| ANT-16 (TB-4) | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Role | Heavy bomber |
| National origin | Soviet Union |
| Manufacturer | Tupolev |
| First flight | 3 July 1933 |
| Status | Retired |
| Primary user | Soviet Union |
| Number built | One |
| Developed from | Tupolev TB-3 |
| Variants | ANT-20 |
The Tupolev ANT-16 (also known as the TB-4; Russian: Тяжелый Бомбардировщик – Heavy Bomber) was an experimental heavy bomber aircraft designed and tested in the Soviet Union in the early 1930s.
Design and development
Conceptually representing evolution of the TB-3 bomber, the ANT-16 was designed under the doctrine that size and payload were more important for a bomber than speed because it would be able to protect itself with defensive armament.[1] The twin 5 by 1.8 by 1.8 metres (16.4 ft × 5.9 ft × 5.9 ft) bomb bays were the largest in the world at that time and presented many design challenges in order to preserve structural rigidity of the airframe.[1]
The sole prototype first flew on 3 July 1933 with M. M. Gromov at the controls. The test flight program was completed by 29 September 1933 with disappointing results. The two top-mounted engines performed poorly and a significant portion of thrust generated by the wing-mounted engines was absorbed by the two meter-thick (6 ft 7 in) wing. A proposal to re-equip the aircraft with Mikulin AM-35 engines of 933 kW (1,250 hp) was not implemented.[1] A second prototype was under construction, but was never finished[2] (construction stopped 2 July 1933); some of its parts were used in the ANT-20.
Specifications (ANT-16)
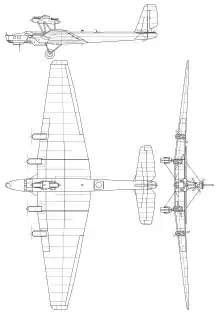
Data from The Osprey Encyclopedia of Russian Aircraft 1875-1995 [3]
General characteristics
- Crew: 12
- Length: 32 m (105 ft 0 in)
- Wingspan: 54 m (177 ft 2 in)
- Height: 17.3 m (56 ft 9 in)
- Wing area: 422 m2 (4,540 sq ft)
- Empty weight: 21,400 kg (47,179 lb)
- Gross weight: 33,280 kg (73,370 lb)
- Fuel capacity: 4,950 kg (10,913 lb) (~7,000 L (1,800 US gal; 1,500 imp gal) at 0.7 s.g.)
- Powerplant: 6 × Mikulin AM-34 V-12 liquid-cooled piston engines, 560 kW (750 hp) each
- Propellers: 2-bladed fixed-pitch propellers
Performance
- Maximum speed: 200 km/h (120 mph, 110 kn) at sea level
- 188 km/h (117 mph; 102 kn) at 5,000 m (16,000 ft)
- Cruise speed: 159 km/h (99 mph, 86 kn)
- Landing speed: 105 km/h (65 mph; 57 kn)
- Range: 1,000 km (620 mi, 540 nmi)
- Combat range: 940 km (580 mi, 510 nmi) with 8,000 kg (17,637 lb) bomb-load
- 2,000 km (1,200 mi; 1,100 nmi) with 2,000 kg (4,409 lb) bomb-load
- Service ceiling: 2,750 m (9,020 ft)
- Time to altitude: 1,000 m (3,300 ft) in 12 minutes 24 seconds
- 2,000 m (6,600 ft) in 34 minutes
- Wing loading: 79 kg/m2 (16 lb/sq ft)
- Power/mass: 0.101 kW/kg (0.061 hp/lb)
- Take-off run: 800 m (2,600 ft) in 36 seconds
- Landing run: 400 m (1,300 ft)
Armament
- Guns: 4x20mm cannon, 10x2 7.62mm DA machine guns
- Bombs: Up to 4,000 kg of bombs[4]
See also
Related development
References
- 1 2 3 Shavrov V.B. (1985). Istoriia konstruktskii samoletov v SSSR do 1938 g. (3 izd.) (in Russian). Mashinostroenie. ISBN 5-217-03112-3.
- ↑ "The Tupolev Giants". AirVectors. Retrieved 14 August 2017.
- ↑ Gunston, Bill (1995). The Osprey Encyclopedia of Russian Aircraft 1875-1995. London: Osprey. pp. 393–394. ISBN 9781841760964.
- ↑ "Tupolev ANT-16 / TB-4 - bomber".