| Testacella Temporal range: | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Shelled Slug, Testacella haliotidea | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Mollusca |
| Class: | Gastropoda |
| Subclass: | Heterobranchia |
| Order: | Stylommatophora |
| Informal group: | Sigmurethra |
| Family: | Testacellidae J. E. Gray, 1840[2] |
| Genus: | Testacella Draparnaud, 1801[3] |
| Type species | |
| Testacella haliotidea Draparnaud, 1801 | |
| Synonyms | |
| |

Testacella is genus of small to medium-large, predatory, air-breathing, land slugs.[4]
They are terrestrial gastropod mollusks in the family Testacellidae, the shelled slugs. They are not often seen because they live underground.
Testacella is the only genus in the family, in other words it is a monotypic family. Testacella is the type genus of the family Testacellidae.[5]
Distribution
Species within this genus of slugs live in north Africa, southern and western Europe, and Britain.[1]
Species
Species within the genus Testacella include:
- Subgenus Testacella Draparnaud, 1801
- Subgenus Testacelloides A. J. Wagner, 1914[6][7]
- † Testacella asinium Serres, 1827
- Testacella bisulcata Risso, 1826[8]
- Testacella bracciai Nardi & Bodon, 2011
- † Testacella bruntoniana Serres, 1851
- † Testacella deshayesii Michaud, 1855
- Testacella fischeriana Bourguignat, 1862
- Testacella gestroi Issel, 1873[8]
- Testacella haliotidea Lamarck, 1801 - the shelled slug, the type species of the genus[8]
- † Testacella lartetii Dupuy, 1850
- Testacella maugei Férussac, 1819[8]
- † Testacella pedemontana Sacco, 1886
- † Testacella pontileviensis de Morgan, 1920
- † Testacella puisseguri Schlickum, 1967
- Testacella riedeli Giusti, Manganelli & Schembri, 1995[8]
- † Testacella sandbergeri Wenz, 1914
- † Testacella schuetti Schlickum, 1967
- Testacella scutulum Sowerby I, 1821[8]
- † Testacella zellii Klein, 1853
- Nomen dubium
- Testacella antillarum Grateloup, 1855
- Synonyms
- Testacella anomala Torres Minquez, 1924: synonym of Testacella haliotidea Draparnaud, 1801
- Testacella barcinonensis Pollonera, 1888: synonym of Testacella haliotidea Draparnaud, 1801
- Testacella catalonica Pollonera, 1888: synonym of Testacella scutulum G. B. Sowerby I, 1821 (original name)
- Testacella dikrangensis Godwin-Austen, 1876: synonym of Girasia dikrangensis (Godwin-Austen, 1876) (original combination)
- Testacella dubia Pollonera, 1888: synonym of Testacella haliotidea Draparnaud, 1801
- Testacella esserana Fagot, 1892: synonym of Testacella haliotidea Draparnaud, 1801
- Testacella europaea de Roissy, 1805: synonym of Testacella haliotidea Draparnaud, 1801
- Testacella galliae Oken, 1816: synonym of Testacella haliotidea Draparnaud, 1801
- Testacella guadeloupensis Lesson, 1838: synonym of Omalonyx unguis (d'Orbigny, 1836) (junior synonym)
- † Testacella larteti Dupuy, 1850 : synonym of † Testacella lartetii Dupuy, 1850 (incorrect subsequent spelling)
- Testacella matheronii Potiez & Michaud, 1838: synonym of Omalonyx unguis (d'Orbigny, 1836) (junior synonym)
- Testacella subtrigona Pollonera, 1888: synonym of Testacella haliotidea Draparnaud, 1801(original name)
- Testacella vagans F. W. Hutton, 1882: synonym of Testacella maugei Férussac, 1819
Description
These slugs have a very small, ear-shaped shell, which is situated far back on their bodies.
In the family Testacellidae, the number of haploid chromosomes lies between 31 and 35 (according to the values in this table).[9]
Habitat
These slugs are rarely observed, but they tend to live in gardens and farms where there is rich soil and a lot of earthworms.
Life habits
These slugs live underground and hunt earthworms. They are usually only seen when they are forced up to the surface because the soil has become completely saturated with rain.
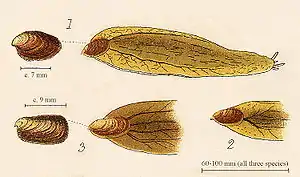
1 - Testacella haliotidea
2 - Testacella scutulum
3 - Testacella maugei
References
- 1 2 "Family summary for Testacellidae". AnimalBase, last modified 8 August 2010, accessed 28 June 2011.
- ↑ Gray J. E. (1840). [A new edition of] A manual of the land and fresh-water shells of the British Isles by W. Turton. Longman, Orme, Brown, Green, and Longmans, London. ix + 324 pp., 12 plates. page 109.
- ↑ Draparnaud J. P. R. (1801). Tableau des mollusques terrestres et fluviatiles de la France. 116 pp. Montpellier, Paris. (Renaud; Bossange, Masson & Besson). page 33, 99.
- ↑ MolluscaBase eds. (2022). MolluscaBase. Testacella Lamarck, 1801. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=818595 on 2022-09-13
- ↑ Bouchet, Philippe; Rocroi, Jean-Pierre; Frýda, Jiri; Hausdorf, Bernard; Ponder, Winston; Valdés, Ángel & Warén, Anders (2005). "Classification and nomenclator of gastropod families". Malacologia. Hackenheim, Germany: ConchBooks. 47 (1–2): 1–397. ISBN 3-925919-72-4. ISSN 0076-2997.
- ↑ Wagner A. J. (1914). Anz. Akad. Wiss. Wien 51: 335.
- ↑ "Testacelloides A.J. Wagner, 1914". Fauna Europaea, last update 27 January 2011, accessed 28 June 2011.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "Species in genus Testacella" (n=6). AnimalBase, accessed 19 January 2011.
- ↑ Barker G. M.: Gastropods on Land: Phylogeny, Diversity and Adaptive Morphology. in Barker G. M. (ed.): The biology of terrestrial molluscs. CABI Publishing, Oxon, UK, 2001, ISBN 0-85199-318-4. 1-146, cited pages: 139 and 142.
External links
- Lamarck, J. B. (1801). Système des animaux sans vertèbres, ou tableau général des classes, des ordres et des genres de ces animaux; Présentant leurs caractères essentiels et leur distribution, d'apres la considération de leurs rapports naturels et de leur organisation, et suivant l'arrangement établi dans les galeries du Muséum d'Histoire Naturelle, parmi leurs dépouilles conservées; Précédé du discours d'ouverture du Cours de Zoologie, donné dans le Muséum National d'Histoire Naturelle l'an 8 de la République. Published by the author and Deterville, Paris: viii + 432 pp
- "Testacella Species"
- "Have You Seen A Shelled Slug Called Testacella!"
- "A predatory (shell) slug (Testacella haliotidea)"