18, 1947, and received commission on December 20, 1947.
- ↑ Recess appointment; formally nominated on January 13, 1949, confirmed by the Senate on January 31, 1949, and received commission on February 2, 1949.
- ↑ Recess appointment; formally nominated on January 5, 1950, confirmed by the Senate on April 4, 1950, and received commission on April 7, 1950.
- ↑ Recess appointment; formally nominated on January 5, 1950, confirmed by the Senate on March 8, 1950, and received commission on March 9, 1950.
- ↑ Recess appointment; formally nominated on January 5, 1950, confirmed by the Senate on April 25, 1950, and received commission on April 26, 1950.
- ↑ Recess appointment; formally nominated on January 5, 1950, confirmed by the Senate on April 28, 1950, and received commission on May 1, 1950.
- ↑ Recess appointment; formally nominated on January 30, 1952, confirmed by the Senate on April 7, 1952, and received commission on April 8, 1952.
- ↑ Recess appointment; formally nominated on January 12, 1956, confirmed by the Senate on June 26, 1956, and received commission on June 27, 1956.
- ↑ Recess appointment; formally nominated on January 12, 1956, confirmed by the Senate on March 1, 1956, and received commission on March 2, 1956.
- 1 2 Recess appointment; formally nominated on January 15, 1962, confirmed by the Senate on March 16, 1962, and received commission on March 17, 1962.
- ↑ Recess appointment; formally nominated on January 15, 1962, confirmed by the Senate on September 20, 1962, and received commission on September 28, 1962.
- ↑ Judge Tenney was nominated by President Kennedy but was appointed to the Court by (i.e., received his commission from) President Johnson.
Chief judges
| Chief Judge | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Knox | 1948–1955 | ||
| Bondy | 1955–1956 | ||
| Clancy | 1956–1959 | ||
| Ryan | 1959–1966 | ||
| Sugarman | 1966–1971 | ||
| Edelstein | 1971–1980 | ||
| MacMahon | 1980–1982 | ||
| Motley | 1982–1986 | ||
| Brieant | 1986–1993 | ||
| Griesa | 1993–2000 | ||
| Mukasey | 2000–2006 | ||
| Wood | 2006–2009 | ||
| Preska | 2009–2016 | ||
| McMahon | 2016–2021 | ||
| Swain | 2021–present | ||
Chief judges have administrative responsibilities with respect to their district court. Unlike the Supreme Court, where one justice is specifically nominated to be chief, the office of chief judge rotates among the district court judges. To be chief, a judge must have been in active service on the court for at least one year, be under the age of 65, and have not previously served as chief judge.
A vacancy is filled by the judge highest in seniority among the group of qualified judges. The chief judge serves for a term of seven years, or until age 70, whichever occurs first. The age restrictions are waived if no members of the court would otherwise be qualified for the position.
When the office was created in 1948, the chief judge was the longest-serving judge who had not elected to retire, on what has since 1958 been known as senior status, or declined to serve as chief judge. After August 6, 1959, judges could not become or remain chief after turning 70 years old. The current rules have been in operation since October 1, 1982.
Succession of seats
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See also
- Courts of New York
- For the People, a 2018 fictional television drama about the lawyers and judges of the Southern District
- List of current United States district judges
- List of judges of the United States Bankruptcy Court for the Southern District of New York
- List of lawsuits involving Donald Trump
- List of United States federal courthouses in New York
References
- ↑ "Southern District of New York". United States Department of Justice. November 13, 2014.
- ↑ "The Mother Court: A.K.A., the Southern District Court of New York".
- ↑ Weiser, Benjamin; Rashbaum, William K. (March 10, 2017). "With Preet Bharara's Dismissal, Storied Office Loses Its Top Fighter". New York Times.
In past presidential transitions, the storied office, long known to be so independent of Washington that some people referred to it as the Sovereign District of New York, has in large measure moved forward unaffected by politics.
- ↑ Weiser, Benjamin (January 29, 2009). "A Steppingstone for Law's Best and Brightest". The New York Times. Retrieved July 24, 2019.
- ↑ 28 U.S.C. § 112(b),(c).
- ↑ "Homepage | U.S District Court".
- ↑ Berthelsen, Christian (October 11, 2021). "Wall Street Enforcer Becomes First Black U.S. Attorney for Manhattan". Bloomberg.com. Retrieved October 12, 2021.
- ↑ "Southern District of New York 225th Anniversary". history.nysd.uscourts.gov. Retrieved December 14, 2018.
- 1 2 Asbury Dickens, A Synoptical Index to the Laws and Treaties of the United States of America (1852), p. 386.
- 1 2 3 4 U.S. District Courts of New York, Legislative history, Federal Judicial Center.
- ↑ "92 STAT. 885" (PDF).
- ↑ Taylor, Susan (April 15, 2022). "110 Years Later: Titanic Lawsuits Follow Tragedy | In Custodia Legis". The Library of Congress. Retrieved April 18, 2023.
- ↑ District), United States District Court (New York : Southern (1918). The "Lusitania." Opinion of Court, United States District Court, Southern District of New York. American association for international conciliation.
- ↑ "Slocum Disaster, June 15, 1904". National Archives. August 15, 2016. Retrieved April 18, 2023.
- ↑ "United States v. Rosenberg, 109 F. Supp. 108 (S.D.N.Y. 1953)". Justia Law. Retrieved April 18, 2023.
- ↑ "United States v. Hiss, 107 F. Supp. 128 (S.D.N.Y. 1952)". Justia Law. Retrieved April 18, 2023.
- ↑ Birmingham, Kevin (2013). "The Prestige of the Law: Revisiting Obscenity Law and Judge Woolsey's "Ulysses" Decision". James Joyce Quarterly. 50 (4): 991–1009. ISSN 0021-4183. JSTOR 24598724.
- ↑ Dunlap, David W. (June 30, 2016). "1971 | Supreme Court Allows Publication of Pentagon Papers". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved April 18, 2023.
- ↑ Hurtado, Patricia (February 2, 2011). "Maersk Pirate's Lawyers Seek 27-Year Prison Term". Bloomberg.com. Retrieved October 27, 2023.
- ↑ Forrest, Katherine B. (August 23, 2017). "Matt Hosseinzadeh, Plaintiff, v. Ethan Klein and Hila Klein, Defendants". United States District Court, S.D. New York (cv-3081). Retrieved December 12, 2017.
- ↑ Hamilton, Colby. "Cohen's 'Blind Loyalty' Leads to 3-Year Prison Term", New York Law Journal via Law.com, December 12, 2018. Retrieved December 12, 2018.
- ↑ "Ex-Trump lawyer Cohen jailed for 36 months". BBC News. December 12, 2018. Retrieved December 12, 2018.
- ↑ "Reality Show Cast Member Jennifer Shah Sentenced to 78 Months in Prison for Running Nationwide Telemarketing Fraud Scheme". January 6, 2023.
- ↑ | docket = 22-cv-10016
- ↑ "Future Judicial Vacancies | United States Courts". www.uscourts.gov. Retrieved January 6, 2024.
- ↑ . April 9, 1814 – via Wikisource.
External links
- Official website for the U.S. District Court for the Southern District of New York
- Official website for the U.S. Bankruptcy Court for the Southern District of New York
- Official website for the U.S. Attorney's Office for the Southern District of New York
- Official website of the Southern District Court Reporters