| Urengoy gas field | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Country | Russia |
| Region | Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug |
| Offshore/onshore | onshore |
| Coordinates | 66°06′N 76°54′E / 66.1°N 76.9°E |
| Operator | Gazprom dobycha Urengoy |
| Partner | Gazprom |
| Field history | |
| Discovery | 1966 |
| Start of production | 1978 |
| Production | |
| Current production of oil | 16,500 barrels per day (~8.22×105 t/a) |
| Current production of gas | 25,152×106 cu ft/d (712.2×106 m3/d) |
| Estimated gas in place | 353,000×109 cu ft (10,000×109 m3) |
| Producing formations | Cretaceous sandstones |
The Urengoy gas field in the northern West Siberia Basin is the world's second largest natural gas field after South Pars / North Dome Gas-Condensate field. It lies in the Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug, Tyumen Oblast, Russia, just south of the Arctic circle. It is named after the settlement of Urengoy. The gas field is operated by Gazprom Dobycha Urengoy[1] and serviced by the town of Novy Urengoy, founded in 1973.
History

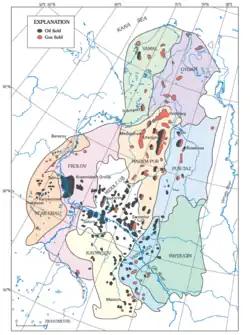
Urengoy gas field was discovered in June 1966.[2] The first drilling hole hit gas on 6 July 1966 and the field started production in 1978. On 25 February 1981, Urengoy extracted its first one hundred billion cubic meters (1011 m³) of natural gas. From January 1984, Urengoy gas started to be exported to Western Europe through the Urengoy–Pomary–Uzhhorod pipeline. A fire hit the Urengoy in 2021 which led to an increase in natural gas prices.[1] In June 2022 the gas field caught fire again.[1]
Production
The Urengoyskoye conventional gas field has over ten trillion cubic meters (1013 m³) in total deposits.[1] It recovered by the end of 2021 more than 90% of its reserves. Its current output is six times lower than at its peak from 1985 to 1996, but this accounts still to 3% of the country's natural gas output.[3] The Urengoy gas field extracts 230 billion cubic meters of natural gas per year, plus condensate and oil.[1] In September 2013, Gazprom announced that a total of 6.5 trillion cubic meters of gas had been produced.[4]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 Staalesen, Atle (16 June 2022). "Russia's biggest natural gas field is ablaze". The Barents Observer.
- ↑ Christian Wüst (2007-12-18). "How Long Will Siberia's Gas Last?". Der Spiegel. Retrieved 2009-10-31.
- ↑ "Urengoyskoye (Urengoysky) Conventional Gas Field, Russia". Offshore Technology. 2021-12-03. Retrieved 2022-12-29.
- ↑ "Gazprom Dobycha Urengoy sets new record". Gazprom. Retrieved 2014-03-04.
External links
- Gazprom dobycha Urengoy Archived 2012-05-11 at the Wayback Machine