| Symphysis | |
|---|---|
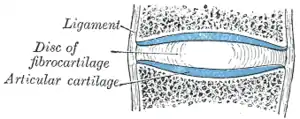 Diagrammatic section of a symphysis. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Symphysis |
| TA98 | A03.0.00.017 |
| TA2 | 1531 |
| FMA | 7498 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
A symphysis (/ˈsɪm.fɪ.sɪs/, pl. symphyses[1]) is a fibrocartilaginous fusion between two bones. It is a type of cartilaginous joint, specifically a secondary cartilaginous joint.
- A symphysis is an amphiarthrosis, a slightly movable joint.
- A growing together of parts or structures.
Unlike synchondroses, symphyses are permanent.[2]
Examples
The more prominent symphyses are:
- the pubic symphysis
- sacrococcygeal symphysis
- intervertebral disc between two vertebrae
- in the sternum, between the manubrium and body
- mandibular symphysis, in the jaw
Symphysis disorders
Pubic symphysis diastasis
Pubic symphysis diastasis is an extremely rare complication that occurs in women who are giving birth. Separation of the two pubic bones during delivery at the symphyseal joint is extremely rare. Typically, during the birthing process, there is a sound that can be heard by the human ear to detect that there could be a case of symphyseal diastasis. There is pain that is associated with symphyseal diastasis that can make simple everyday tasks truly unbearable. A few of the medical techniques that are used to fully confirm a diagnosis of symphyseal diastasis are "radiography, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging." Many overlook their pain that they experience after delivering their child, and just account the pain as postpartum which delays the diagnosis and treatment for symphyseal diastasis.[3]
The common cause of this disorder is when there is a high energy event that is occurring like vaginal child birth. Sometimes symphyseal diastasis is known as "Floating Pubic Symphysis (FPS)." Treatments for this disorder include "external fixation, subcutaneous fixation, internal fixation, and percutaneous cannulated screw fixation." This problem must be resolved immediately because it can cause other problems like "hemorrhagic shock and rectal, urogenital, and vaginal injuries".[4]
Often, patients with pubic symphysis diastasis are able to benefit from non-operative procedures to heal them and take away their pain. When the non-operative procedures prove to be unhelpful, the doctors have to resort to surgical procedures to ease the pain and fix the problem. Even though this illness is extremely rare, there have been treatments that have been discovered.[5]
This disease doesn't only occur within postpartum mothers. Many athletes experience symphyseal diastasis when they are playing in their sports fields. The symptoms include groin pain and increased pain when participating in weight bearing activities. Even without proof or diagnosis of a hernia, there can be major pain and soreness experienced in the area of the symphysis.[5]
References
- ↑ "SYMPHYSIS | Meaning & Definition for UK English | Lexico.com". Archived from the original on February 4, 2021.
- ↑ "Module - Introduction to Joints". Retrieved 2016-07-27.
- ↑ Chawla, Jaya Jethra; Arora, Devendra; Sandhu, Namrita; Jain, Megha; Kumari, Anju (November 2017). "Pubic Symphysis Diastasis: A Case Series and Literature Review". Oman Medical Journal. 32 (6): 510–514. doi:10.5001/omj.2017.97. ISSN 1999-768X. PMC 5702981. PMID 29218129.
- ↑ Song, Wenhao; Zhou, Dongsheng; He, Yu (2017-03-07). "Biomechanical characteristics of fixation methods for floating pubic symphysis". Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research. 12 (1): 38. doi:10.1186/s13018-017-0541-z. ISSN 1749-799X. PMC 5341422. PMID 28270223.
- 1 2 Arner, Justin W.; Albers, Marcio; Zuckerbraun, Brian S.; Mauro, Craig S. (2017-12-11). "Laparoscopic Treatment of Pubic Symphysis Instability With Anchors and Tape Suture". Arthroscopy Techniques. 7 (1): e23–e27. doi:10.1016/j.eats.2017.08.045. ISSN 2212-6287. PMC 5786148. PMID 29379710.
External links