| Tyrosine ammonia lyase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC no. | 4.3.1.23 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Tyrosine ammonia lyase (EC 4.3.1.23, L-tyrosine ammonia-lyase, TAL or Tyrase) is an enzyme in the natural phenols biosynthesis pathway. It transforms L-tyrosine into p-coumaric acid.[1][2][3]
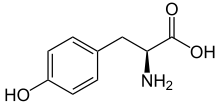
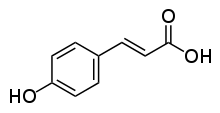 + Ammonia + H+
+ Ammonia + H+
L-tyrosine = trans-p-hydroxycinnamate + NH3
See also
- EC 4.3.1.24 (phenylalanine ammonia-lyase)
- EC 4.3.1.25 (phenylalanine/tyrosine ammonia-lyase)
References
- ↑ Louie GV, Bowman ME, Moffitt MC, Baiga TJ, Moore BS, Noel JP (December 2006). "Structural determinants and modulation of substrate specificity in phenylalanine-tyrosine ammonia-lyases". Chemistry & Biology. 13 (12): 1327–38. doi:10.1016/j.chembiol.2006.11.011. PMC 2859959. PMID 17185228.
- ↑ Watts KT, Mijts BN, Lee PC, Manning AJ, Schmidt-Dannert C (December 2006). "Discovery of a substrate selectivity switch in tyrosine ammonia-lyase, a member of the aromatic amino acid lyase family". Chemistry & Biology. 13 (12): 1317–26. doi:10.1016/j.chembiol.2006.10.008. PMID 17185227.
- ↑ Schwede TF, Rétey J, Schulz GE (April 1999). "Crystal structure of histidine ammonia-lyase revealing a novel polypeptide modification as the catalytic electrophile". Biochemistry. 38 (17): 5355–61. doi:10.1021/bi982929q. PMID 10220322.
External links
- Tyrosine+ammonia-lyase at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- www.hhmi.org
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.