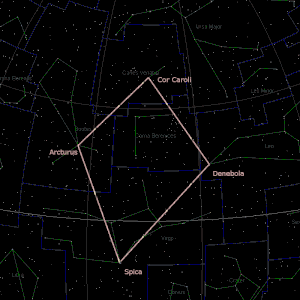
Great Diamond map by WikiSky
The Great Diamond, also called the Diamond of Virgo, is an asterism that can be seen during spring evenings in the Northern Hemisphere.[1] It is composed of the following stars:
- Cor Caroli (α CVn), in Canes Venatici
- Denebola (β Leo), the tail of Leo
- Spica (α Vir), the wheat of Virgo
- Arcturus (α Boo), the brightest star in Boötes
The Great Diamond is larger than the Big Dipper.[2] The three southernmost stars are sometimes regarded as being their own asterism, the Spring Triangle.
Lying within the Great Diamond is the set of stars traditionally assigned to Coma Berenices. Many nearby galaxies, including galaxies in the Virgo Cluster, are within this asterism, and some of these galaxies can easily be observed with amateur telescopes.
See also
External links
- Four-Star Sight: The Celestial Diamond (SPACE.com) 19 May 2006 06:16 am ET
- MAP (Space.com)
- The Great Diamond on WikiSky: DSS2, SDSS, GALEX, IRAS, Hydrogen α, X-Ray, Astrophoto, Sky Map, Articles and images
- Virgo's diamond
References
- ↑ "Great Diamond of Virgo – Constellation Guide". www.constellation-guide.com. Retrieved 2023-02-16.
- ↑ Ian (2020-08-07). "The Great Diamond | Facts, Information, History & Formation". The Nine Planets. Retrieved 2023-02-08.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.