
Fiscal policy is any changes the government makes to the national budget to influence a nation's economy.[1] "An essential purpose of this Financial Report is to help American citizens understand the current fiscal policy and the importance and magnitude of policy reforms essential to make it sustainable. A sustainable fiscal policy is explained as the debt held by the public to Gross Domestic Product which is either stable or declining over the long term" (Bureau of the fiscal service). The approach to economic policy in the United States was rather laissez-faire until the Great Depression. The government tried to stay away from economic matters as much as possible and hoped that a balanced budget would be maintained.[2] Prior to the Great Depression, the economy did have economic downturns and some were quite severe. However, the economy tended to self-correct so the laissez faire approach to the economy tended to work.
President Franklin D. Roosevelt first instituted fiscal policies in the United States in The New Deal. The first experiments did not prove to be very effective, but that was in part because the Great Depression had already lowered the expectations of business so drastically.[3]
History
The Great Depression

The Great Depression struck countries in the late 1920s and continued throughout the entire 1930's. It affected some countries more than others, and the effects in the US were detrimental. In 1933, 25 percent of all workers were unemployed in America.[4] Many families starved or lost their homes. Some tried traveling to the West to find work, also to no avail.
The Great Depression showed the American population that there was a growing need for the government to manage economic affairs. The size of the federal government began rapidly expanding in the 1930s, growing from 553,000 paid civilian employees in the late 1920s to 953,891 employees in 1939. The budget grew substantially as well. In 1939, federal receipts of the administrative budget were 5.50 percent of Gross National Product, GNP, while federal expenditures were 9.77 percent of GNP. These numbers were up significantly from 1930, when federal receipts averaged 3.80 percent of GNP while expenditures averaged 3.04 percent of GNP.
Another contributor to changing the role of government in the 1930s was President Franklin Delano Roosevelt. FDR was important because of his creation of the New Deal, which was a program that would offer relief, recovery, and reform to the American nation.[5] In terms of relief, new organizations, such as the Works Progress Administration, saved many U.S. lives. The reform aspect was indeed the most influential in the New Deal, for it forever changed the role of government in the U.S. economy. In essence, it was the beginning of fiscal policy. It was the first time that the government took an active role in attempting to secure American individuals from unseen drastic changes in the market.[6]
Although the relief and reform aspects of the New Deal proved to be effective for Americans, recovery was an issue that did not. Unemployment rates remained very high throughout the 1930s.[4] It was still difficult for Americans to find jobs. This problem diminished when the government called for many industries to convert to military production in the early 1940s[7] in order to prepare for World War II.
World War II and effects
World War II forced the government to run huge deficits, or spend more than they were economically generating, in order to keep up with all of the production the US military needed. By running deficits, the economy recovered, and America rebounded from its drought of unemployment.[8] The military strategy of full employment had a huge benefit: the government’s massive deficits were used to pay for the war, and ended the Great Depression.[9] This phenomenon set the standard and showed just how necessary it was for the government play an active role in fiscal policy.[8]
The Employment Act of 1946 was enacted by the government to keep the economy from plunging back into a post-war depression. The act declared the continuing policy and responsibility of the federal government to use all reasonable means to promote maximum (not full) employment, production, and purchasing power.[10] In addition to focusing on keeping unemployment rates low, the act called for the creation of the Council of Economic Advisors.[11] This council had the task of assisting the president in appointing members to the Joint Economic Committee in the United States Congress and continuing to develop the role of fiscal policy in the United States.[11]
Modern fiscal policy
The United States government has tended to spend more money than it takes in, indicated by a national debt that was close to $1 billion at the beginning of the 20th century. The budget for most of the 20th century followed a pattern of deficits during wartime and economic crises, and surpluses during periods of peacetime economic expansion.
In 1971, at Bretton Woods, the US went off the gold standard allowing the dollar to float. Shortly after that, the price of oil was pegged to gold rather than the dollar by OPEC. The 70s were marked by oil shocks, recessions and inflation in the US. From fiscal years 1970 to 1997; although the country was nominally at peace during most of this time, the federal budget deficit accelerated, topping out (in absolute terms) at $290 billion for 1992.
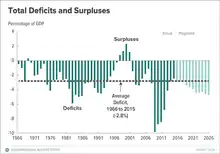
In contrast, from FY 1997–2001, gross revenues exceeded expenditures and a surplus resulted. However, it has been argued that this 'balanced budget' only constituted a surplus in the public debt (or on-budget), in which the Treasury Department borrowed increased tax revenue from intragovernmental debt holdings (namely the Social Security Trust Fund), thus adding more interest on Treasury bonds. In effect, the four year 'surplus' was only in public debt holdings, while the National Debt Outstanding increased every fiscal year (the lowest deficit in FY 2000 was $17.9 Billion)[12][13][14][15][16][17][18] However, after a combination of the dot-com bubble burst, the September 11 attacks, a dramatic increase in government spending (primarily in defense for military operations in Afghanistan and Iraq) and a $1.35 trillion tax cut, the budget returned to a deficit basis. The budget went from a $236 billion surplus in fiscal year 2000 to a $413 billion deficit in fiscal year 2004. In fiscal year 2005, the deficit began to shrink due to a sharp increase in tax revenue. By 2007, the deficit was reduced to $161 billion; less than half of what it was in 2004 and the budget appeared well on its way to balance once again.
Fiscal policy is the application of taxation and government spending to influence economic performance. The main aim of adopting fiscal policy instruments is to promote sustainable growth in the economy and reduce the poverty levels within the community. In the past, fiscal policy instruments were used solve the economic crisis such as the great recession and during the financial crisis. They are effective in jump-starting growth, supporting the financial systems, and mitigating the economic crisis on the vulnerable groups especially the low-income earners and the poor. The most commonly applied fiscal policy instruments are government spending and taxes. The government increases or reduces its budget allocation on public expenditure to ensure vital goods and services are provided to the citizens. For instance, expenditure on infrastructural projects not only increases access to more roads but also creates jobs to the public and also increases the amount money in circulation thereby spurring economic growth. On the other hand, reduction of income and value added taxes increase the amount of disposable income that individuals direct to consumption and investment expenditures. Increasing income taxes reduce disposable income while it increases the tax base for public spending. Fiscal policy instruments are effective in poverty reduction and promotion of the community living standards. Increasing public expenditure ensures that vital public goods and services are availed to the public. Moreover, it helps in creation of employment opportunities, triggering economic growth, and ensuring sustainable growth and development. Tax reduction and cash transfers’ helps in increasing disposable income and transferring resources from the rich to the poor in the community. Fiscal policy instruments can be used to achieve balanced growth in an economy. Federal policies are system of laws, course of actions, regulatory measures, and priorities set by the Federal government in guiding decisions on issues relating to public interest. In most cases, public policy decisions are carried out by the group of people who represent the public, different interests, and beliefs. The policies define all the actions that the Federal government take in order to address issues like security, education, unemployment, poverty reduction among others. Federal policies assist the Federal government in conducting national affairs responsibly. For instance, they inform the government on where to prioritize their funding and support in order to achieve the macroeconomic objectives. For instance, the government is charged with the responsibility of providing education, security, and healthcare. Increased funding on these key priority areas helps in improving public access to the services thereby improving the standards of living of the citizens. Assuring access to the services and sustaining their provision helps in poverty reduction. Policies like unemployment insurance ensures that citizens are insured and unemployment benefits given to eligible workers who have lost their jobs out of their control. Policies helps in cushioning the public against the eventualities in the labor market that may be due to competition or economic performance hence adversely affecting the average citizens. Federal policies cuts across all sectors in the economy and seeks to link the operations of the Federal government and State governments in achieving sustained growth and development, poverty reduction, provision of basic goods and services to the citizens.
In late 2007 to early 2008, the economy would enter a particularly bad recession as a result of high oil and food prices, and a substantial credit crisis leading to the bankruptcy and eventual federal take over of certain large and well established mortgage providers. In an attempt to fix these economic problems, the United States federal government passed a series of costly economic stimulus and bailout packages. As a result of this, in fiscal year 2008, the deficit would increase to $455 billion and is projected to continue to increase dramatically for years to come due in part to both the severity of the current recession and the high-spending fiscal policy the federal government has adopted to help combat the nation's economic woes. As a result, the federal budget deficit increased to $1.2 trillion in fiscal year 2009, or 9.8% of the gross domestic product (GDP). Over subsequent years both the economy and the deficit recovered to some extent, and the government enacted several laws with significant budget impact, including the Affordable Care Act in 2010, the Budget Control Act in 2011, and the American Taxpayer Relief Act in 2012.[19] The Congressional Budget Office projected a $534 billion deficit in fiscal year 2016, or 2.9 percent of GDP. If current policy remains unchanged, the CBO projects the deficit will increase to 4.9 percent of GDP by 2026, or a cumulative total of $9.3 trillion over the period.[20] As a percentage of the GDP, within the context of the national economy as a whole, the highest deficit was run during fiscal year 1946 at nearly 30% of GDP, but that rebounded to a surplus by 1947. By contrast, deficits during the 1980s reached 5–6% of GDP and the deficit for 2005 was 2.6% of GDP, close to the post-World War II average. In 2009, the deficit was 9.8% of GDP, the highest since World War II.[21]
See also
References
- ↑ Heakal, Reem. "What is Fiscal Policy". Retrieved 24 February 2011.
- ↑ "Laissez-Faire". u-s-history.com. Retrieved 1 March 2011.
- ↑ "Fiscal Policy". Encyclopædia Britannica (Encyclopædia Britannica Online ed.). 2011. Retrieved 23 February 2011.
- 1 2 Schwenk, Albert E. "Compensation from before WW I through the Great Depression". United States Department of Labor.
- ↑ Bryant, Joyce. "The Great Depression and New Deal". yale.edu. Retrieved 8 March 2011.
- ↑ "FDR's New Deal". schmoop.com.
- ↑ backend. "The American Economy during WWII". eh.net. Archived from the original on 15 March 2011. Retrieved 8 March 2011.
- 1 2 Lipsky, John. "Fiscal policy challenges in post-crisis world". Retrieved 11 March 2011.
- ↑ "America's Great Depression". ametecon dot com. Retrieved 11 March 2011.
- ↑ Fisher, Louis. "Employment Act of 1946". Major Acts of Congress. Retrieved 11 March 2011.
- 1 2 "FULL EMPLOYMENT ACT OF 1946". The Gale Group. Retrieved 11 March 2011.
- ↑ "The Myth of the Clinton Surplus".
- ↑ Gordon, John Steele (21 May 2009). "Why Government Can't Run a Business". Wall Street Journal.
- ↑ "Clip: Senate Session - C-SPAN Video Library". Archived from the original on 2012-09-25. Retrieved 2014-07-01.
- ↑ "The U. S. Government".
- ↑ http://www.cbpp.org/cms/index.cfm?fa=view&id=1654
- ↑ "The only way to fix Social Security - Aug. 20, 2008".
- ↑ "The Surplus Hoax". 3 November 2000.
- ↑ https://www.fiscal.treasury.gov/fsreports/rpt/finrep/fr/15frusg/CitizensGuide2015.pdf Financial Report of the United States Government 2015, "Citizens Guide to the Fiscal Year 2015," published 2016-02-26
- ↑ https://www.cbo.gov/publication/51384 Congressional Budget Office, "Updated Budget Projections: 2016 to 2026," published 2016-03-24
- ↑ https://trumpwhitehouse.archives.gov/omb/budget/Historicals Budget of the United States Government, Fiscal Year 2017, "Historical Tables: Summary of Receipts, Outlays, and Surpluses or Deficits (-) as Percentages of GDP: 1930–2021," retrieved 2016-06-11
External links
- Savings rate viz Fiscal Deficit Historical comparism of the Savings rate viz Fiscal Deficit ( since 1981 )