| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Thiolan-2-imine | |||
Other names
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.226.745 | ||
PubChem CID |
|||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
| Properties | |||
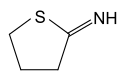
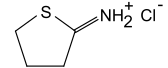
| C4H7NS C4H7NS·HCl | |||
| Molar mass | 101.17 (free base) 137.63 (HCl)[1] | ||
| Appearance | Powder | ||
| Boiling point | 198–201[1] °C (388–394 °F; 471–474 K) (HCl) | ||
| 100 mg/mL (HCl)[1] | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |||
2-Iminothiolane is a cyclic thioimidate compound also known as Traut's reagent. It is a thiolating reagent that reacts with primary amine groups, such as those of amino acids, to form sulfhydryl groups.
Application
2-Iminothiolane reacts with primary amines efficiently at pH 7 to 9, creating amidine compounds with a sulfhydryl group. Thus it allows for crosslinking or labeling of molecules such as proteins through use of disulfide or thioether conjugation. It was first used to thiolate a subunit of ribosome in E. coli in 1973 by Robert Traut, its namesake, and his colleagues.[2]
It also reacts with aliphatic and phenolic hydroxyl groups at high pH, albeit at a much slower rate.[3]

The reaction of 2-iminothiolane with an amine group of a peptide.
References
- 1 2 3 "2-Iminothiolane hydrochloride". Sigma-Aldrich.
- ↑ Traut, R. R.; Bollen, A; Sun, T. T.; Hershey, J. W.; Sundberg, J; Pierce, L. R. (1973). "Methyl 4-mercaptobutyrimidate as a cleavable cross-linking reagent and its application to the Escherichia coli 30S ribosome". Biochemistry. 12 (17): 3266–73. doi:10.1021/bi00741a019. PMID 4581787.
- ↑ "Traut's Reagent Instructions" (PDF). Thermo Scientific. Retrieved 2015-07-08.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.