Thevetins are a group of poisonous cardiac glycosides. They are obtained especially from the seeds of a West Indian shrub or small tree (Cascabela thevetia syn. Thevetia nereifolia) of the dogbane family (Apocynaceae).[1] Hydrolysis products include glucose, digitalose, and a sterol.[1]
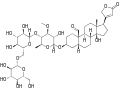 Thevetin A (C42H64O19)
Thevetin A (C42H64O19)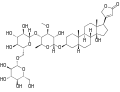 Thevetin B (C42H66O18)
Thevetin B (C42H66O18)
References
- 1 2 "Thevetin". merriam-webster.com.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.