 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
PEI, Ultem | |
| Identifiers | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.126.800 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| Properties | |
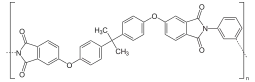
| (C37H24O6N2)n | |
| Molar mass | Variable |
| Appearance | Amber-to-transparent solid |
| Density | 1.27 g/cm3 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Polyetherimide (PEI; branded as Ultem[1]) is an amorphous, amber-to-transparent thermoplastic with characteristics similar to the related plastic PEEK. When comparing PEI to PEEK, the former is cheaper but has lower impact strength and a tighter temperature range.[2]
Due to its adhesive properties and chemical stability it became a popular bed material for FFF 3D printers.
Structure
The molecular formula of the PEI monomer is C37H24O6N2 and the molecular weight is 592.61 g/mol.[3] It contains phthalimide and bisphenol A sub-units.
Properties
The glass transition temperature of PEI is 217 °C (422 °F). Its amorphous density at 25 °C is 1.27 g/cm3(.046 lb/in³). It is prone to stress cracking in chlorinated solvents. Polyetherimide is able to resist high temperatures while maintaining stable electrical properties over a wide range of frequencies. This high strength material offers excellent chemical resistance and ductile properties suitable for various applications, even those involving steam exposure.[4]
References
- ↑ "Ultem". Curbell Plastics. Retrieved 2 November 2023.
- ↑ http://www.mcmaster.com/#ultem/=otzvqt Referenced Oct 7, 2013
- ↑ Scott, Chris. "polyetherimide information and properties". www.polymerprocessing.com. Retrieved 2018-04-30.
- ↑ "Injection Molding Material Selection Guide". www.abtecinc.com. Retrieved 2018-04-30.